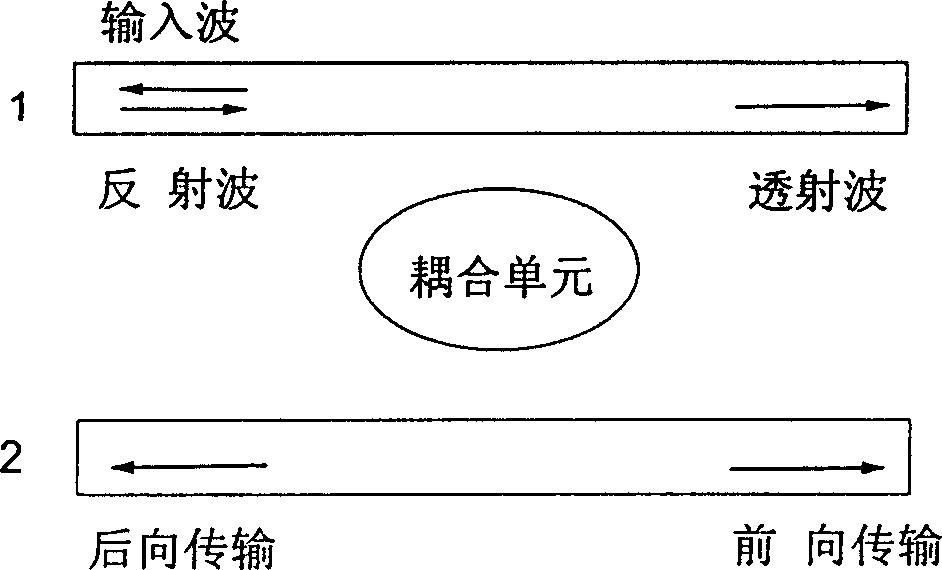
Photon crystal wavelength division mutiplex device
A technology of wavelength division multiplexing devices and photonic crystals, applied in the coupling of optical waveguides, electrical components, electromagnetic wave transmission systems, etc., can solve problems such as design and manufacturing complexity, achieve time reduction, optimization process reduction, and increase the number of channels Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
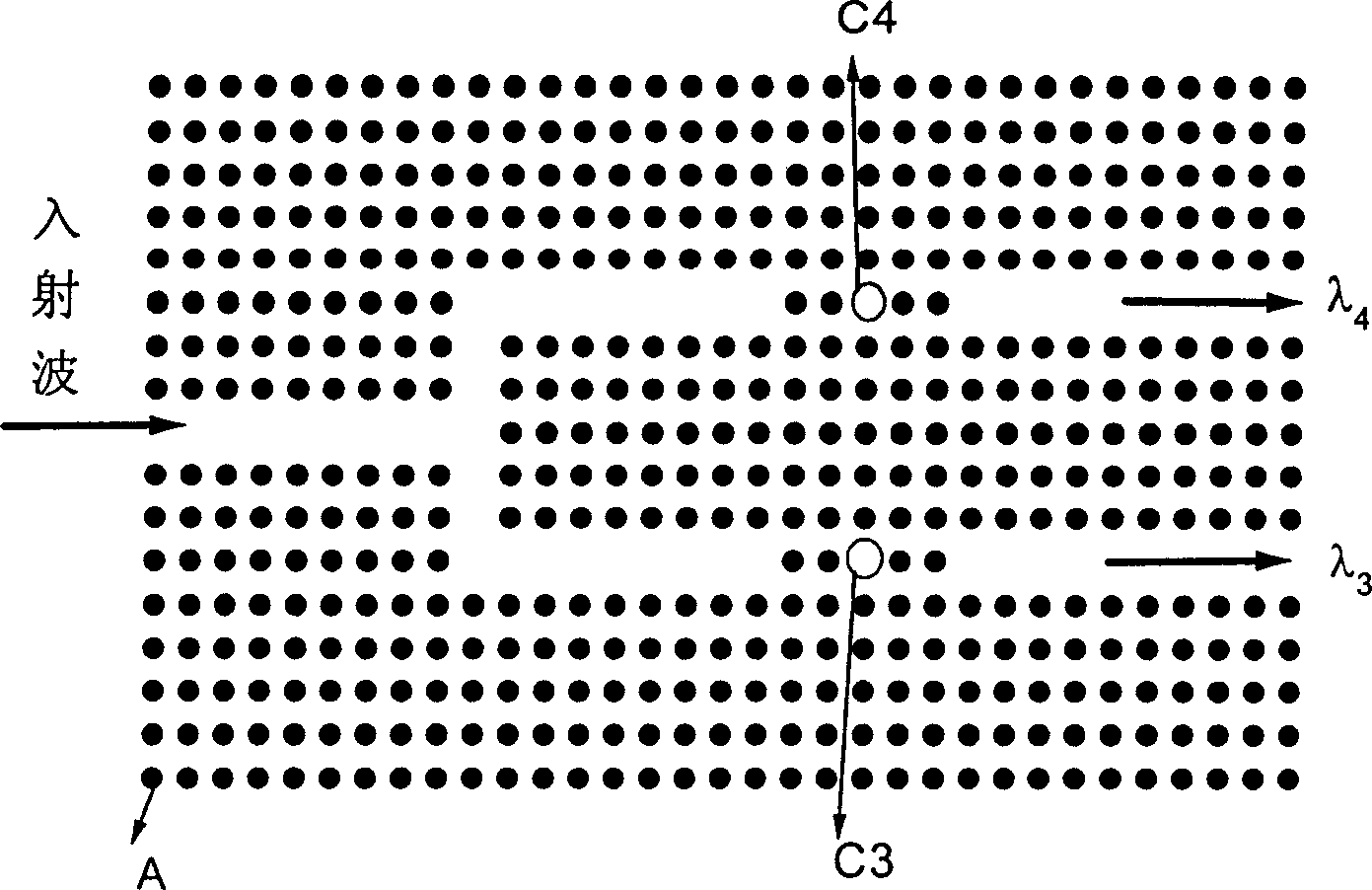
[0025] image 3 It is a device for wave resolution with two channels, where A represents the dielectric cylinder "atom" that constitutes a two-dimensional photonic crystal; C3 and C4 are introduced defects (microcavities). The wavelengths of the defect modes introduced by these defects are λ 3 and lambda 4 . When the wavelengths are λ 3 and lambda 4 When the incident wave enters the photonic crystal along the photonic crystal waveguide, it undergoes resonant coupling with C3 and C4, λ 3 and lambda 4 It comes out from the lower and upper waveguide ports respectively, which completes the function of separating different frequencies. This is the simplest photonic crystal wave resolution device. The two optical paths are symmetrical, that is, the path from the defect to the entrance of the light wave is consistent. Respectively image 3 and Figure 4 When a line of light source is placed at the entrance of the waveguide, the light wave will be coupled into the waveguide,...
Embodiment 2
[0027] Figure 8 It is a structural schematic diagram of a device for wave resolution with 4 channels, similar to Embodiment 1, it can also separate light waves of 4 different frequency bands. where C7, C8, C9 and C10 are introduced defects, and their defect modes correspond to λ 7 , lambda 8 , lambda 9 and lambda 10 . In two dimensions, this photonic crystal is a square photonic crystal. The black dots in it represent a dielectric cylinder, while the surroundings represent another dielectric cylinder. The radius of the dielectric cylinder is chosen to be 0.1858 times the lattice constant, the dielectric constant is 8.4, and the dielectric constant of the surrounding medium is 1.04. The radii of the dielectric cylinders of the four introduced defects C7, C8, C9, and C10 are all 0.3545 times the lattice constant, and the dielectric constants are 5.7, 6.5, 7.0, and 4.5, respectively. Using the multiple scattering method, one can get Figure 9 The wave solution is shown w...
Embodiment 3
[0029] Design a device for wave resolution with 16 channels (such as Figure 10 As shown), 16 symmetrical defects constitute 16 channels for symmetrical wave resolution. Among them, C11, C12, C13, ..., C26 are different defects, forming 16 defect states, and the center frequencies of these defect states are λ 11 , lambda 12 , lambda 13 ,...,λ 26 . In this way, 16 signals of different frequencies can be detected from the outlet. The structure can be two-dimensional or three-dimensional, and can be easily expanded to 32, 64 or even more channels. Moreover, the structural design is very simple, that is, the principle of symmetry is followed, so that the direct coupling efficiency of all channels is the highest.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com