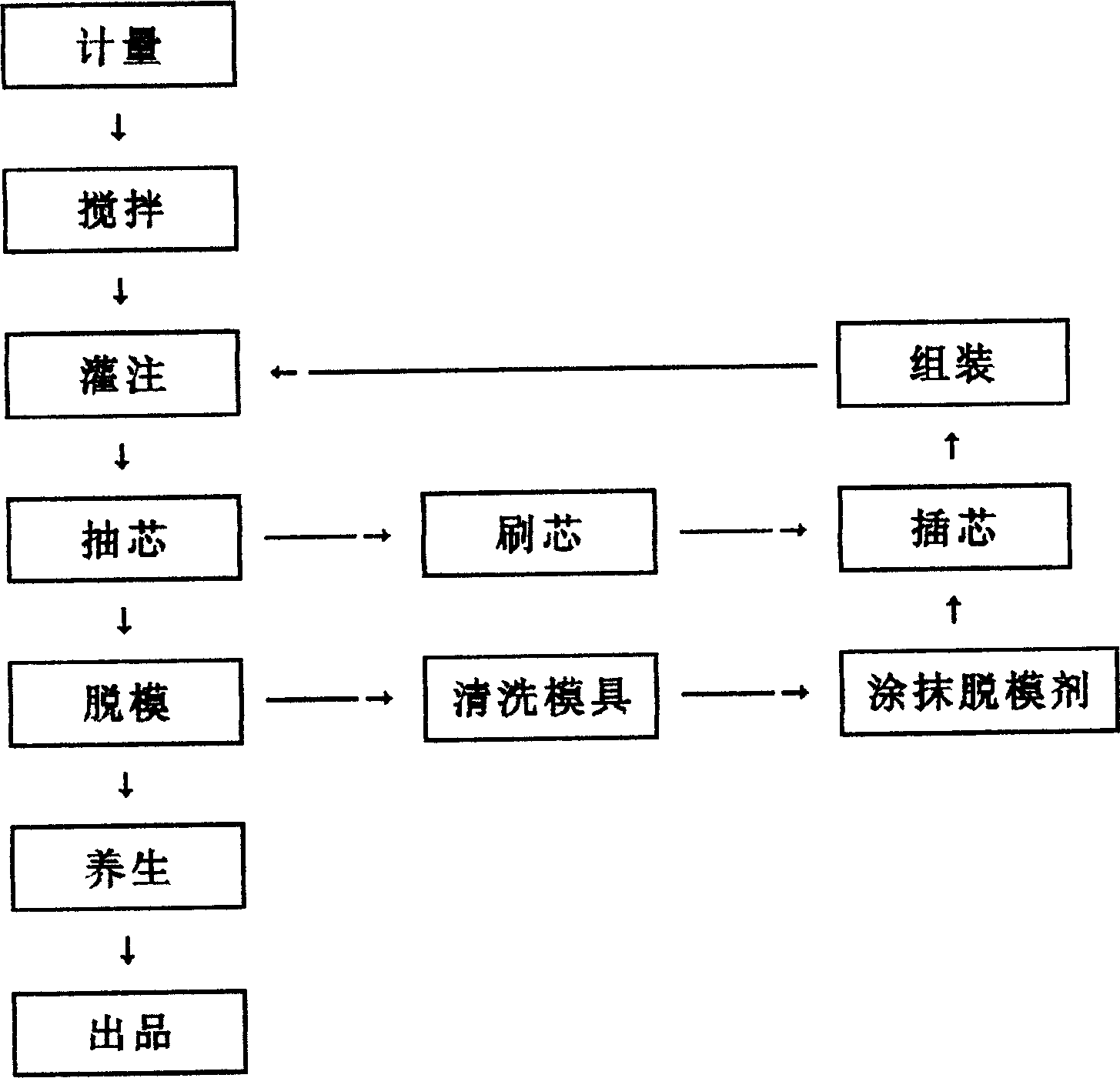
Light porous building-brick and processing technology thereof
A porous block, lightweight technology, applied in the field of building materials, can solve the problems of waste of foundation and main materials, difficult gaps of GRC slats, limited application scope, etc., and achieves the effect of low production cost, novel processing technology and cost reduction.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0027] To prepare a release agent, add 200kg of warm water to the reactor, measure 10kg of stearic acid, pour it into the reactor, heat to 50°C, then add 2kg of ammonia water (concentration: 24%), seal and stir until the stearic acid is completely Convert it into ammonium stearate, pour it into a plastic container, add cold water to dilute to the desired consistency, and set it aside for later use;
[0028] To prepare the activator, take 200kg of calcium hydrogen phosphate and 1kg of calcium lignosulfonate, put them into a reaction kettle, add water to mix and stir evenly, filter to remove impurities, and set aside;
[0029] Weigh 53kg of fly ash, 30kg of gypsum powder, 14kg of cement, 4kg of lime, and take 0.075kg of alkali-resistant glass filaments (the length of the glass filaments is preferably 3-5cm, which can enhance the flexural strength of the block) and scatter them into the fly ash and gypsum. In powder and cement, weigh 3kg of plastic foam particles (waste foam for ...
Embodiment 2
[0034] To prepare a release agent, add 160kg of warm water to the reaction kettle, measure 8kg of stearic acid, pour it into the reaction kettle, heat to 45°C, then add 1.5kg of ammonia water (concentration is 26%), seal and stir until the stearic acid All converted into ammonium stearate, poured into a plastic container, diluted with cold water to the desired consistency, and kept cool for later use;
[0035] To prepare the activator, take 180kg of calcium hydrogen phosphate and 0.9kg of calcium lignosulfonate, put them into a reaction kettle, add water to mix and stir evenly, filter to remove impurities, and set aside;
[0036]Weigh 37kg of fly ash, 30kg of gypsum powder, 28kg of cement, and 3kg of lime, disperse 0.075kg of alkali-resistant glass filaments into the fly ash, gypsum powder, and cement, weigh 3kg of waste plastic foam particles, and crush them until the particle size is 3 -7mm, put the above raw materials into the vertical mixer in turn, add 55kg of water, 7kg ...
Embodiment 3
[0040] Prepare mold release agent, add 240kg of warm water in the reactor, weigh 12kg of stearic acid, pour it into the reactor, heat to 55°C, then add 2.4kg of ammonia water (concentration is 25%), seal and stir until the stearic acid All converted into ammonium stearate, poured into a plastic container, diluted with cold water to the desired consistency, and kept cool for later use;
[0041] To prepare the activator, take 260kg of calcium hydrogen phosphate and 1.3kg of calcium lignosulfonate, put them into a reaction kettle, add water to mix and stir evenly, filter to remove impurities, and set aside;
[0042] Weigh 35kg of fly ash, 35kg of gypsum powder, 30kg of cement, 3kg of lime, 0.05kg of alkali-resistant glass wool, 4kg of waste plastic foam particles, 6kg of activator, and 60kg of water. , to test the main performance indicators, all of which can reach the industry standard.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com