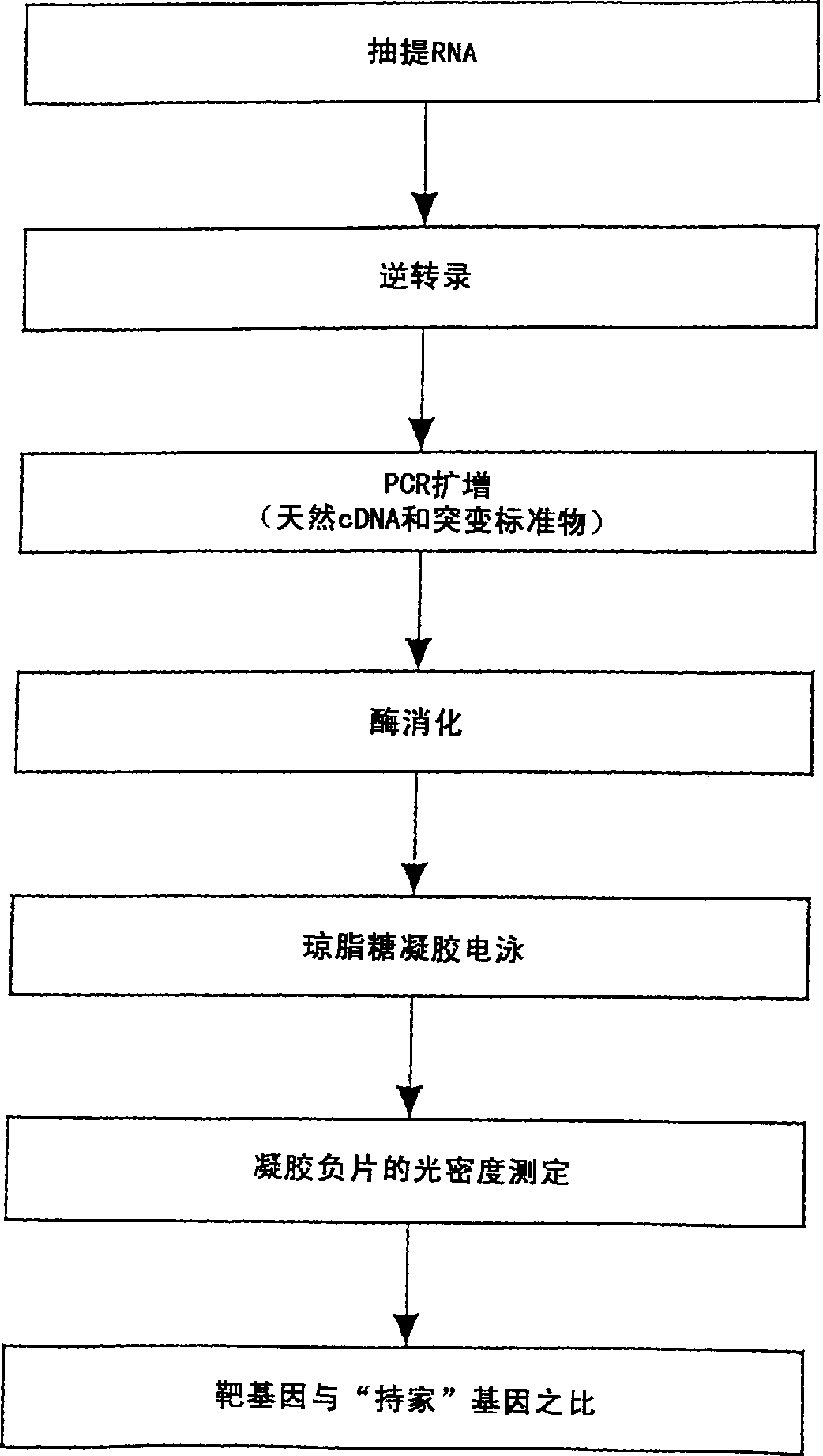
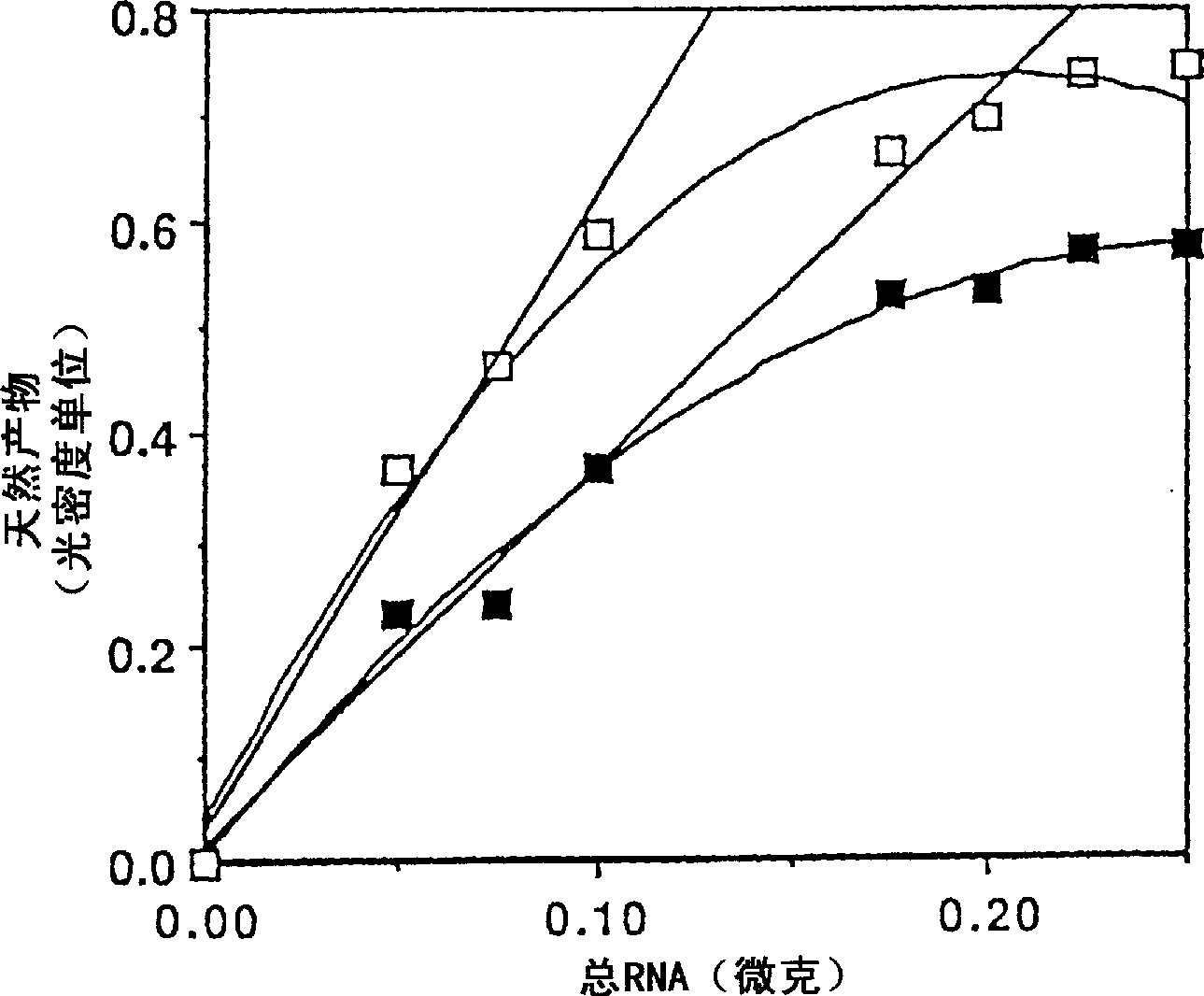
Method for quantitative measurement of gene expression using multiplex competitive reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction
A technology for quantitative determination and gene expression, applied in enzyme production/bioreactors, specific-purpose bioreactors/fermentors, separation methods, etc., can solve the problems of sample addition error and inconvenience between tubes of amplification conditions
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0052] Primers and internal competing templates for mutations were prepared as follows: The ideal sequence was prepared with Oligo -TM Primer analysis software (National Biosciences, Hamel, Mn.) identified. Primers were prepared using an Applied Biosystems Model 391 PCR-Mate DNA Synthesizer. The primer sequences are described below.
[0053] Glutathione peroxidase (GSH-Px) (Chada et al., Genomics 6:268-271, 1990)
[0054] The "outer" primers used to amplify native and mutated templates yielded products 354 bp long. The "outer" primer is
[0055] SEQ.I.D.No.1) (Chada et al., Genomics 6:268-271, 1990)
[0056] Position 241 5'-GGGCCTGGTGGTGCTTCGGCT-3' (encoding the sense strand) corresponds to bases 241-261 of the cloned sequence, and
[0057] SEQ.I.D.No.2) (Chada et al., Genomics 6:268-271, 1990)
[0058] Position 574 5'-CAATGGTCTGGAAGCGGCGGC-3' (encodes antisense strand), which anneals to bases 574-594.
[0059] The "internal" primer used to synthesize the mutated intern...
Embodiment
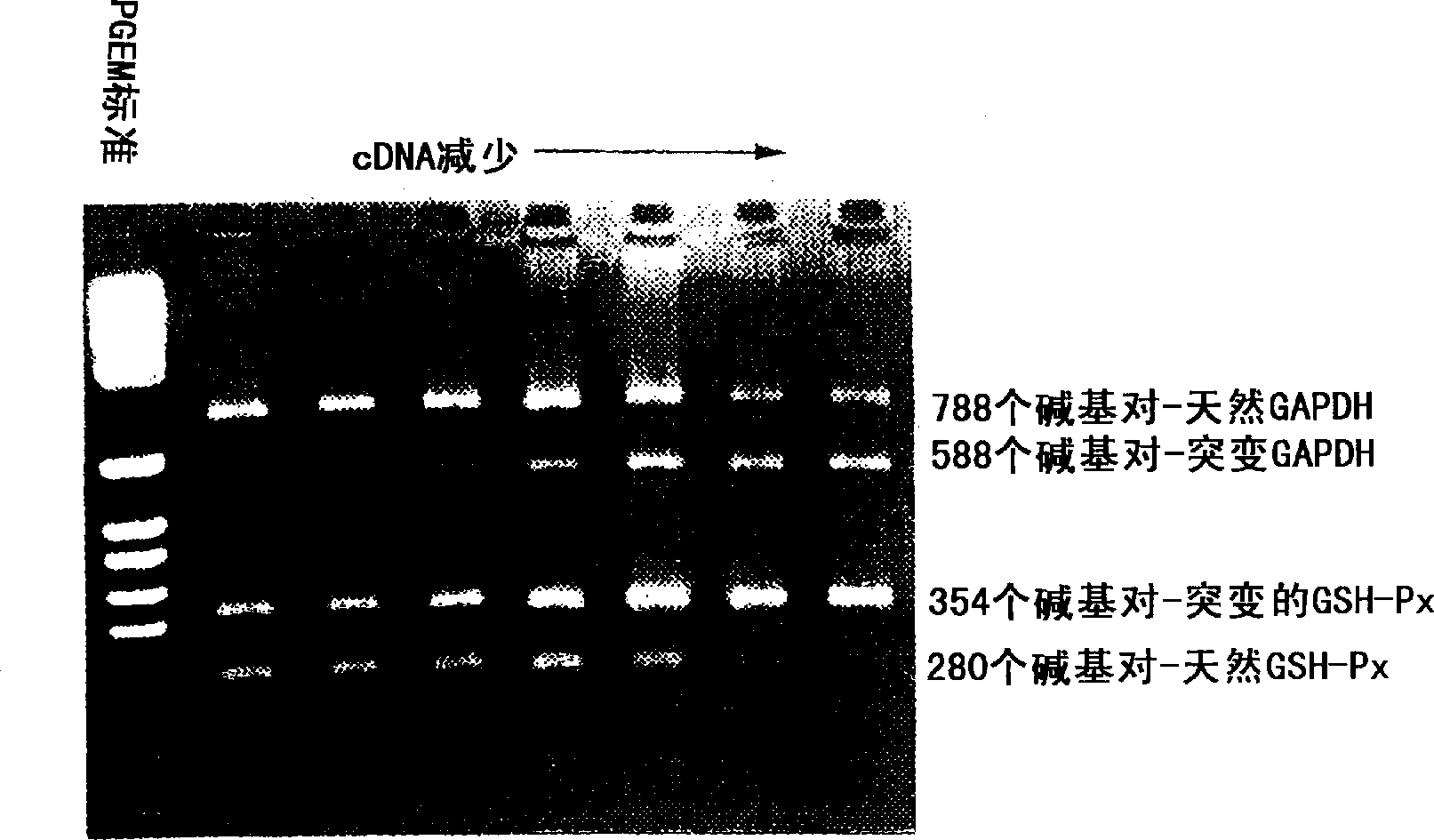
[0120] Serial dilutions of BEP2D cDNA were co-amplified with constant amounts of internal standard competition templates (10 attomoles each) for each single-base mutation before assaying. The negative of the gel ( figure 2 shown) were analyzed by densitometry to quantify the individual bands.
[0121] NN
N M
N M
MM
[0122] Wherein N = the ratio of single-stranded natural products before heavy annealing, M = the ratio of single-stranded mutant products before heavy annealing, NN (or N 2 ) = fraction of double-stranded natural products after heavy annealing, 2NM = fraction of heterodimers formed after heavy annealing, and MM (or M 2 ) = proportion of double-stranded mutation products after heavy annealing.
[0123] Heterodimers were counted indirectly because they were not restricted and had the same electrophoretic mobility as undigested homodimers. Therefore, heterodimers were detected by densitometry along with undigested homodimers. To q...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com