Catalytic conversion method for preparing light olefins by using C4-C6 distillates
A catalytic conversion method, C4 fraction technology, applied in the field of catalytic conversion, to achieve the effect of improving cracking conversion efficiency, improving feed characteristics, and increasing overall effective conversion rate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
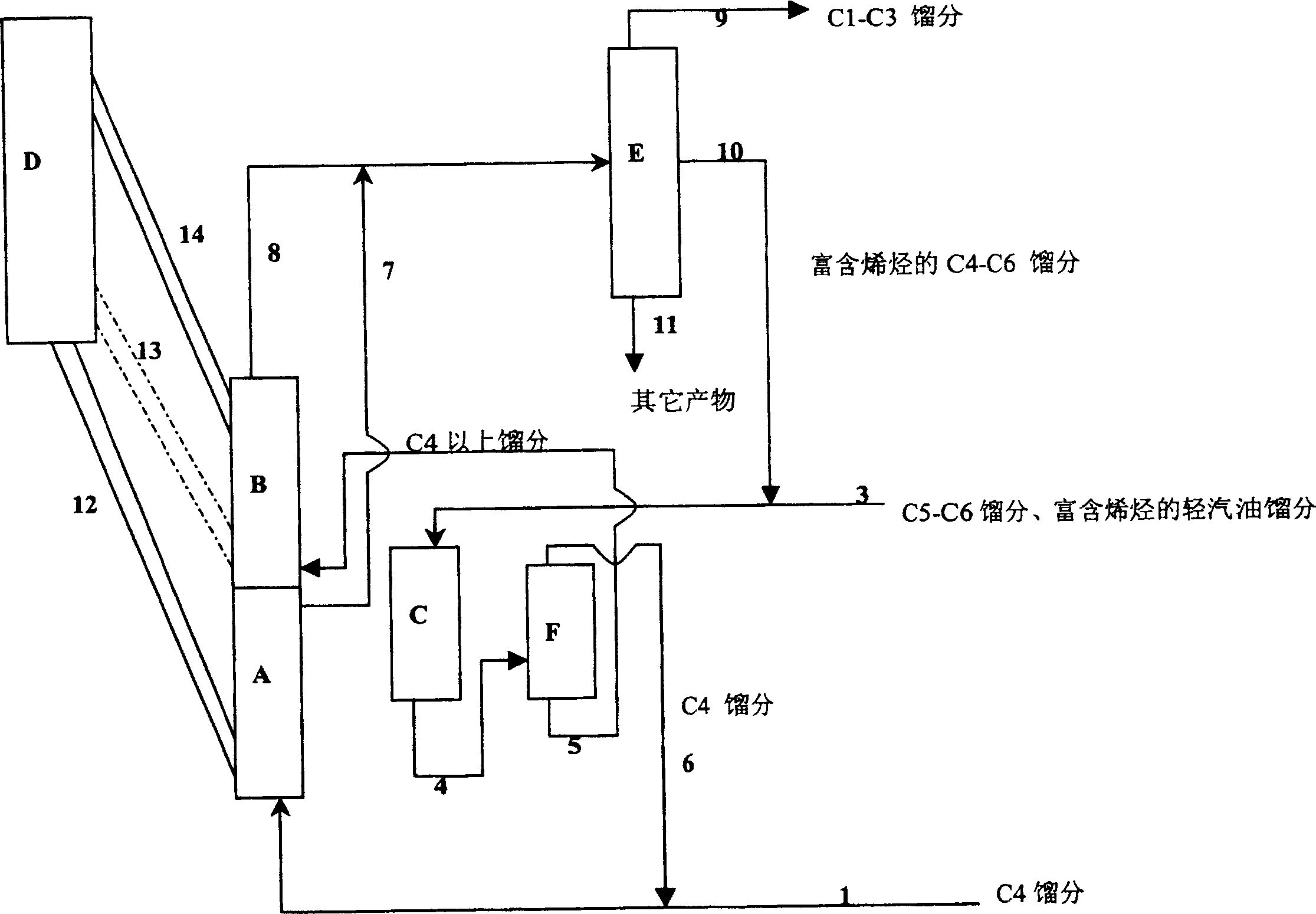
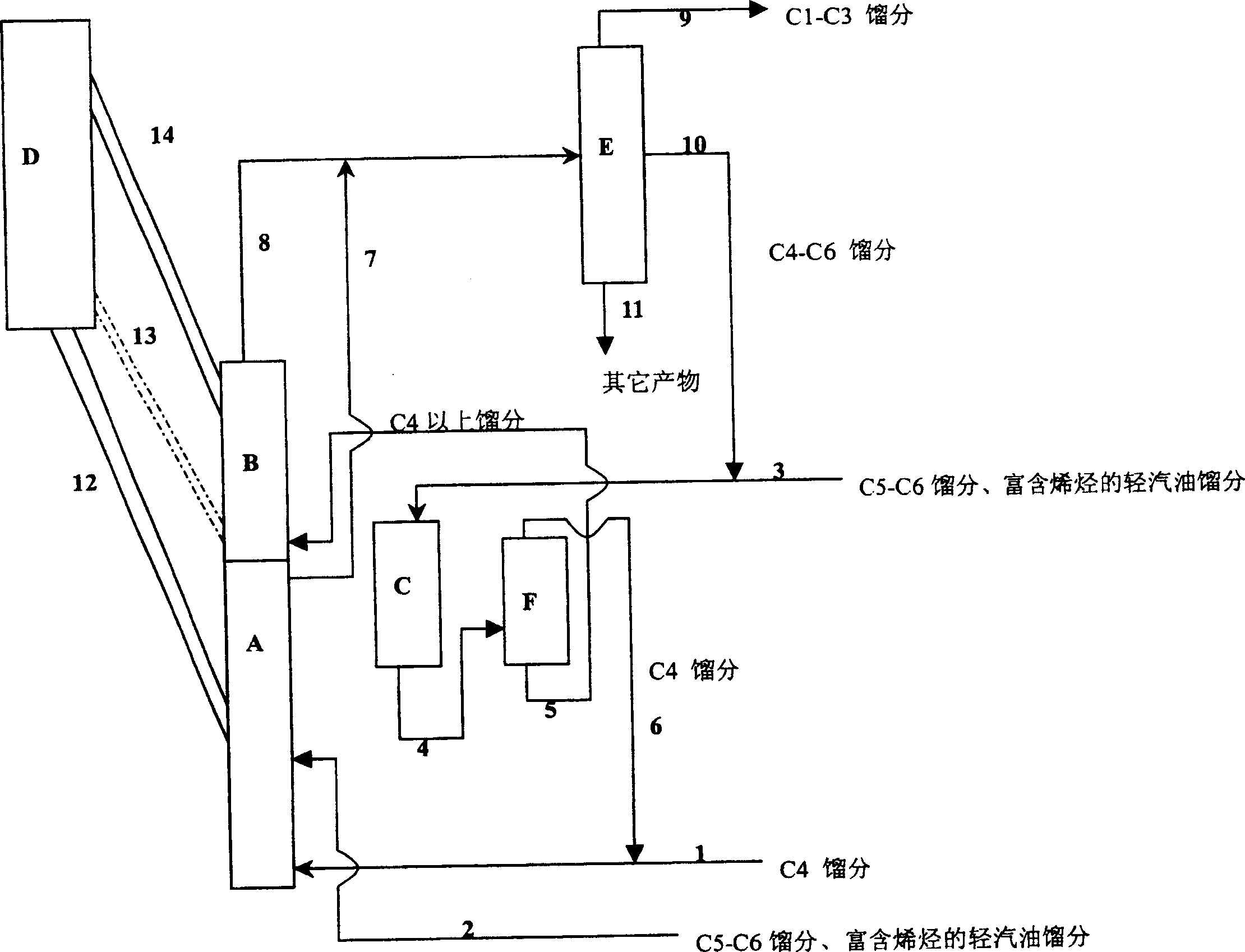
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0041] This example illustrates the case of using gaseous hydrocarbons rich in C4 fractions as raw materials and using a CIP catalyst to conduct a single-pass catalytic conversion test under relatively high severity conditions in a small fluidized bed reactor.
[0042] As shown in Table 3, the gaseous hydrocarbons rich in C4 cuts enter the fluidized bed reactor, and the reaction temperature is 650-680 ° C, the pressure at the top of the reactor is 200 kPa, and the water-hydrocarbon mass ratio is 0.08:1. Contact and react with catalyst. The reaction product, steam and spent agent are separated in the settler, and the reaction product is separated to obtain gaseous product and liquid product, while the spent agent is stripped by water vapor to remove the hydrocarbon products adsorbed on the spent agent. The stripped spent catalyst is contacted with heated hot air for regeneration, and the regenerated catalyst is then subjected to a new catalytic conversion reaction. The test co...
Embodiment 2
[0046] This example illustrates the case of carrying out a catalytic conversion test in a small fluidized bed reactor using a CIP catalyst with combined feed of gaseous hydrocarbons rich in C4 fractions and light gasoline fractions.
[0047] As shown in Table 3, the gaseous hydrocarbons rich in C4 fractions first enter the fluidized bed reactor, and contact and react with the CIP catalyst at a reaction temperature of 680 ° C, so that an appropriate amount of coke is formed on the catalyst, and the catalyst is not decomposed. Charred regeneration, and continue to feed the light gasoline fraction shown in Table 2 and continue to contact with the catalyst for reaction. The reaction product, steam and spent agent are separated in the settler, and the reaction product is separated to obtain gaseous product and liquid product, while the spent agent is stripped by water vapor to remove the hydrocarbon products adsorbed on the spent agent. The stripped spent catalyst is regenerated by...
Embodiment 3
[0054] This example illustrates the oligomerization of gaseous hydrocarbons rich in C4 fractions in a down-flow fixed-bed reactor.
[0055] The test device is a descending fixed bed, the maximum bed height can reach 50cm, the bed diameter is 2.2cm, and the catalyst storage capacity can be 50-100g. The catalyst is a high-silicon-aluminum-ratio molecular sieve with a five-membered ring (MFI) structure, and its specific preparation method is as described in Example 1 of CN1072032C. According to molecular sieve: aluminum sol (as Al 2 o 3 Calculated): kaolin (produced in Suzhou, China) = 35:15:50 dry basis weight ratio mixed and extruded into trilobal strips on the extruder, crushed and sieved after drying, 100g was taken and packed into a fixed bed reactor conduct experiment. In the experiment, when the gauge pressure of the system is 4.0MPa and the temperature is in the range of 190-260℃, the space velocity by weight is 0.256h -1 Gather C 4 Raw material, C in the reaction pr...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| boiling point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com