Magnetic random access memory
A technology of random access memory and magnetoresistive devices, which is applied in the direction of static memory, digital memory information, information storage, etc., can solve the problem of narrow width, insufficient reduction of wiring current density, large storage capacity, high-capacity wiring reliability writing input errors etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
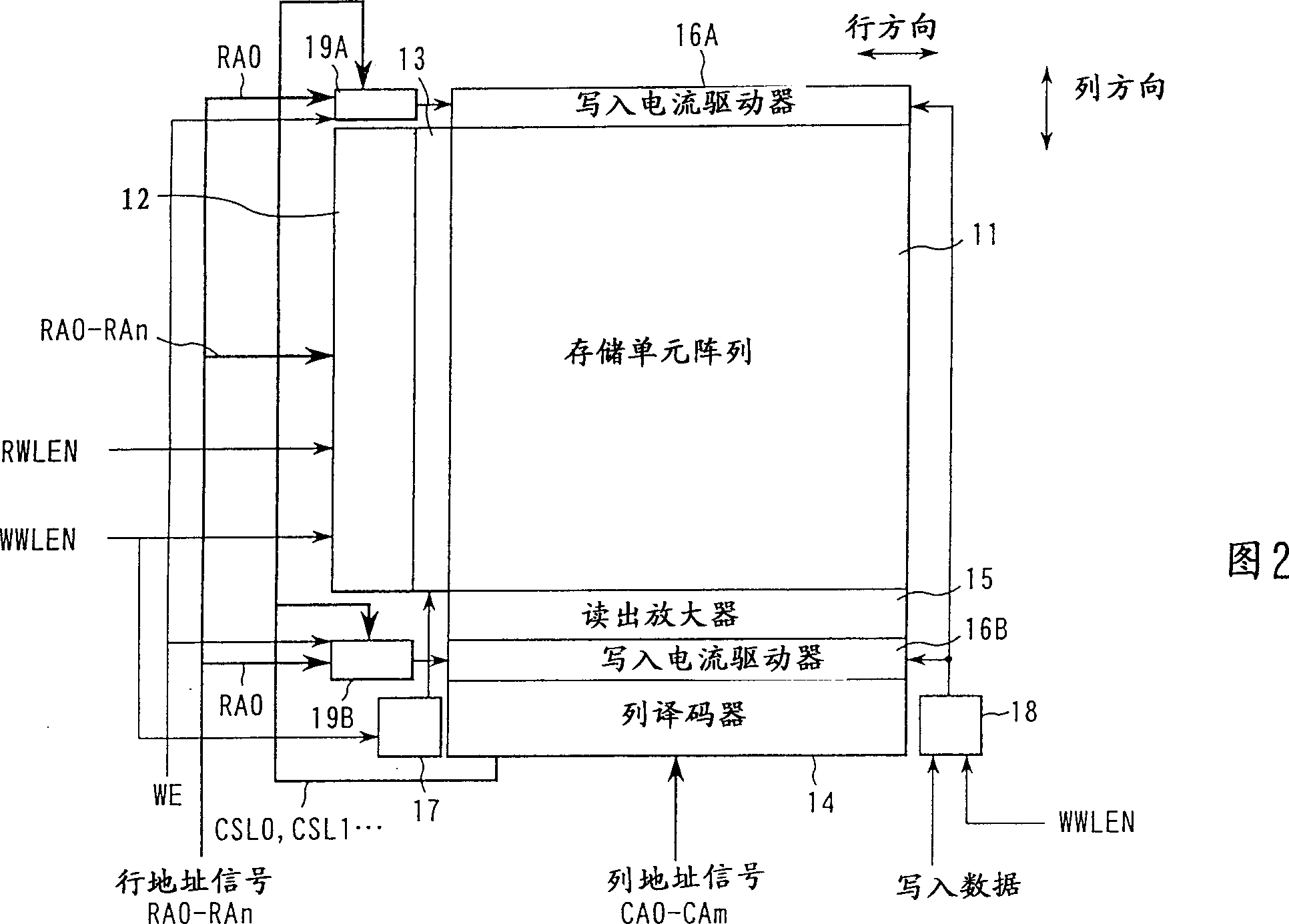
[0045] FIG. 2 shows the main part of the magnetic random access memory as Embodiment 1 of the present invention.
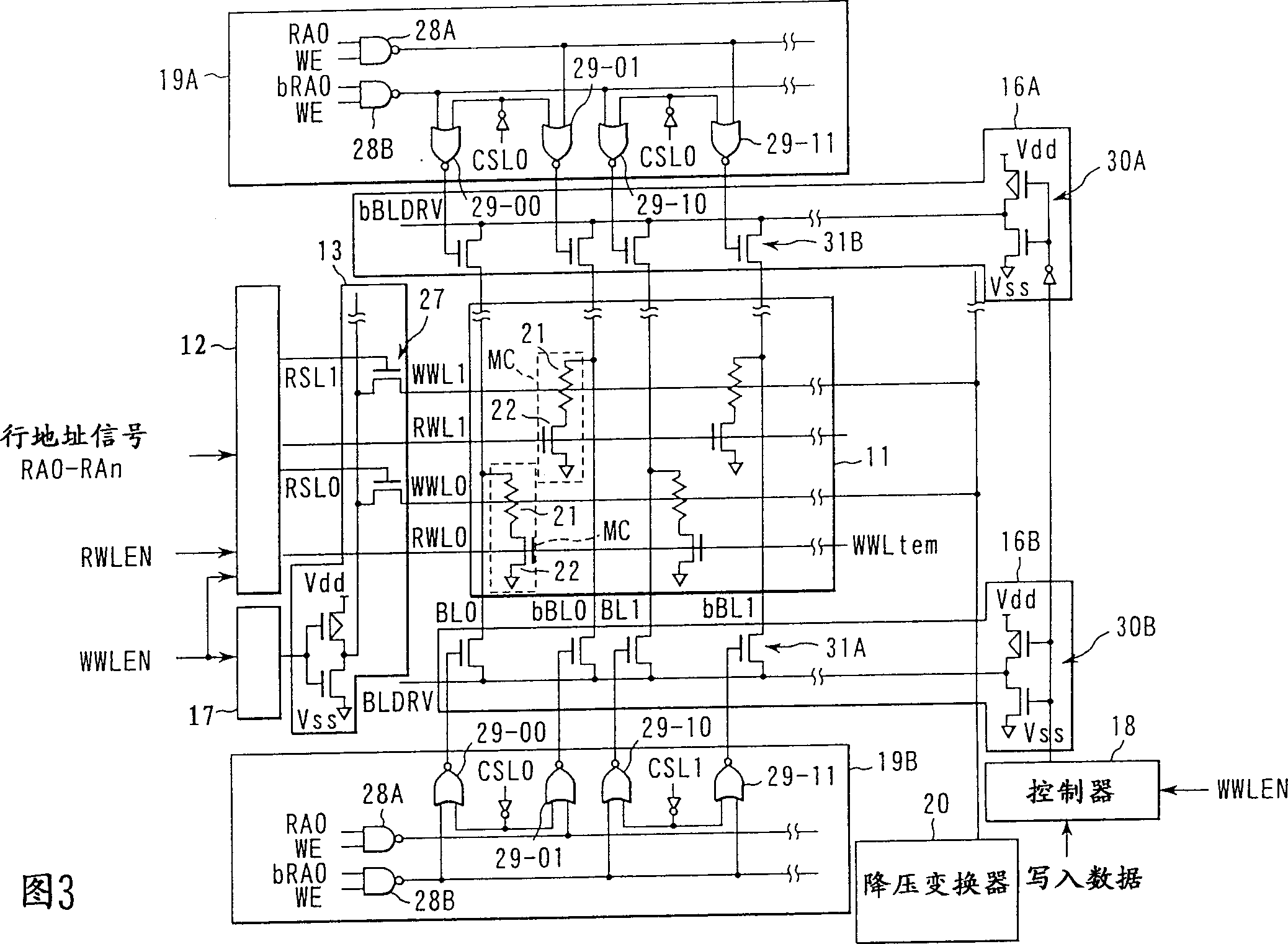
[0046] At the end of the memory cell array 11 in the row direction, a row decoder 12 is arranged. Row address signals RA0-RAn are input to row decoder 12 . Row decoder 12 enters an active state when write word line enable signal WWLEN or read word line enable signal RWLEN becomes enabled.
[0047] At the time of writing, row decoder 12 selects a write word line (row) WWL of memory cell array 11 based on row address signals RA0-RAn. The write word line WWL is used to make the magnetization directions of the two magnetic layers of the memory cell parallel or antiparallel together with the bit line BL to be described later. The WWL driver 13 functions to drive the selected write word line WWL.
[0048] The controller 17 enters the active state when the write word line enable signal WWLEN is in the enabled state. The controller 17 can be constituted by, for exampl...
Embodiment 2
[0109]Magnetic random access memory (MRAM) can perform random writing to any bit in the memory cell array. Here, as a method for increasing the writing bandwidth, for example, a method of fixing a row address and then writing to a memory cell located at the intersection of a row specified by the row address and a plurality of columns is known.
[0110] In MRAM, it is not preferable to simultaneously perform a write operation on all of a plurality of columns in order to increase a write current, since insufficient peak current supply and adverse effects such as radiation of electromagnetic waves may occur.
[0111] In this case, for example, the column selection signal CSLi for selecting a column is sequentially input with a time shift, and the data writing to the memory cell is performed one column at a time, without writing to all of the plurality of columns at the same time. into action.
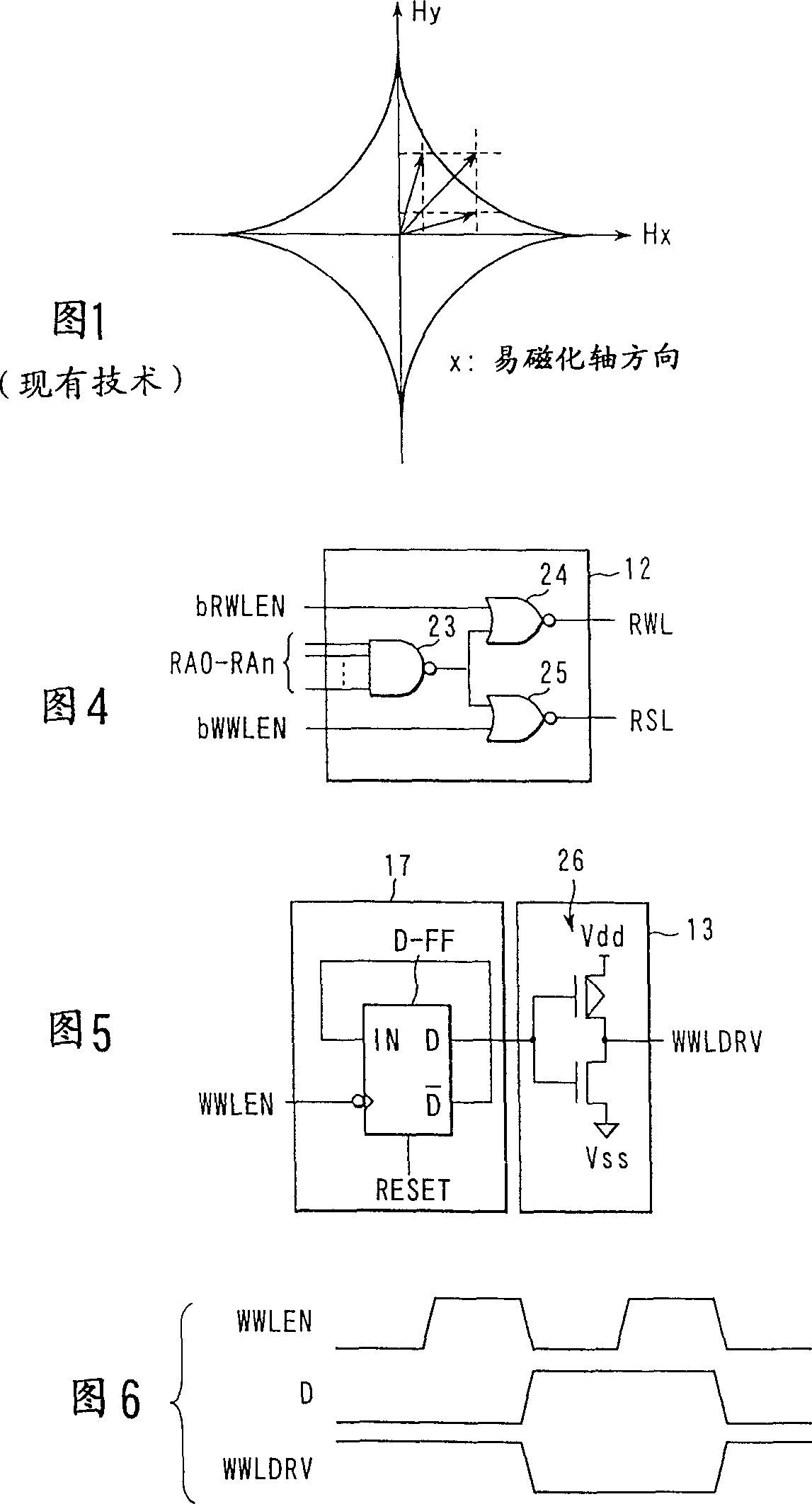
[0112] Here, as can be seen from the star-shaped curve in FIG. 10 , when the magnetiz...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com