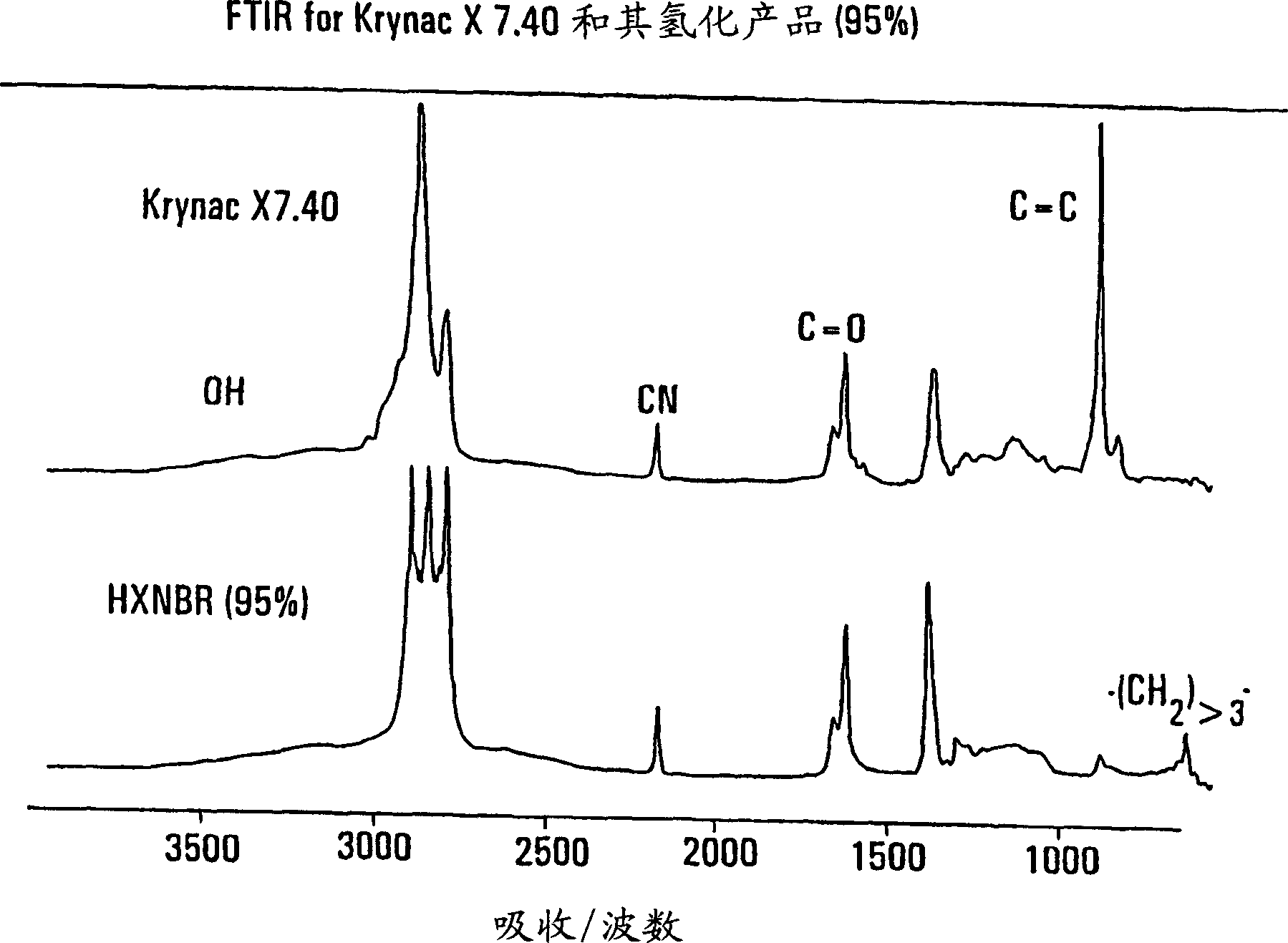
Process for hydrogenating carboxylated nitrile rubber, the hydrogenated rubber and its use
A hydrogenation reaction, carboxylic acid technology, applied in chemical instruments and methods, rubber layered products, other chemical processes, etc., can solve the problems of uncertain product quality, production stoppage, difficult to control the amount of acid, etc., and achieve excellent wear resistance. good low temperature flexibility, excellent adhesion effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0048] Laboratory tests were carried out with 6% polymer in 2.7 kg chlorobenzene, 184 g of methacrylic acid-acrylonitrile-butadiene statistical terpolymer containing 28% by weight acrylonitrile, 7% methacrylic acid, 65% butadiene, ML 1+4 / 100°C=40 (Krynac X 7.40, available from Bayer) was charged to a 2 US gallon Parr high pressure reactor. In the case of thorough stirring, with pure H 2 (100-200 psi) degas the reactor three times. The temperature of the reactor is raised to 130° C., and under a hydrogen atmosphere, 0.139 g (0.076 phr) of tris(triphenylphosphine)-rhodium(I) chloride in 60 ml of monochlorobenzene having an oxygen content of less than 5 ppm—catalyst A solution of triphenylphosphine (TPP) and 2.32 g of the cocatalyst was charged to the reactor. The temperature of the reactor was raised to 138°C and the pressure of the reactor was set at 1200 psi (83 atm). The temperature of the reactor and the pressure of hydrogen were kept constant throughout the reaction. Af...
Embodiment 2
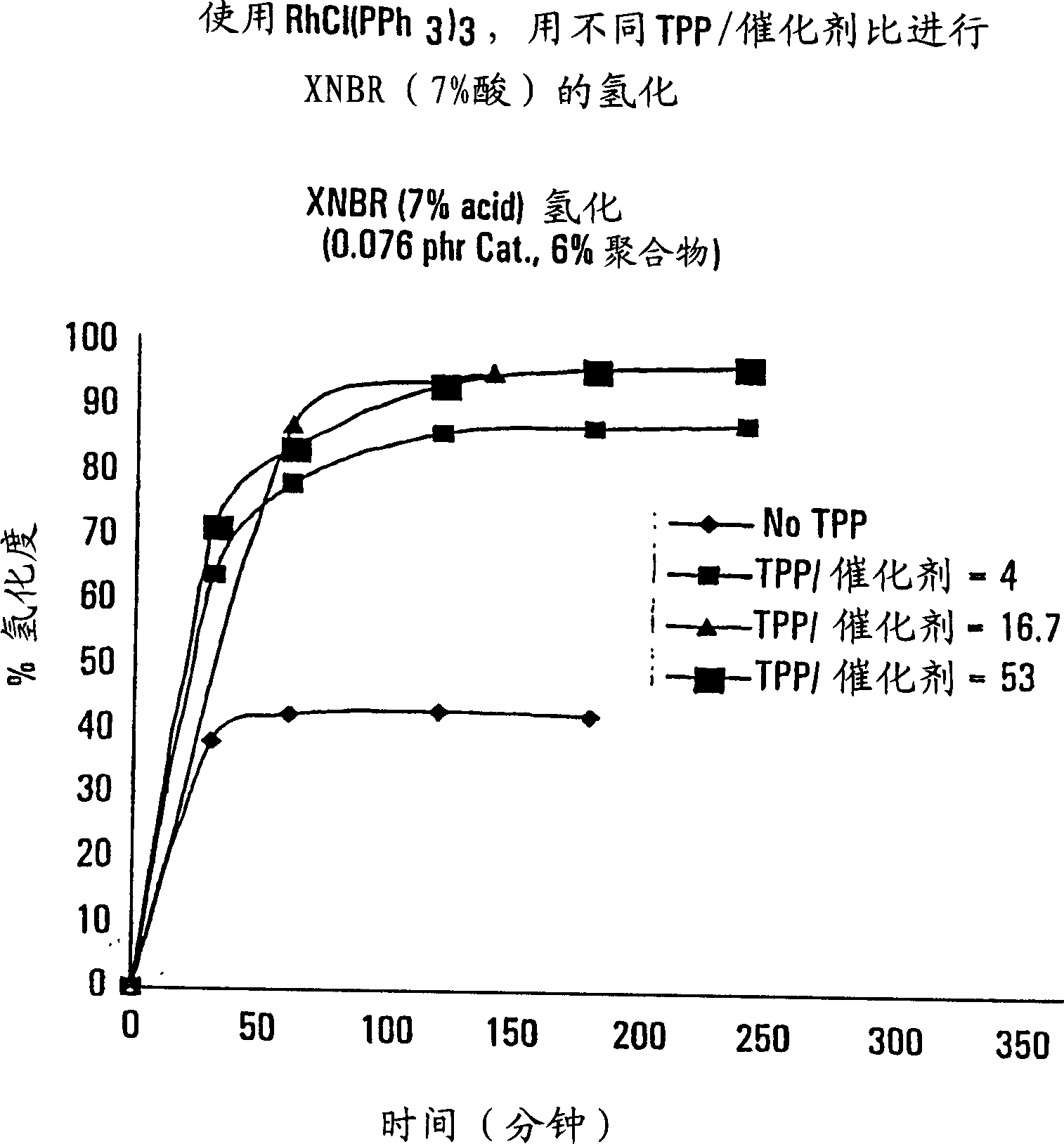
[0052] Krynac X 7.40 polymer was used in the presence of different amounts of co-catalyst triphenylphosphine (TPP), i.e. 0-4% by weight (based on solid rubber), or a co-catalyst / catalyst ratio of 0-53, and as a polymer solution The catalyst of 0.076% concentration by weight of the terpolymer in the hydrogenation reaction was carried out according to Example 1. the following figure 2 and Table 1 gives the results of the hydrogenation reaction. It is obvious that the presence of cocatalysts can significantly promote the hydrogenation reaction of polymers. Those operations without cocatalyst and those without the process according to the invention are comparative experiments.
[0053] Table 1 Hydrogenation of XNBR (7.0% acid) was performed using different ratios of triphenylphosphine (TPP) to catalyst.
[0054] Catalyst: 0.076phr*, 6% polymer
[0055] *Parts per 100 parts by weight rubber
Embodiment 3
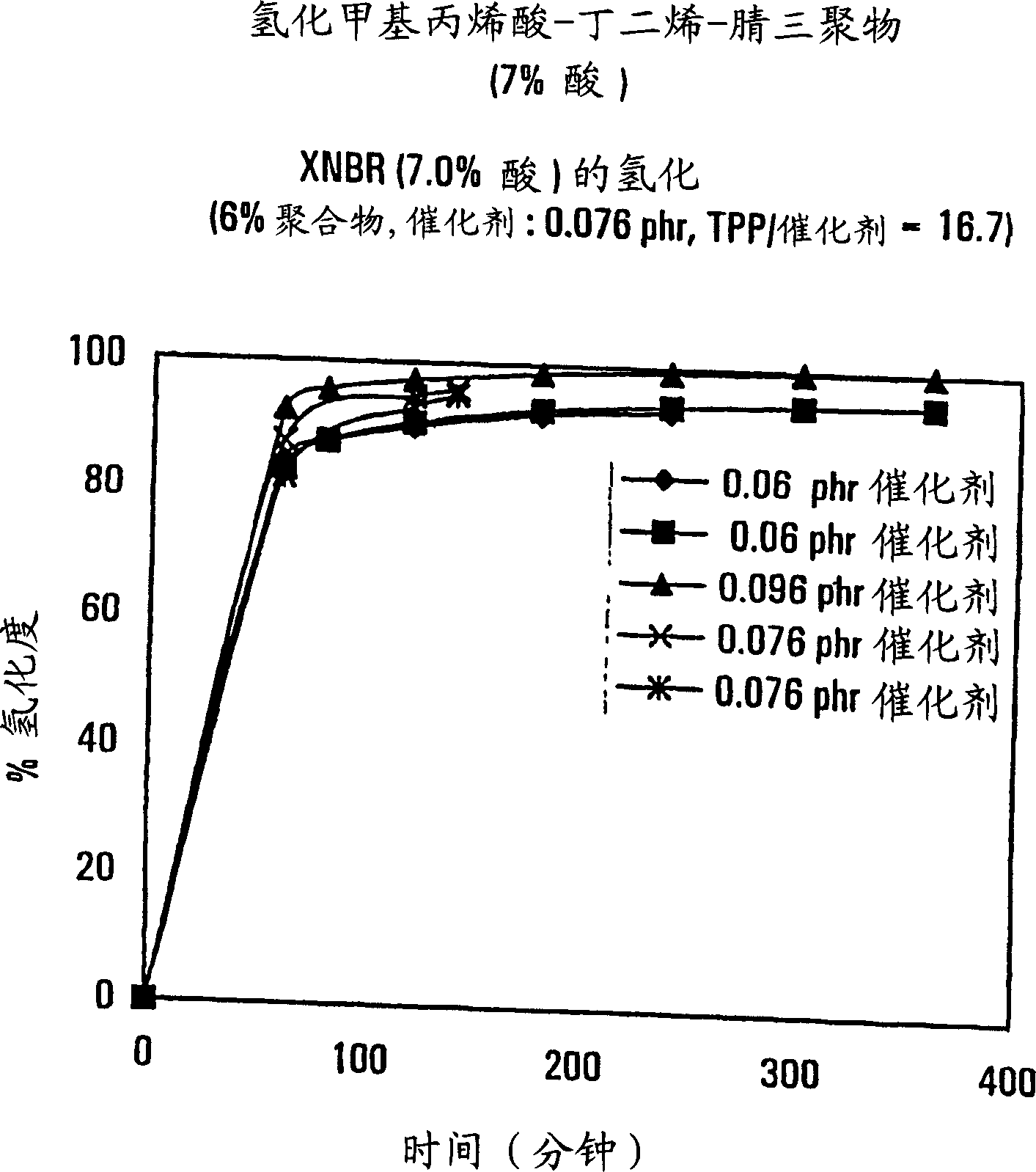
[0057] Another methacrylic acid-acrylonitrile-butadiene copolymer (7% acid, 28% ACN, 65% butadiene) is carried out hydrogenation reaction according to the step of embodiment 1, the difference is that the amount of catalyst is different from the implementation Example 1 is different. The degree of hydrogenation obtained is in the range of 93-99.5%. The results of these experiments are shown in Table 2 and image 3 shown.
[0058] Table 2 Hydrogenation of XNBR (7.0% acid).
[0059] 0.06 wt% Rh, 12% polymer
TPP: Catalyst = 16.7:1
0.096 wt% Rh, 12% polymer
TPP: Catalyst = 16.7:1
time (minutes)
% degree of hydrogenation
%RDB
time (minutes)
% degree of hydrogenation
%RDB
0
0
100
0
0
100
60
84.4
15.6
60
92.4
7.6
80
87.4
12.6
80
95.5
4.5
120
90
10
120
97.2
...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com