Semiconductor storage device
A storage device and semiconductor technology, applied in the direction of information storage, static memory, digital memory information, etc., can solve the problems of shortening the storage unit time, reducing the writing time, small chip size, etc., and achieve chip size reduction and simplification of the structure , the effect of reducing the unit area
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 Embodiment approach
[0067] Hereinafter, embodiments of the present invention will be described with reference to the drawings. [first embodiment]
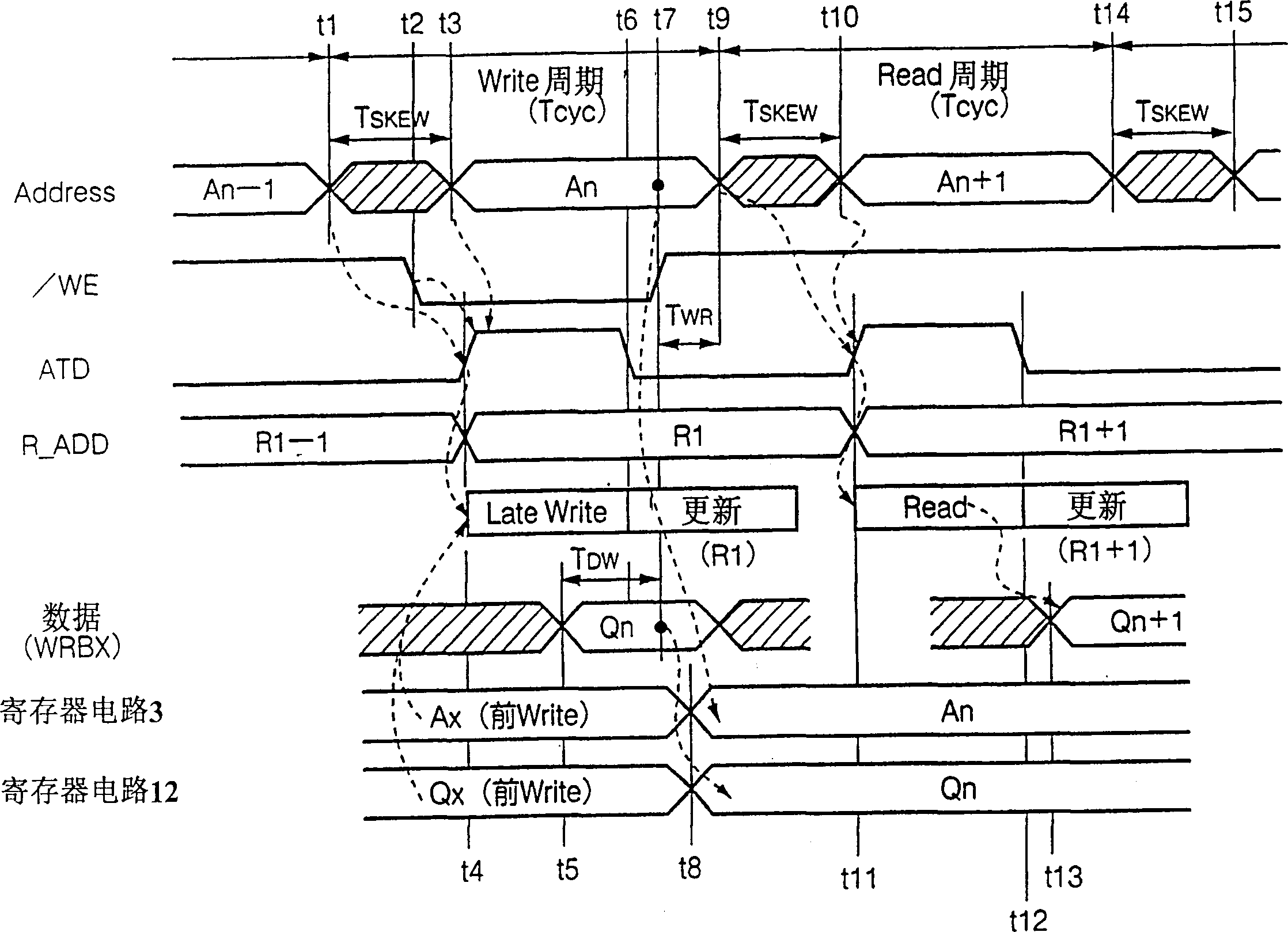
[0068] First, the present embodiment will be briefly described. As described in the first related art to the third related art above, if reading and writing corresponding to external access requests are performed after updating, the address access time T AA Increase. Therefore, in this embodiment, when there is an access request from the outside, the update is performed after reading or writing corresponding to the access request. However, relying solely on this, the problems pointed out in the third related art and the fourth related art also arise. Therefore, this embodiment implements a late write (Late Write) method to write to the memory cell, thereby shortening the writing time and storage cycle.
[0069] That is, in the storage cycle that is provided with an external write request, only the provided write address and write data are put int...
no. 2 Embodiment approach
[0204] In the first embodiment, in one storage cycle (cycle time T cyc ) to perform delayed write and update or read and update. On the other hand, in this embodiment, for example, by performing two accesses (delayed writing or reading) and one update in two consecutive storage cycles, the cycle time is shortened compared with the first embodiment, in order to realize High speed.
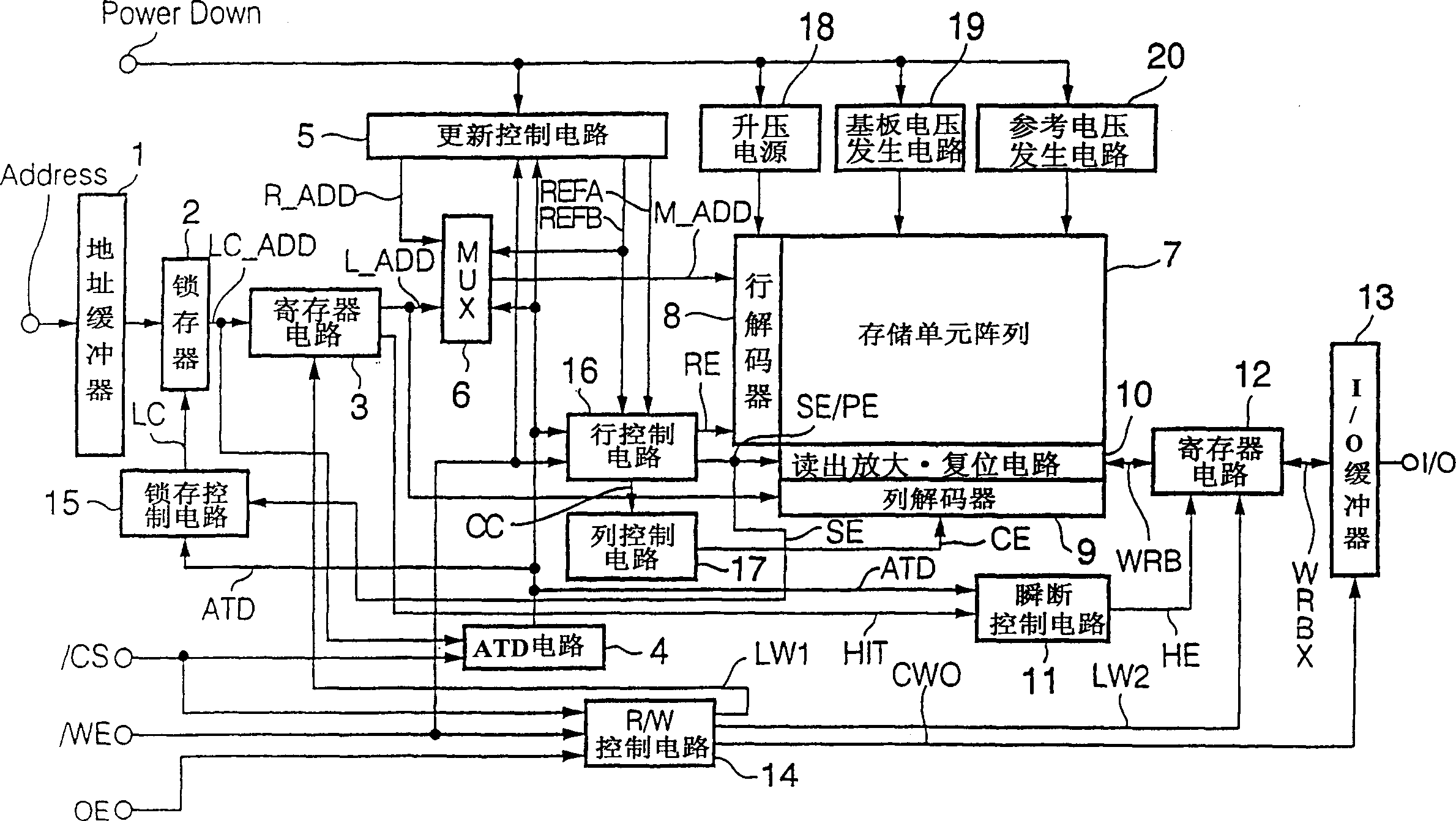
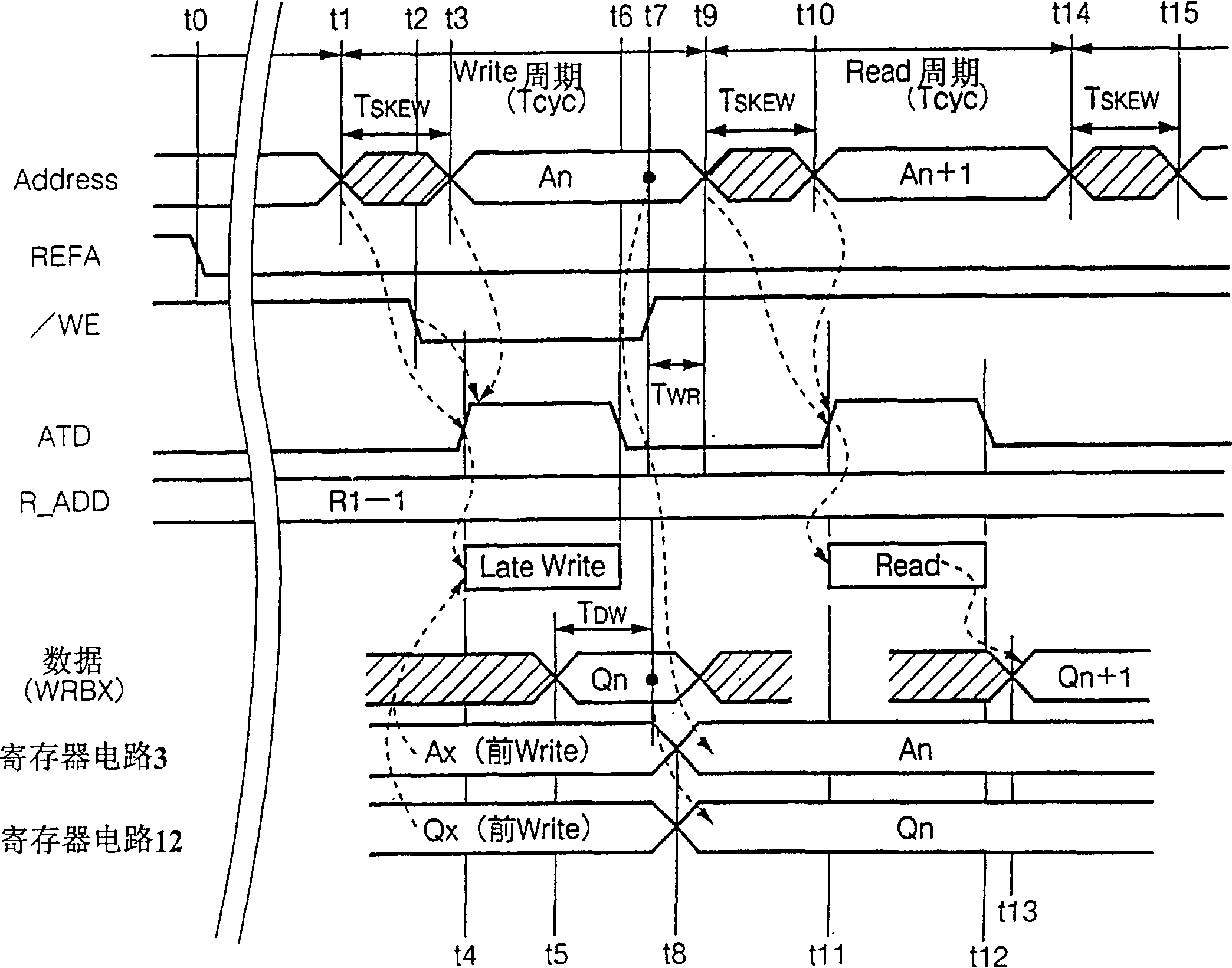
[0205] Figure 8 Shown is a block diagram showing the configuration of the semiconductor memory device according to the present embodiment, and the components and figure 1 The same use the same symbol. and figure 1 The difference is that the ATD circuit 4 is replaced by an ATD circuit 24 , and refresh control signals REFA, REFB are input to the ATD circuit 24 . As described below, the generation timing of the address change detection signal ATD in this embodiment is slightly different from that in the first embodiment.
[0206] That is, in the first embodiment, the ATD circuit 4 generates a po...
no. 3 Embodiment approach
[0215] In the first and second embodiments described above, the memory cycle is shortened by delaying writing. On the other hand, in this embodiment, the following conditions are added to the conditions of the first embodiment. In this way, instead of delaying writing as in the first embodiment, the actual writing to the memory cell is performed during the storage cycle with a write request, so that the advantages of shortening the storage cycle and the like can be obtained similarly to the first embodiment. Effect.
[0216] That is, in the first embodiment and the like, it is considered that the write data is determined later than the fall of the write enable signal / WE and after the address time lag period. In this embodiment, when determining the specifications of the semiconductor memory device, not only the write enable signal / WE but also the write data during the address skew period are taken into consideration. In this way, as in the case of delayed writing, the writ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com