Driving circuit with low current loss
A technology for driving circuits and level shifting circuits, which is applied in the direction of reducing power consumption, logic circuits, logic circuit coupling/interface using field effect transistors, etc., and can solve problems such as large current consumption
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
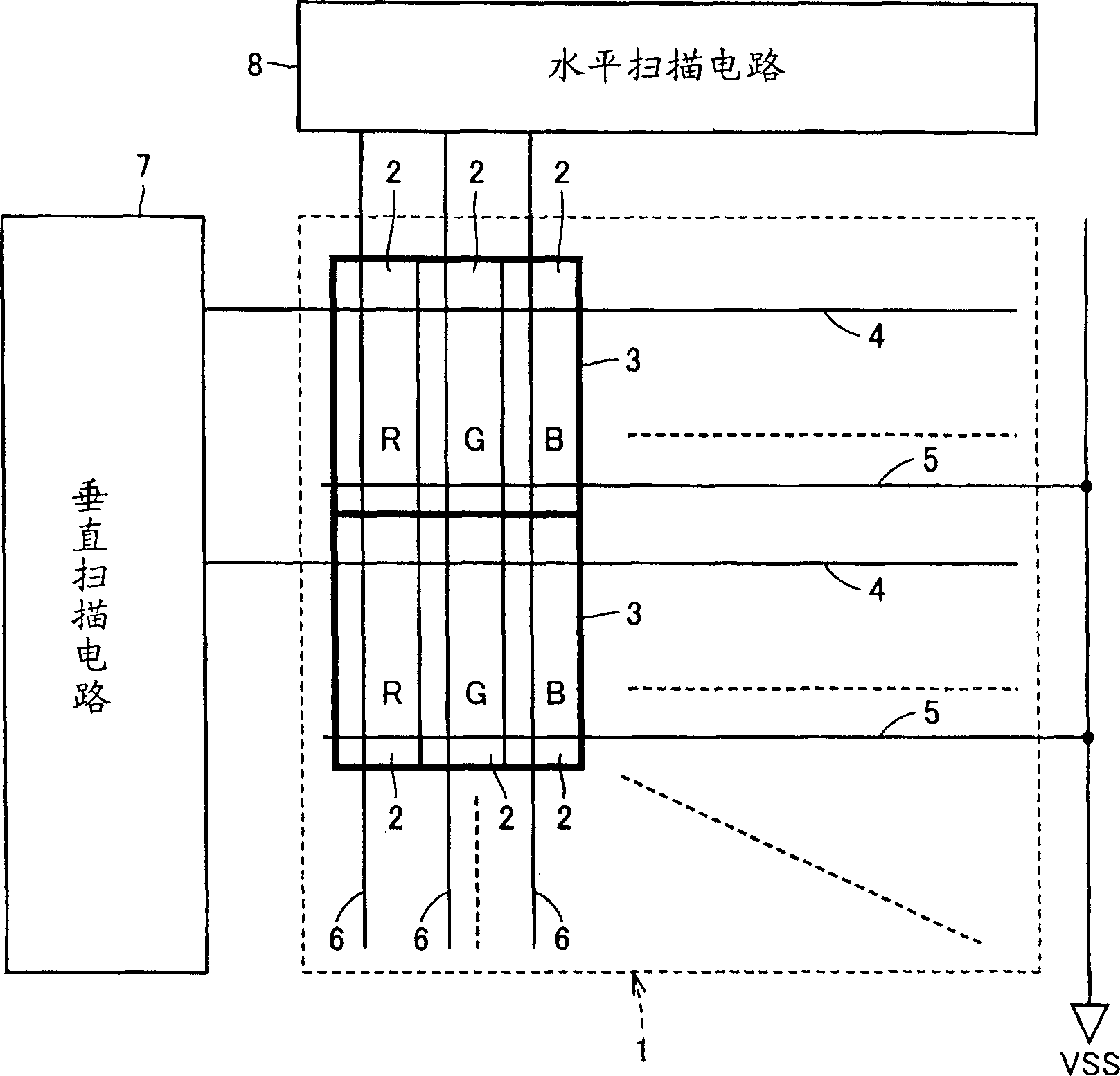
[0092] figure 1 It is a block diagram showing the configuration of the color liquid crystal display device according to Embodiment 1 of the present invention. exist figure 1 Among them, the color liquid crystal display device includes a liquid crystal panel 1, a vertical scanning circuit 7, and a horizontal scanning circuit 8, and is installed in, for example, a mobile phone.
[0093] The liquid crystal panel 1 includes a plurality of liquid crystal cells 2 arranged in multiple rows and columns, scanning lines 4 and common potential lines 5 corresponding to each row, and data lines 6 corresponding to each column.
[0094] The liquid crystal cells 2 are arranged in groups of three in each row. R, G, and B color filters are respectively provided in the three liquid crystal cells 2 of each group. Three liquid crystal cells 2 of each group constitute one pixel 3 .
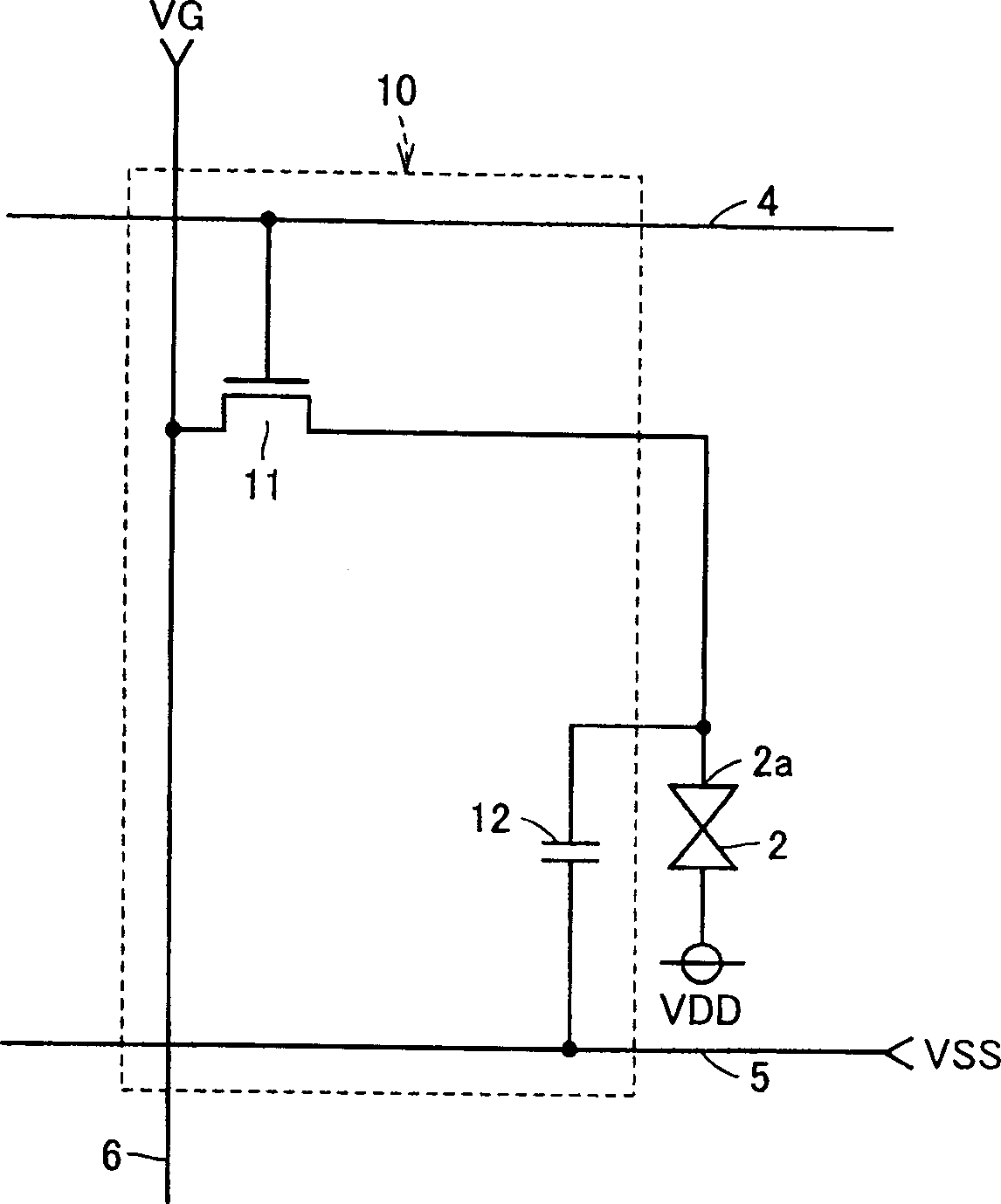
[0095] Such as figure 2 As shown, a liquid drive circuit 10 is provided in each liquid crystal cell 2 . The...
Embodiment 2
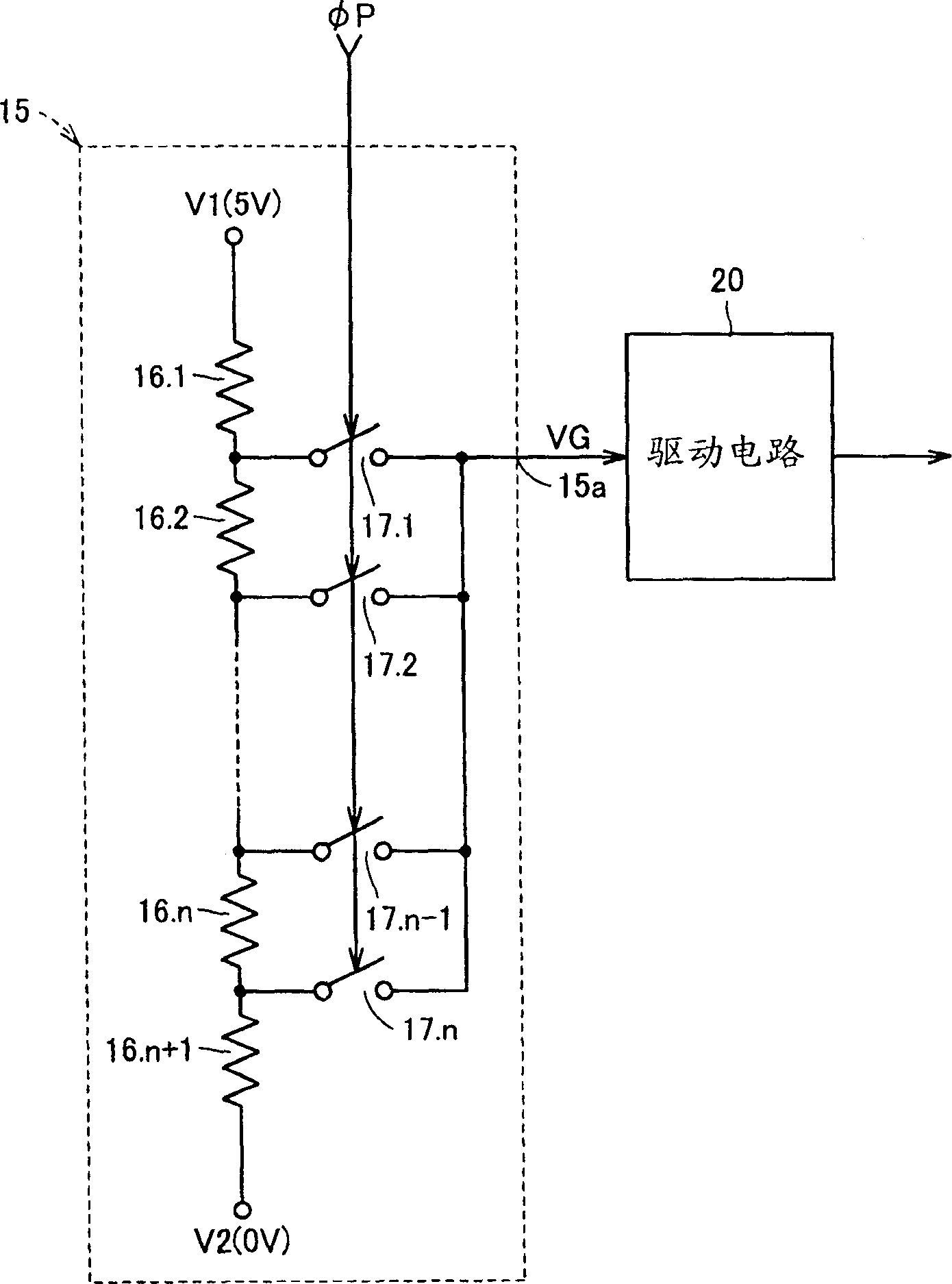
[0140] In Example 1, although the threshold voltages of all transistors of the same polarity are assumed to be the same, actually, the threshold voltages of transistors may vary due to fluctuations in manufacturing conditions or the like. VI is not equal to VO if a difference occurs in the threshold voltages of the transistors. In Embodiment 2, this problem can be solved.
[0141] Figure 10 It is a circuit diagram showing the structure of the level shift circuit 40 of the driving circuit of Embodiment 2 of the present invention, and is the same as Figure 4 Figure 21 of the level shift circuit for comparison. refer to Figure 10 , level shift circuit 40 with Figure 4 The difference of the level shift circuit 21 is that the N-type transistors 23 and P Type transistor 24.
[0142] The respective fuses 41.1-41.m are formed of aluminum wiring or the like for connecting transistors to each other. One side electrodes of the fuses 41.1-41.m are all connected to the node N22....
Embodiment 3
[0148] Figure 11 It is a circuit diagram showing the structure of the level shift circuit 45 of the driving circuit of Embodiment 3 of the present invention, and is the same as Figure 4 A diagram of the level shifting circuit 2 5 for comparison. refer to Figure 11 , level shift circuit 45 with Figure 4 The difference of the level shift circuit 25 is that the N-type transistor 26 and the P-type transistor 27 are replaced by fuses 46.1-46.m, N-type transistors 47.0-47.m and P-type transistors 48.0-48.m.
[0149] The respective fuses 46.1-46.m are formed of aluminum wiring or the like for connecting transistors to each other. The electrodes on one side of the fuses 46.1-46.m are all connected to the nodes of the fourth power supply potential V4.
[0150] Set the gate amplitude of N-type transistor 47.0-47.m and Figure 4 The gate amplitudes of the N-type transistors 26 are the same. The drain of the N-type transistor 47.0 is connected to the node of the fourth power suppl...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com