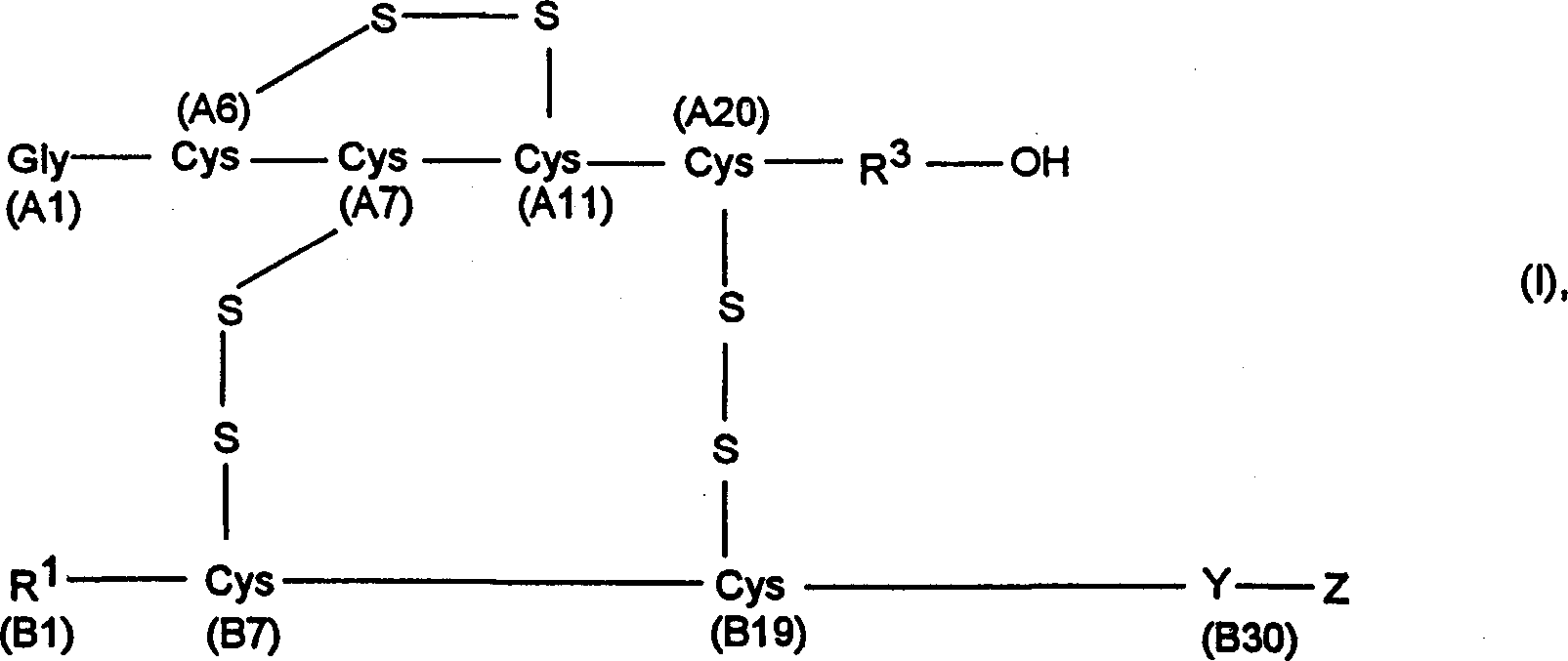
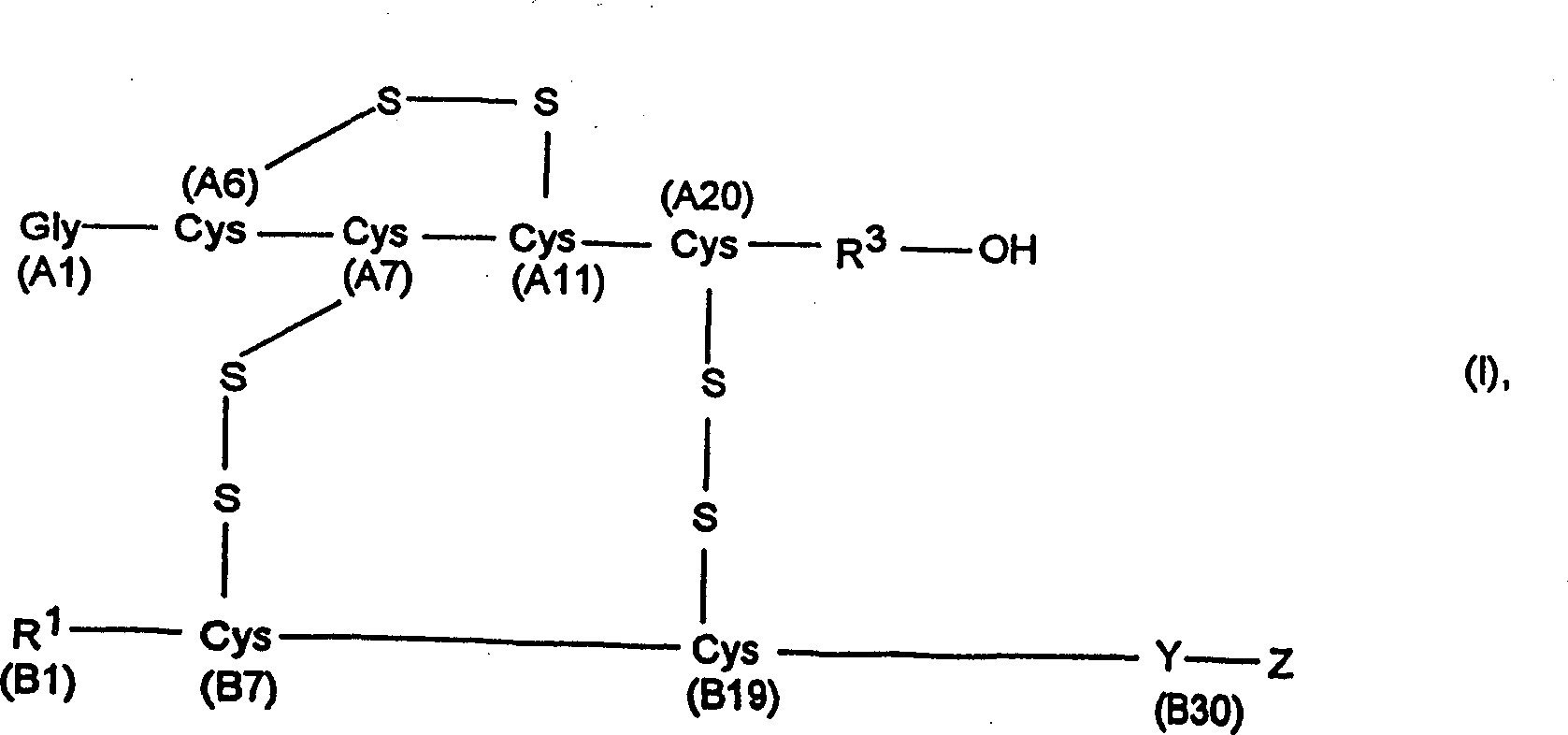
Process for obtaining insulin and insulin derivatives having correctly bonded crystine bridges
An insulin derivative, cystine bond technology, applied in microorganism-based methods, biochemical equipment and methods, insulin, etc., can solve problems such as loss
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0094] Embodiment 1 (comparative example, prior art)
[0095] Genetically modified E. coli cells were fermented (EP 0 489 780) to produce a fusion protein having the following amino acid sequence.
[0096] Proinsulin sequence 1 (SEQ ID NO.: 4):
[0097] Ala Thr Thr Ser Thr Gly Asn Ser Ala Arg Phe Val Asn Gln HisLeu
[0098] Cys Gly Ser His Leu Val Glu Ala Leu Tyr Leu Val Cys Gly GluArg
[0099]Gly Phe Phe Tyr Thr Pro Lys Thr Arg Arg Glu Ala Glu Asp LeuGln
[0100] Val Gly Gln Val Glu Leu Gly Gly Gly Pro Gly Ala Gly Ser LeuGln
[0101] Pro Leu Ala Leu Glu Gly Ser Leu Gln Lys Arg Gly Ile Val GluGln
[0102] Cys Cys Thr Ser Ile Cys Ser Leu Tyr Gln Leu Glu Asn Tyr CysAsn
[0103] Proinsulin sequence 1 corresponds to formula II, where
[0104] X is the C-peptide of human insulin (SEQ ID NO.: 3)
[0105] Y is threonine (B30),
[0106] R 1 is phenylalanine (B1),
[0107] R 2 is a peptide with 10 amino acid residues,
[0108] R 3 For asparagine (A21) and
[0109] A2-A20 ...
Embodiment 2
[0135] Embodiment 2 (method of the present invention)
[0136] A fusion protein having the amino acid sequence shown in Example 1 (proinsulin sequence 1. SEQ ID NO.: 4) was prepared by fermenting genetically modified Escherichia coli cells (EP 0 489 780).
[0137] The expressed fusion protein with proinsulin sequence 1 aggregated in E. coli cells to form inclusion bodies. After the fermentation culture is over, the cells are separated by centrifugation, the cells are broken by conventional high-pressure homogenization, and finally the inclusion bodies of the released fusion protein are separated by centrifugation.
[0138] 5 kg of cysteine hydrochloride hydrate was added to the fusion protein aqueous suspension containing 40 kg of fusion protein (as determined by lyophilized samples).
[0139] The suspension containing proinsulin sequence 1 (the concentration of the fusion protein containing insulin determined by HPLC is 50%) was dissolved in 550 L of urea solution with a p...
Embodiment 3
[0144] Embodiment 3 (comparative embodiment, prior art)
[0145] A fusion protein with the following amino acid sequence was prepared by fermentation of genetically modified E. coli cells (EP 0 489 780)
[0146] Proinsulin sequence 2 (SEQ ID NO.: 5):
[0147] Ala Thr Thr Ser Thr Gly Asn Ser Ala Arg Phe Val Asn Gln HisLeu
[0148] Cys Gly Ser His Leu Val Glu Ala Leu Tyr Leu Val Cys Gly GluArg
[0149] Gly Phe Phe Tyr Thr Pro Lys Thr Arg Arg Glu Ala Glu Asp LeuGln
[0150] Val Gly Gln Val Glu Leu Gly Gly Gly Pro Gly Ala Gly Ser LeuGln
[0151] Pro Leu Ala Leu Glu Gly Ser Leu Gln Lys Arg Gly Ile Val GluGln
[0152] Cys Cys Thr Ser Ile Cys Ser Leu Tyr Gln Leu Glu Asn Tyr CysGly
[0153] Proinsulin sequence 2 corresponds to formula II, where
[0154] X is the C-peptide of human insulin (SEQ ID NO.: 3)
[0155] Y is threonine (B30),
[0156] R 1 is phenylalanine (B1),
[0157] R 2 is a peptide with 10 amino acid residues,
[0158] R 3 for glycine (A21) and
[0159] A2-...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com