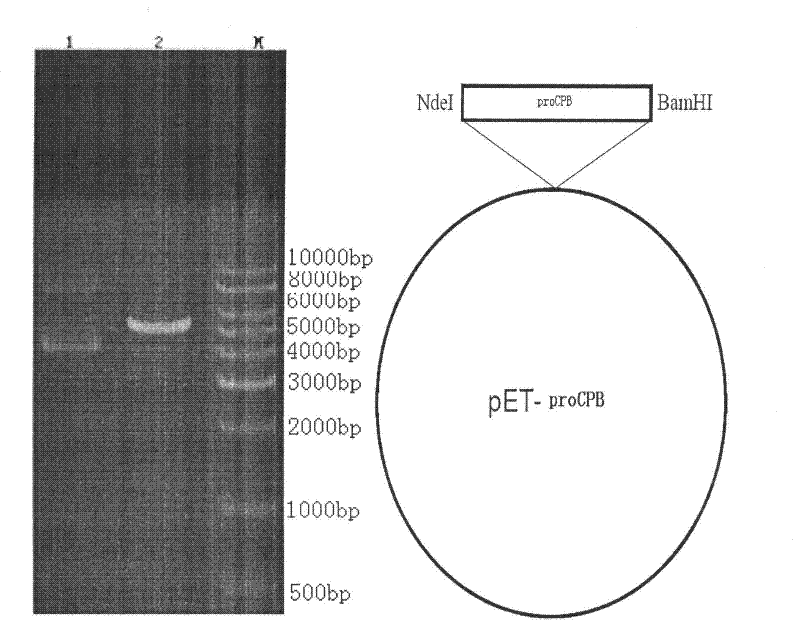
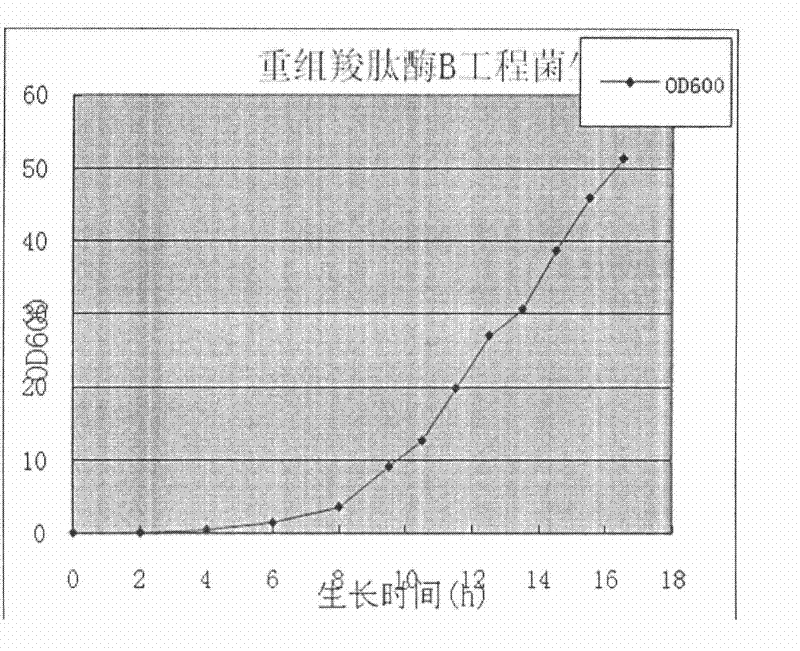
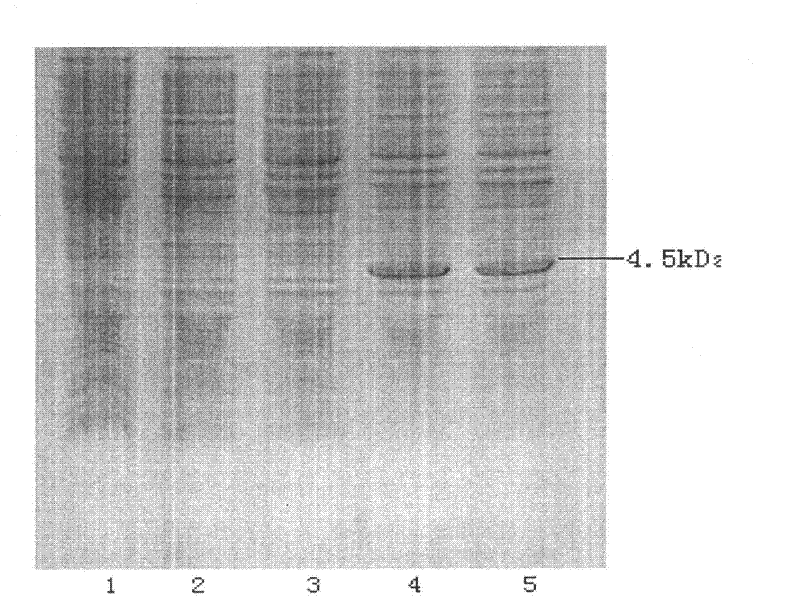
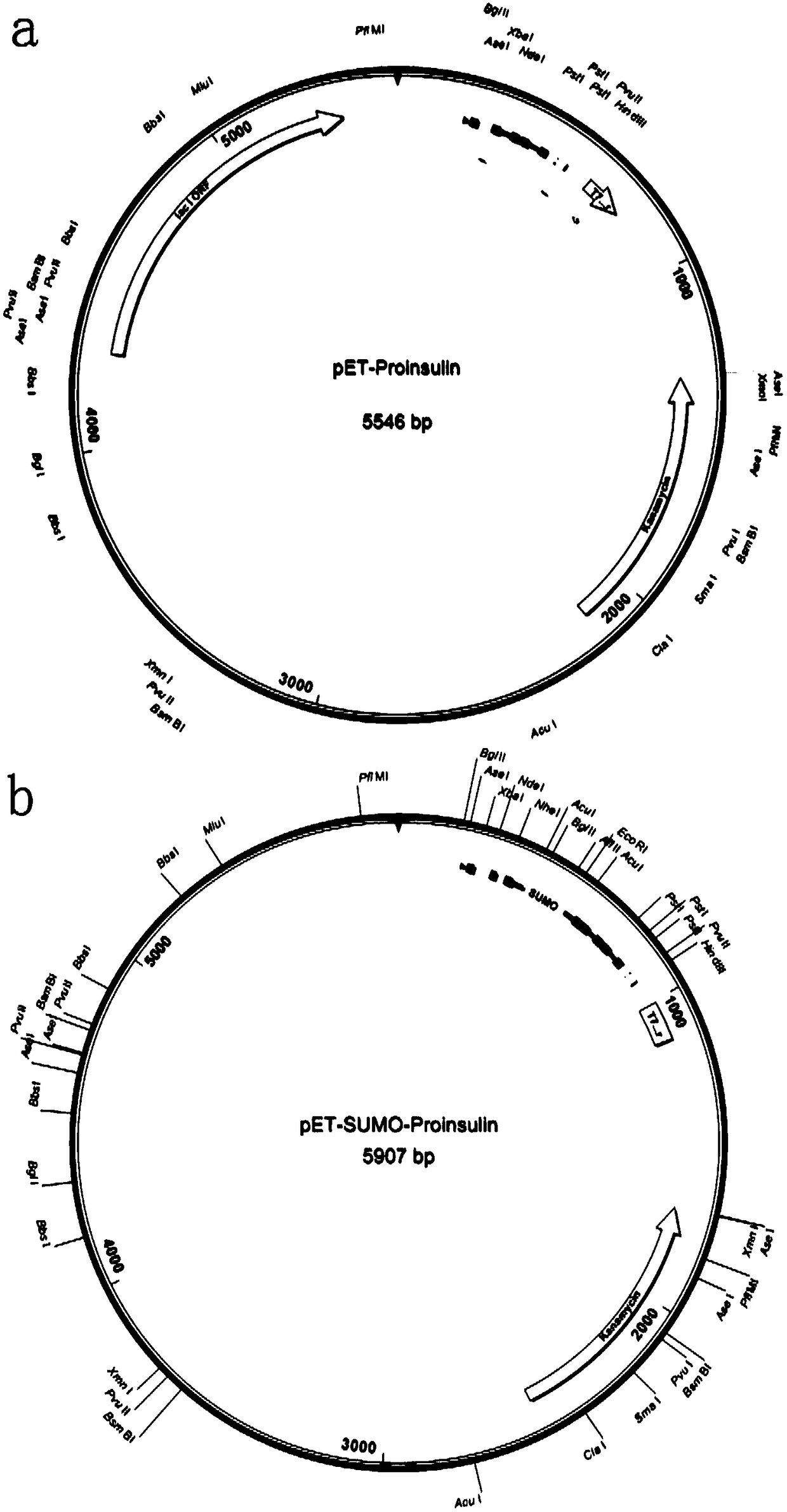
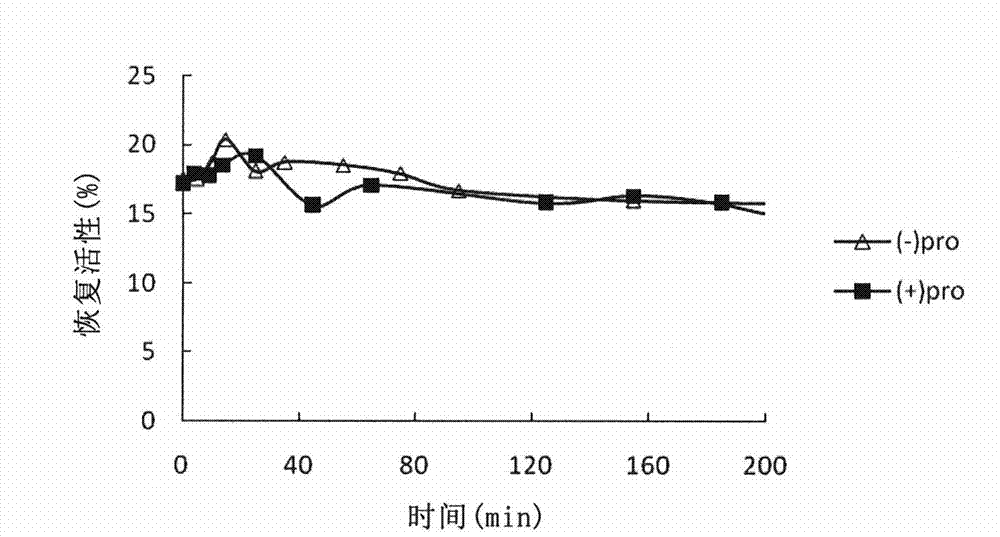
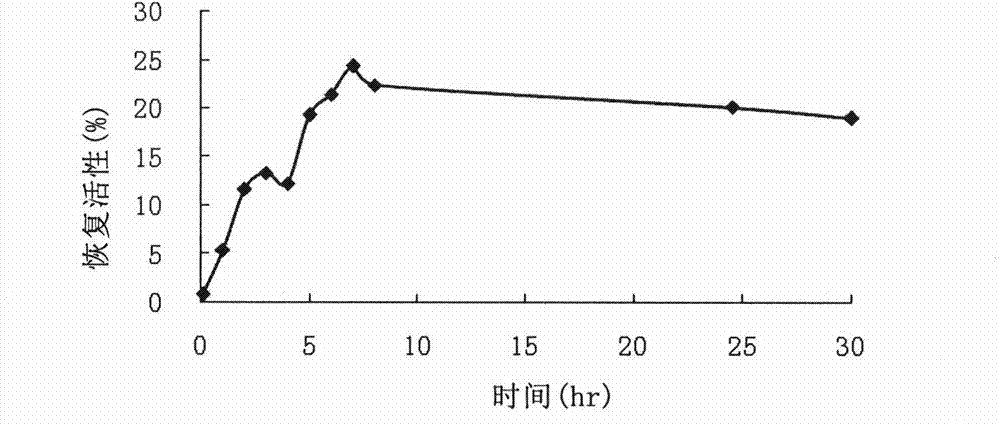
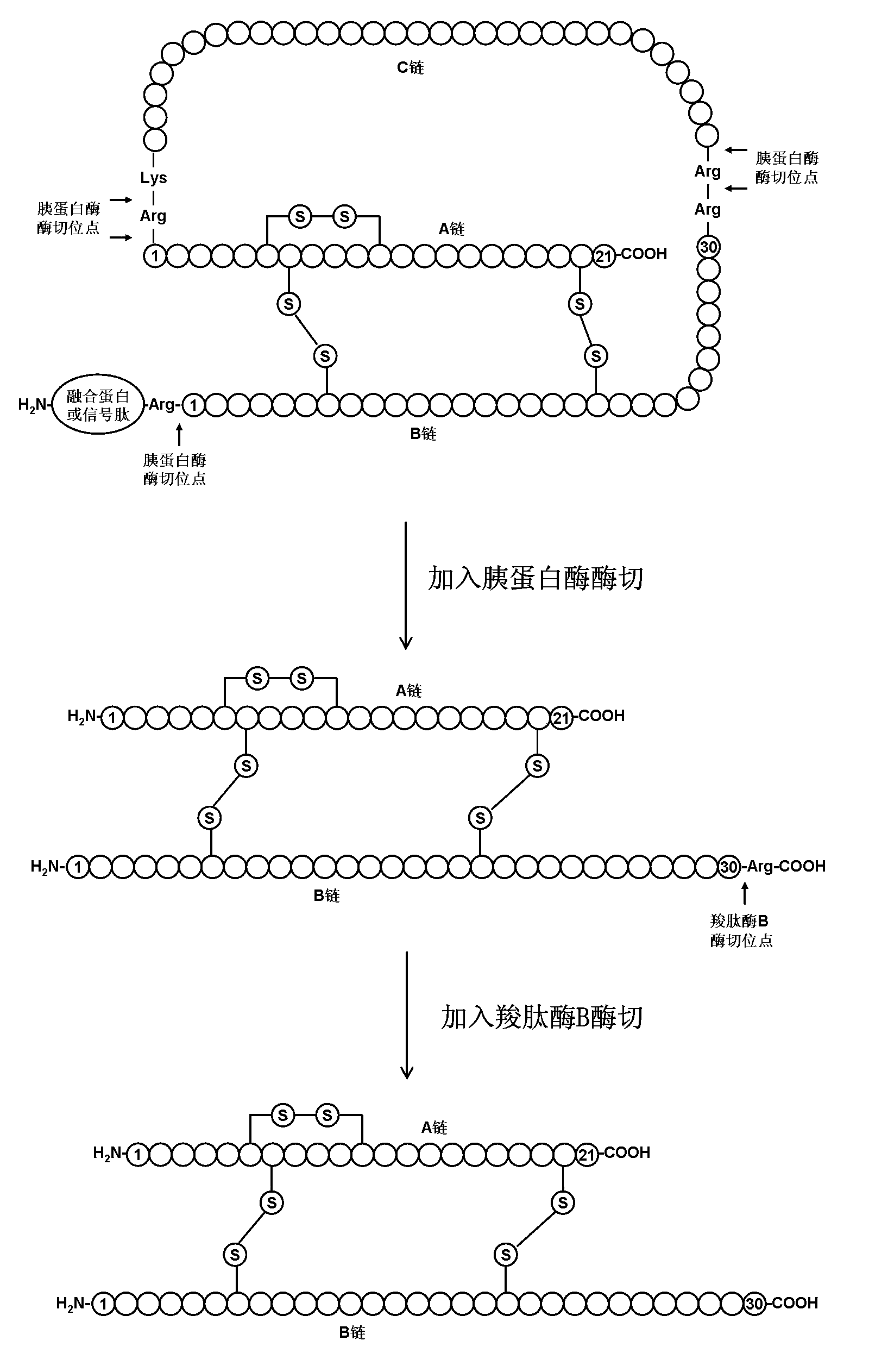
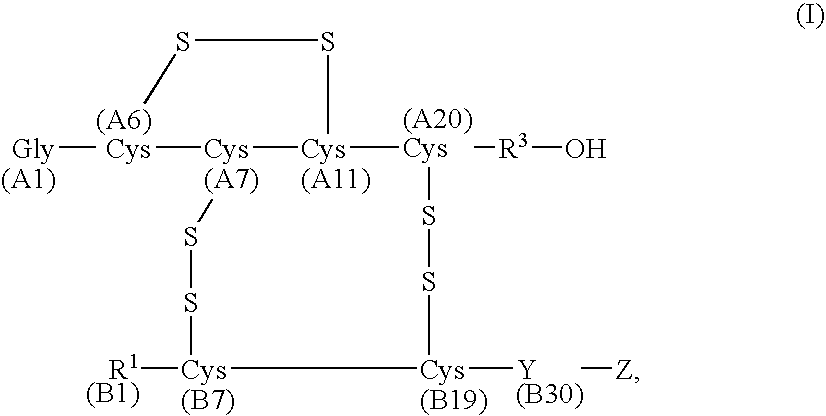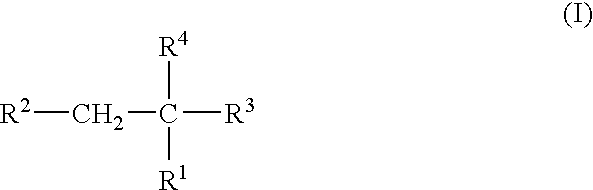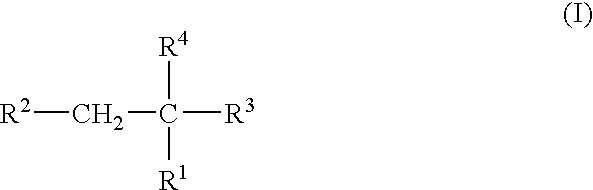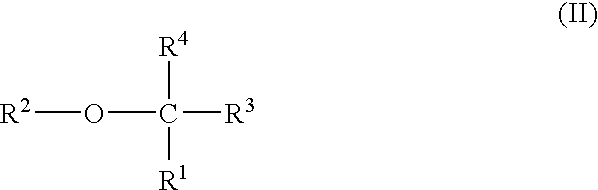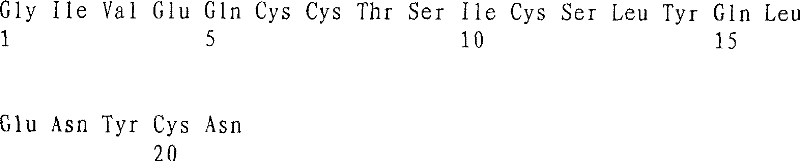Patents
Literature
33 results about "Carboxypeptidase B" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Carboxypeptidase B (EC 3.4.17.2, protaminase, pancreatic carboxypeptidase B, tissue carboxypeptidase B, peptidyl-L-lysine [L-arginine]hydrolase) is a carboxypeptidase that preferentially acts upon basic amino acids, such as arginine and lysine. This serum enzyme is also responsible for rapidly metabolizing the C5a protein into C5a des-Arg, with one less amino acid.
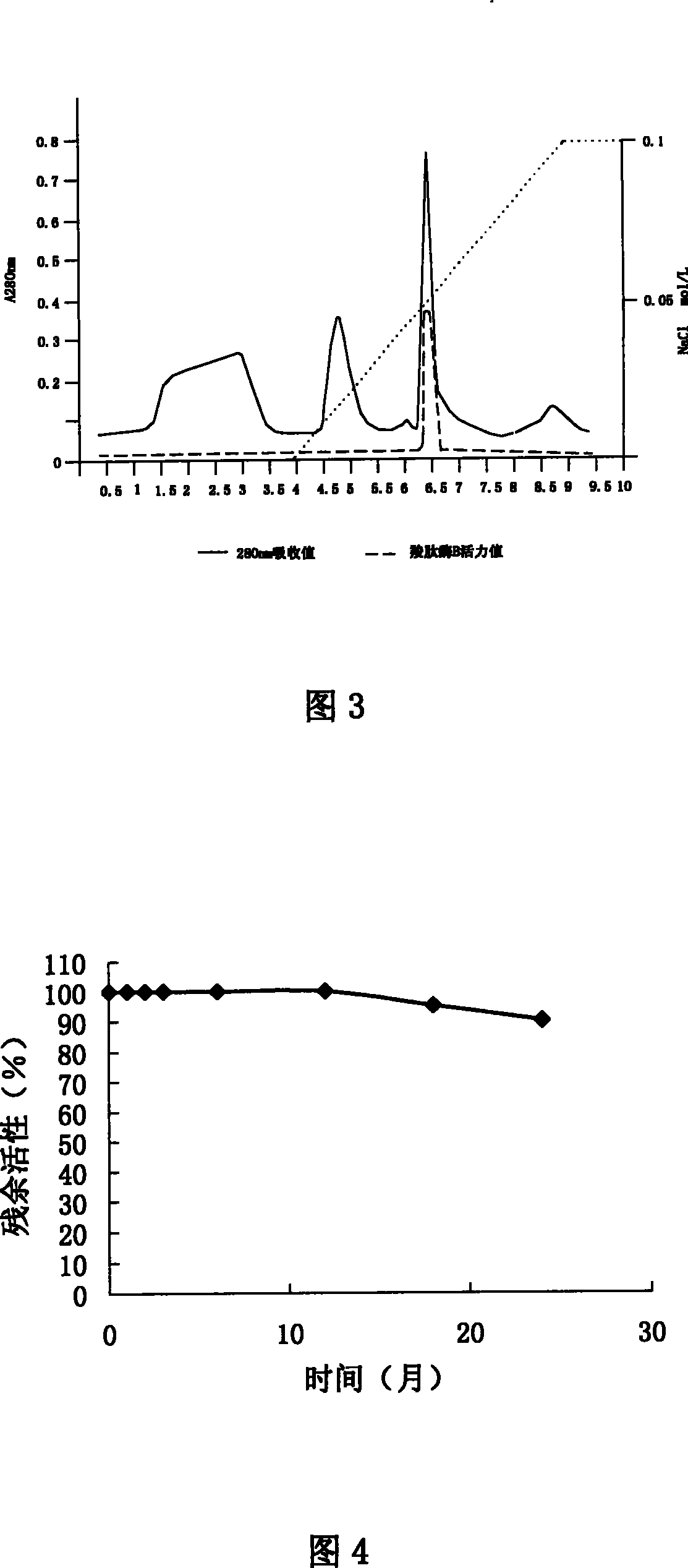
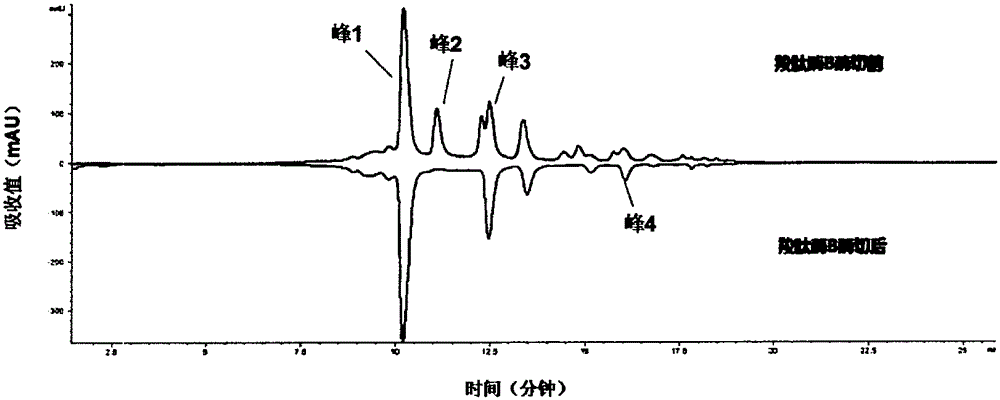
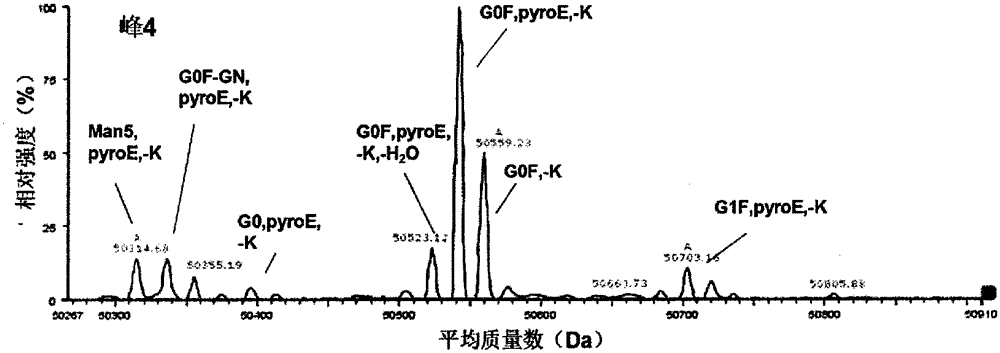
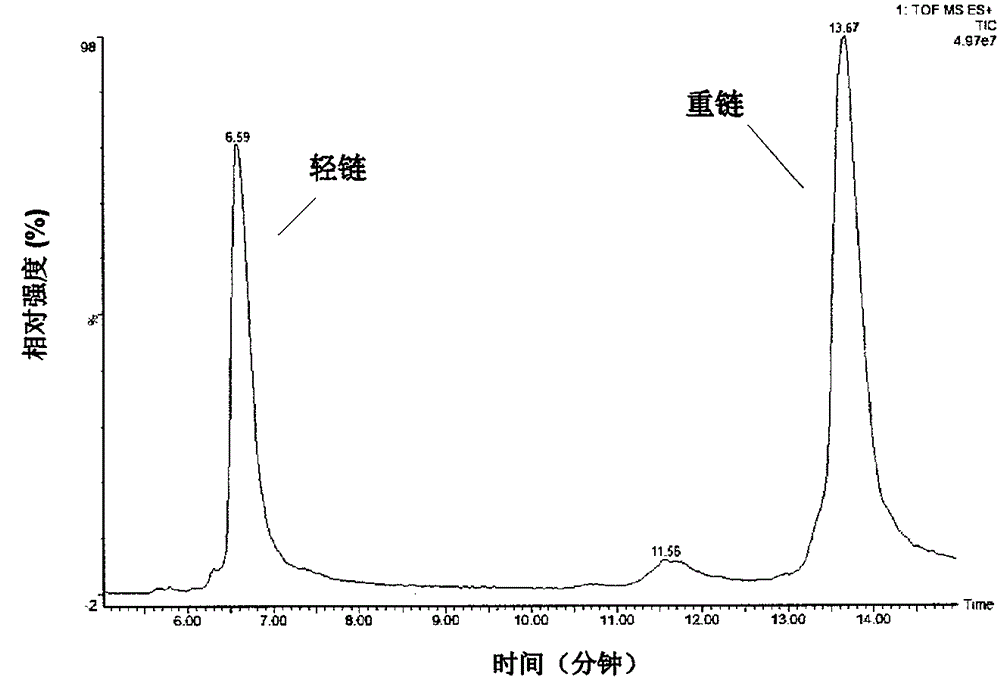
Method for determining immunoglobulin charge isomer glycosylation and terminal modification states
ActiveCN103217499AImprove accuracyEasy to handleComponent separationChromatographic separationRetention time
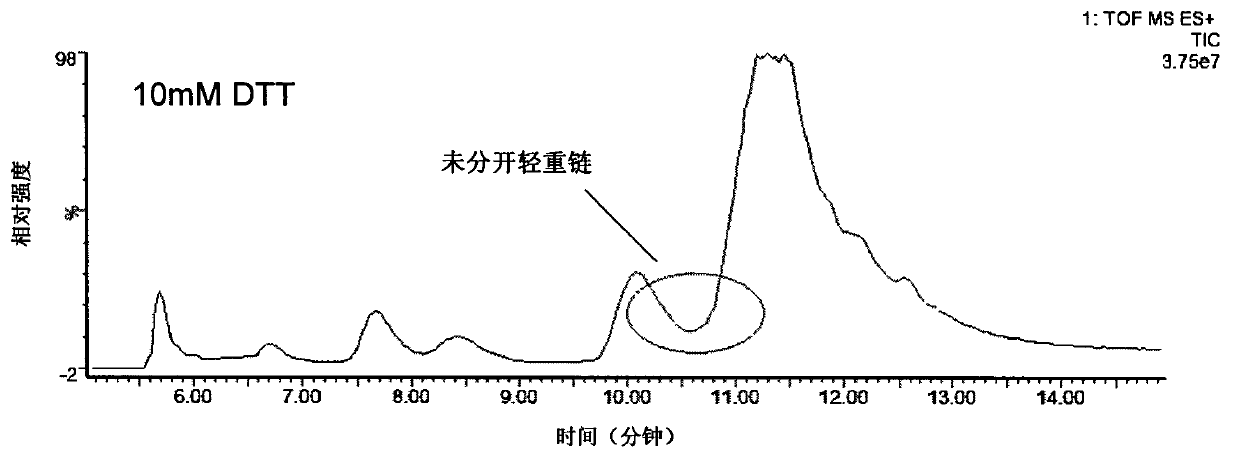
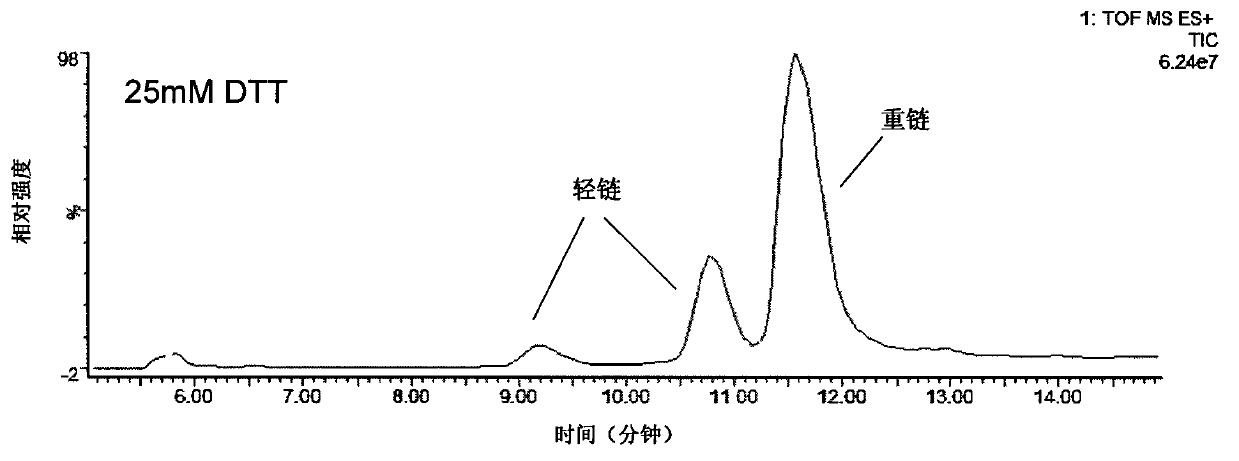
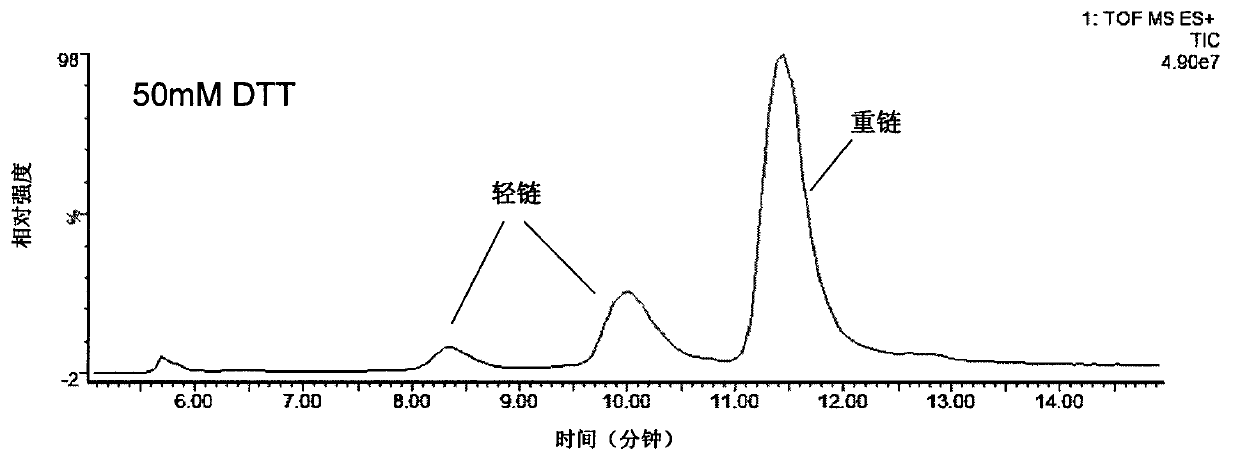
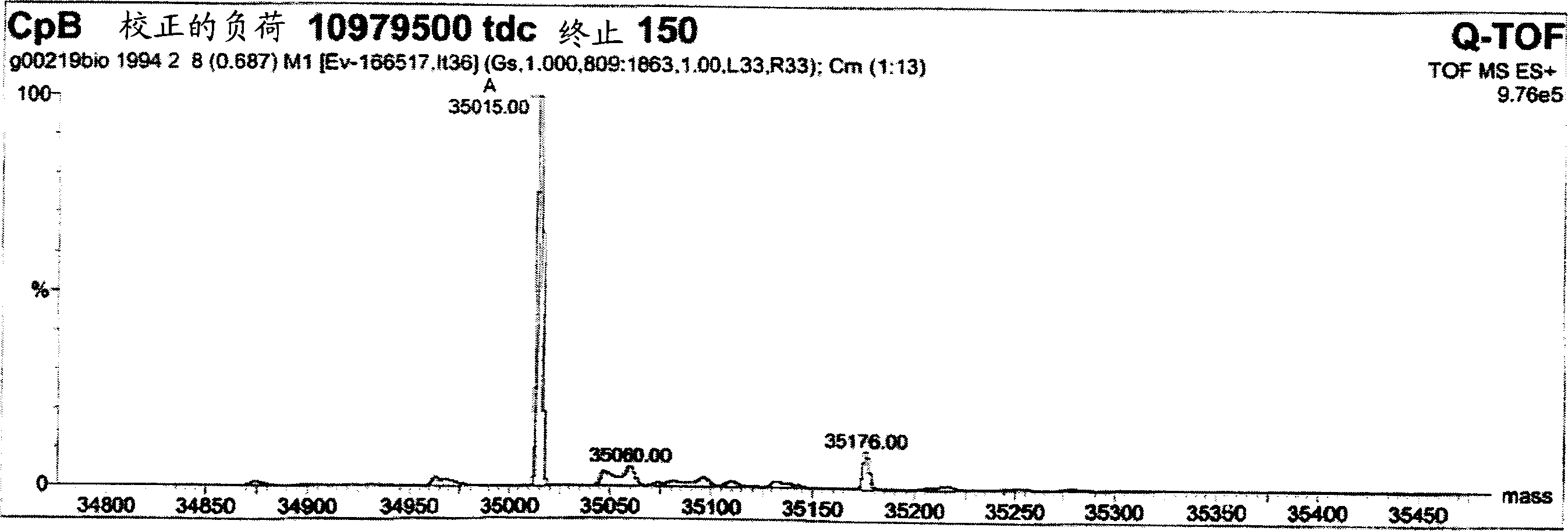
The invention provides a method for determining immunoglobulin charge isomer glycosylation and terminal modification states. With the method, immunoglobulin glycosylation, N-terminal pyroglutamic acidification, and C-terminal de-lysine can be simultaneously determined rapidly. The method comprises the steps that: (1) immunoglobulin before and after carboxypeptidase B digestion are analyzed by using cation exchange chromatography (CEX-HPLC), and different immunoglobulin charge isomers are collected according to retention times after the column; (2) the immunoglobulin component in the step (1) is denatured by using a denaturant, and is reduced by using a reducing agent, such that light chain and heavy chain are split; (3) the light chain and heavy chain in the step (2) are separated with reversed-phase ultrahigh-pressure liquid chromatography; (4) molecular weights of the light chain and heavy chain obtained in the step (3) are determined by using mass spectrometry; and (5) the chromatographic data in the step (3) and the mass spectral data in the step (4) are analyzed, such that the glycosylation and terminal modification states of the immunoglobulin are determined.
Owner:LIVZON MABPHARM
Connecting peptide and polypeptide amalgamation representation method for polypeptide amalgamation representation
The invention discloses connection titanium having the following amino acid sequence of X-Arg-Y-Asp-Asp-Asp-Asp-Lys. The invention also discloses fusion polypeptide with the connection titanium and objective polypeptide. The invention also provides a method for preparing the objective polypeptide. The connection titanium can be cut by enterokinase, Kex2 enzyme and carboxypeptidase B after being connected with the objective polypeptide in series, thereby forming the objective polypeptide without any connection titanium sequence.
Owner:SHANGHAI NEWSUMMIT BIOPHARMA +1
Recombinantly expressed carboxypeptidase b and purification thereof
ActiveCN1624122AImmobilised enzymesPolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifZymogenHost organism
The invention provides a method to produce a protein with carboxypeptidase B activity from a pro-carboxypeptidase B zymogen, derived from a non-animal host organism. Carboxypeptidase B is activated from the zymogen using non-denaturing conditions. Particularly, the activation is performed under conditions that avoid unwanted non-covalent binding of the propeptide to the activated carboxypeptidase B enzyme.
Owner:F HOFFMANN LA ROCHE & CO AG
Process for obtaining insulin and insulin derivatives having correctly bonded crystine bridges
Owner:SANOFI AVENTIS DEUT GMBH
ACE inhibition enzymatic hydrolysate and preparation method and application thereof
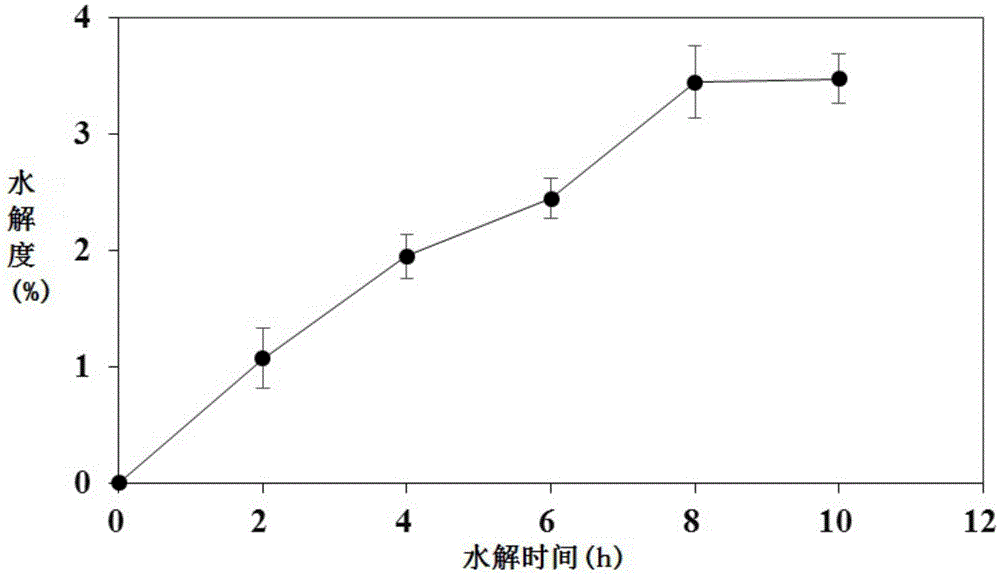
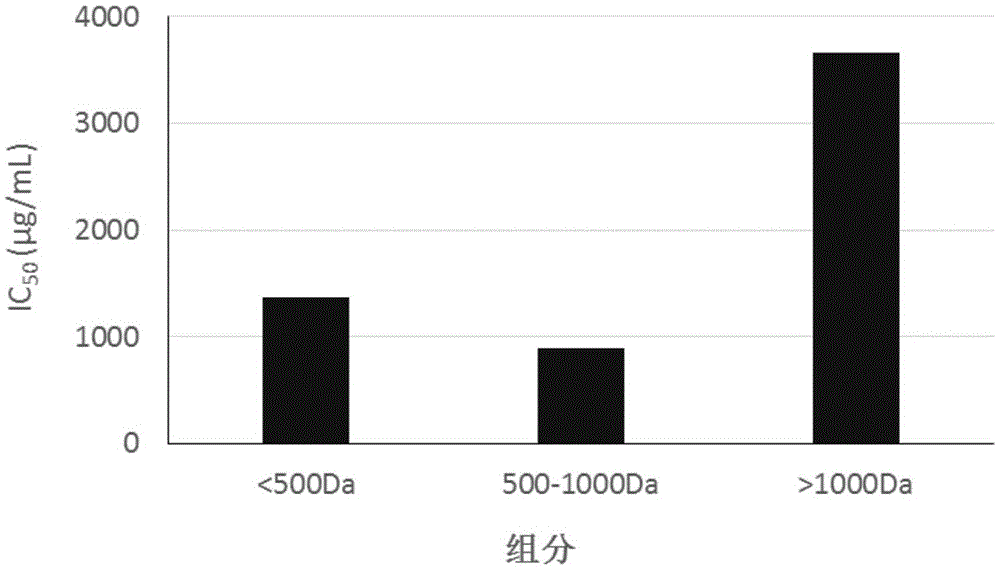
InactiveCN105483196AIncrease profitReduce wasteHydrolysed protein ingredientsFermentationHydrolysateDipotassium phosphate
The invention discloses a preparation method of an ACE inhibition enzymatic hydrolysate. The method comprises the following steps that 1, scallop skirts are washed to be clean, dried, smashed and screened, and scallop skirt powder is obtained; 2, the scallop skirt powder and alpha-chymotrypsin are added to a phosphate buffer solution, even mixing is conducted, a reaction is terminated at high temperature after hydrolysis is conducted, centrifugation is conducted, supernatant is taken, and an alpha-chymotrypsin hydrolysate is obtained; 3, the pH of the alpha-chymotrypsin hydrolysate is adjusted to 7.5 through a dipotassium phosphate solution, carboxypeptidase A and carboxypeptidase B are added, even mixing is conducted, a reaction is terminated at high temperature after hydrolysis is conducted, and a carboxypeptidase A / B hydrolysate is obtained; 4, dialysis is conducted on the carboxypeptidase A / B hydrolysate, a 500-1000 Da component is obtained, and the ACE inhibition enzymatic hydrolysate is obtained. The IC<50> value of the ACE inhibition enzymatic hydrolysate prepared through the preparation method to ACE is 893 micrograms / mL. The ACE inhibition enzymatic hydrolysate can be applied to preparation of depressurizing drugs and / or depressurizing foods.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Process for the preparation of insulin or an insulin derivative in the presence of oxygen
ActiveUS7659363B2Peptide/protein ingredientsPeptide preparation methodsMedicineCysteine Hydrochloride
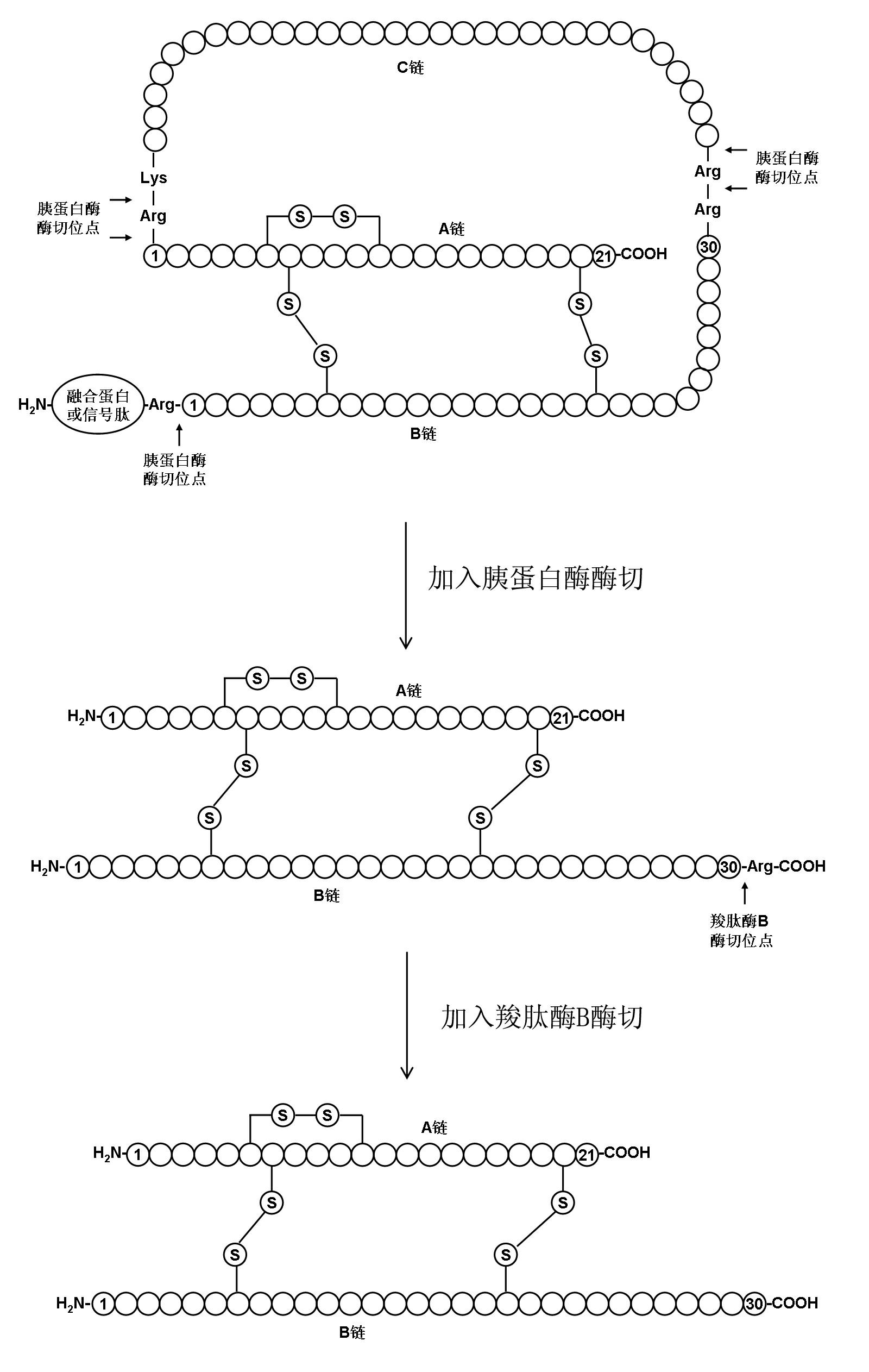
The present invention comprises a process for preparing insulin or an insulin derivative with correctly linked cysteine bridges from a precursor of said insulin or insulin derivative, wherein said precursor is subjected to a folding process in the presence of cysteine or cysteine hydrochloride and a chaotropic auxiliary compound. The insulin or insulin derivative with correctly linked cysteine bridges is obtained by enzymic cleavage by means of trypsin or a trypsin-like enzyme and, where appropriate, additionally by means of carboxypeptidase B and subsequent purification on an adsorber resin, which process is carried out at varied pH and temperature ranges.
Owner:SANOFI AVENTIS DEUT GMBH
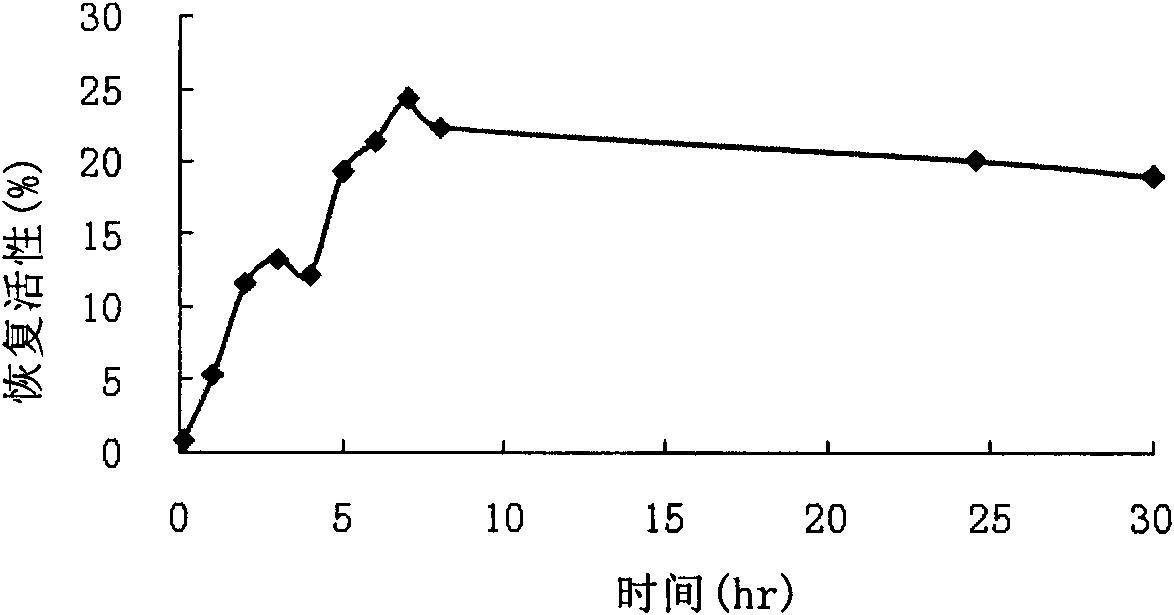
Production and application of high-stability recombination carboxypeptidase B
ActiveCN101967467AImprove stabilityHydrolasesMicroorganism based processesInclusion bodiesCarboxypeptidase B
The invention relates to production and application of high-stability recombination carboxypeptidase B. The invention also discloses a method for producing recombination carboxypeptidase B, which comprises the following steps: (1) carrying out recombinant expression on carboxypeptidase B with a mutated leading sequence at the N terminus to obtain a recombination protein in an inclusion body form; (2) denaturing and renaturing the recombination protein in an inclusion body form to obtain a soluble recombination protein; and (3) removing leading sequences of the carboxypeptidase B with a leading sequence at the N terminus of the soluble recombination protein to obtain the recombination carboxypeptidase B. The invention uses an intramolecular chaperone to enhance the in vitro refolding of the carboxypeptidase B, and the obtained recombination carboxypeptidase B has high stability and can well resist the enzymolysis of trypsase.
Owner:上海雅心生物技术有限公司
Recombinantly expressed carboxypeptidase B and purification thereof
InactiveUS20050142633A1Affect expressionPolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifHydrolasesZymogenBiological activation
The invention provides a method to produce a protein with carboxypeptidase B activity from a pro-carboxypeptidase B zymogen, derived from a non-animal host organism. Carboxypeptidase B is activated from the zymogen using non-denaturing conditions. Particularly, the activation is performed under conditions that avoid unwanted non-covalent binding of the propeptide to the activated carboxypeptidase B enzyme.
Owner:ROCHE DIAGNOSTICS OPERATIONS INC
Process for obtaining insulin or insulin derivatives having correctly bonded cystine bridges
The invention provides a method for obtaining insulin or insulin derivatives correctly boned with cystine bond from the prosoma of the insulin or insulin derivatives. The prosoma undergoes a folding process from the presence of cysteine or cysteine hydrochloride and off-fluid additive, after the folding, the insulin or insulin derivatives are obtained from the prosoma by a method that: enzyme cleavage are carried on by selecting trypsinase or tryptase and optional selecting carboxypeptidase B, then purifications are carried out on polymeric adsorbent.
Owner:SANOFI AVENTIS DEUT GMBH
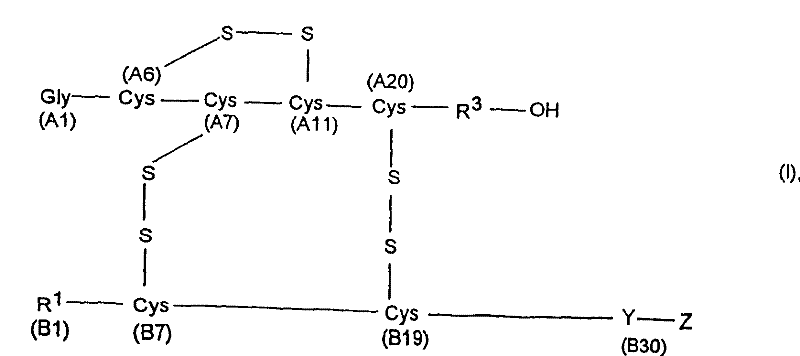
Plasma carboxypeptidase b inhibitors
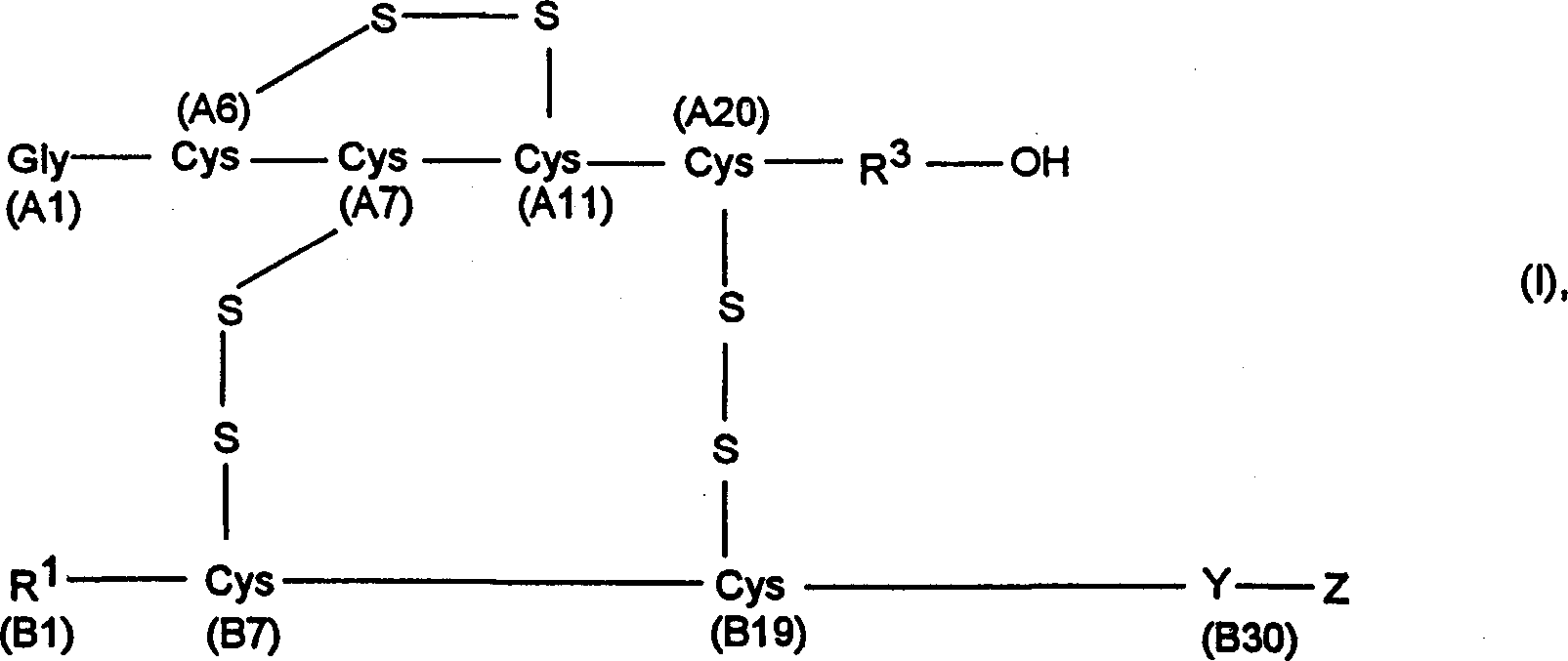
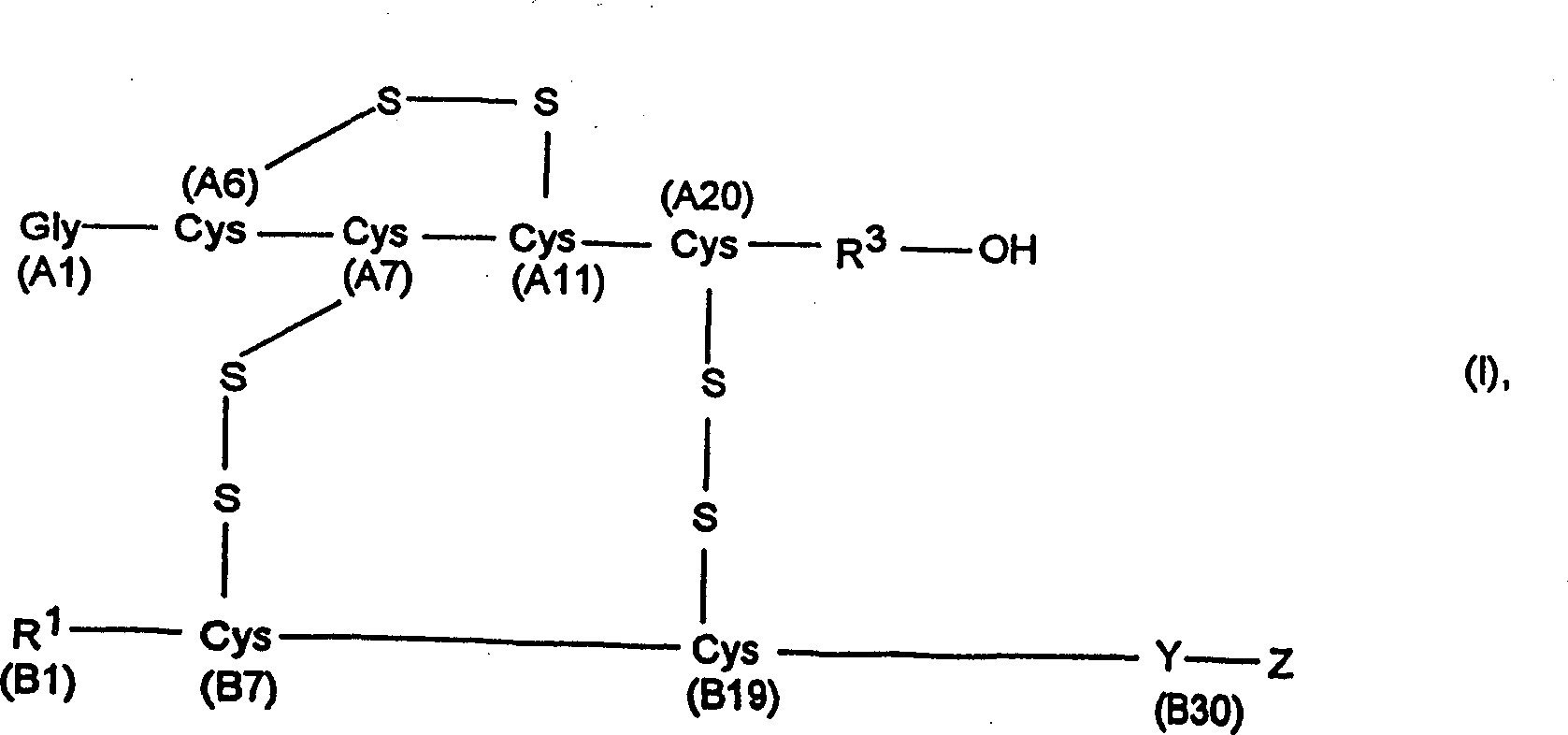
Compounds of the following formula (I), for example: (1), wherein R1, R2, R3, and R4 are described herein, are useful as inhibitors of plasma carboxypeptidase B. Pharmaceutical compositions containing these compounds, methods of using these compounds as antithrombotic agents and processes for synthesizing these compounds are also described herein.
Owner:SCHERING AG
Preparation method of insulin
InactiveCN102628072AFull effectImprove digestion efficiencyPeptide preparation methodsInsulinsEnzymatic digestionInsulin products
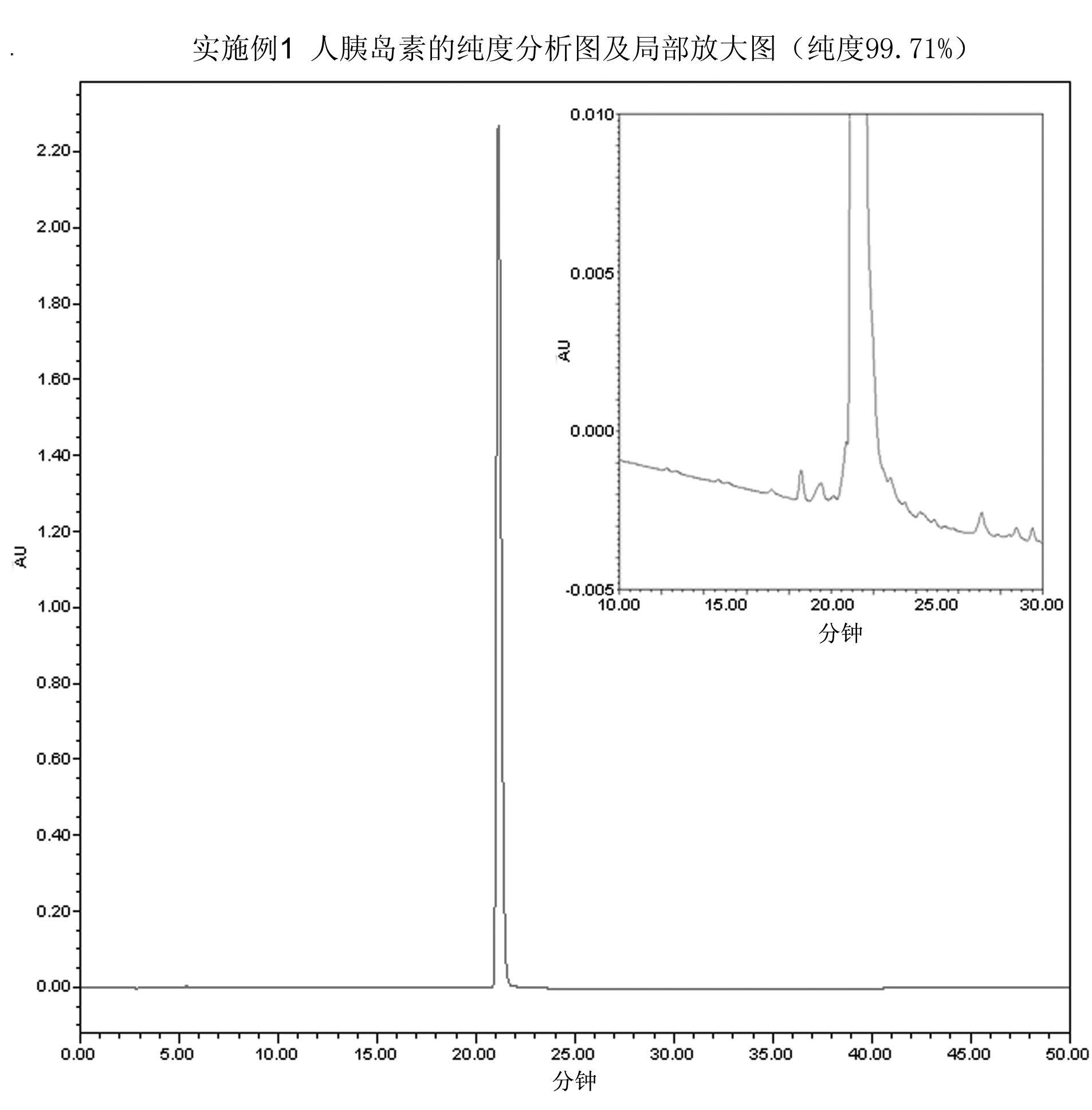
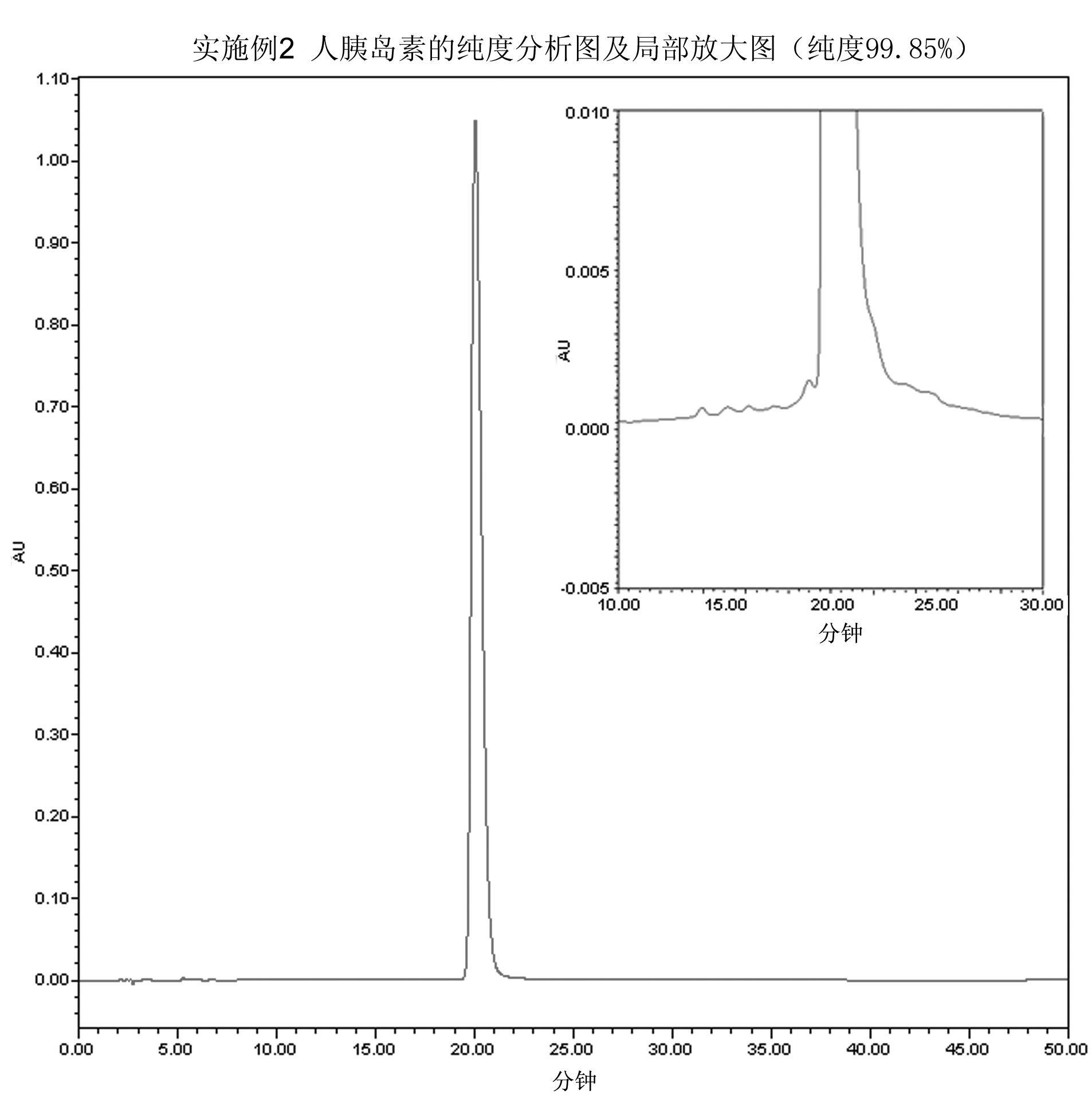
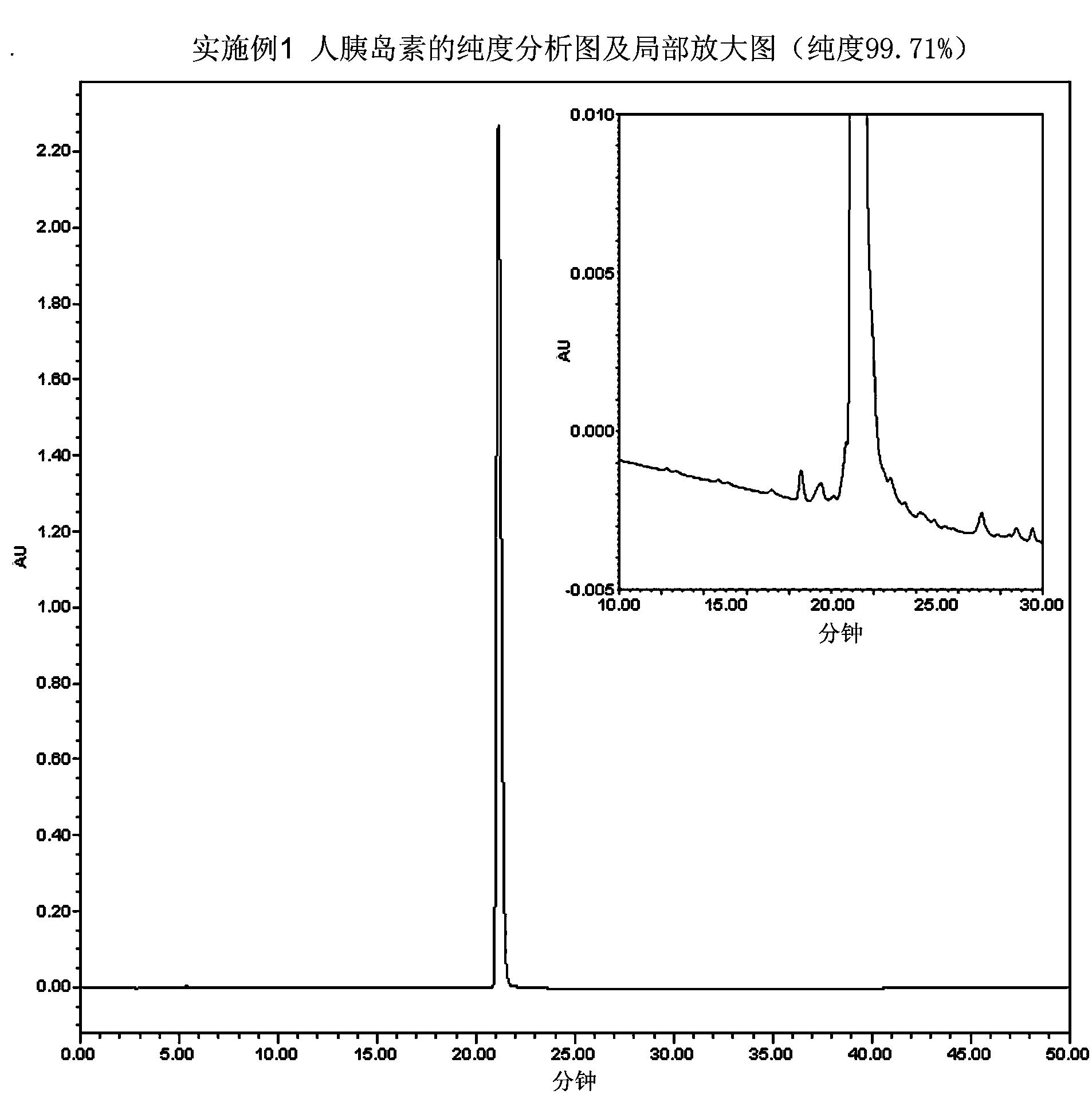
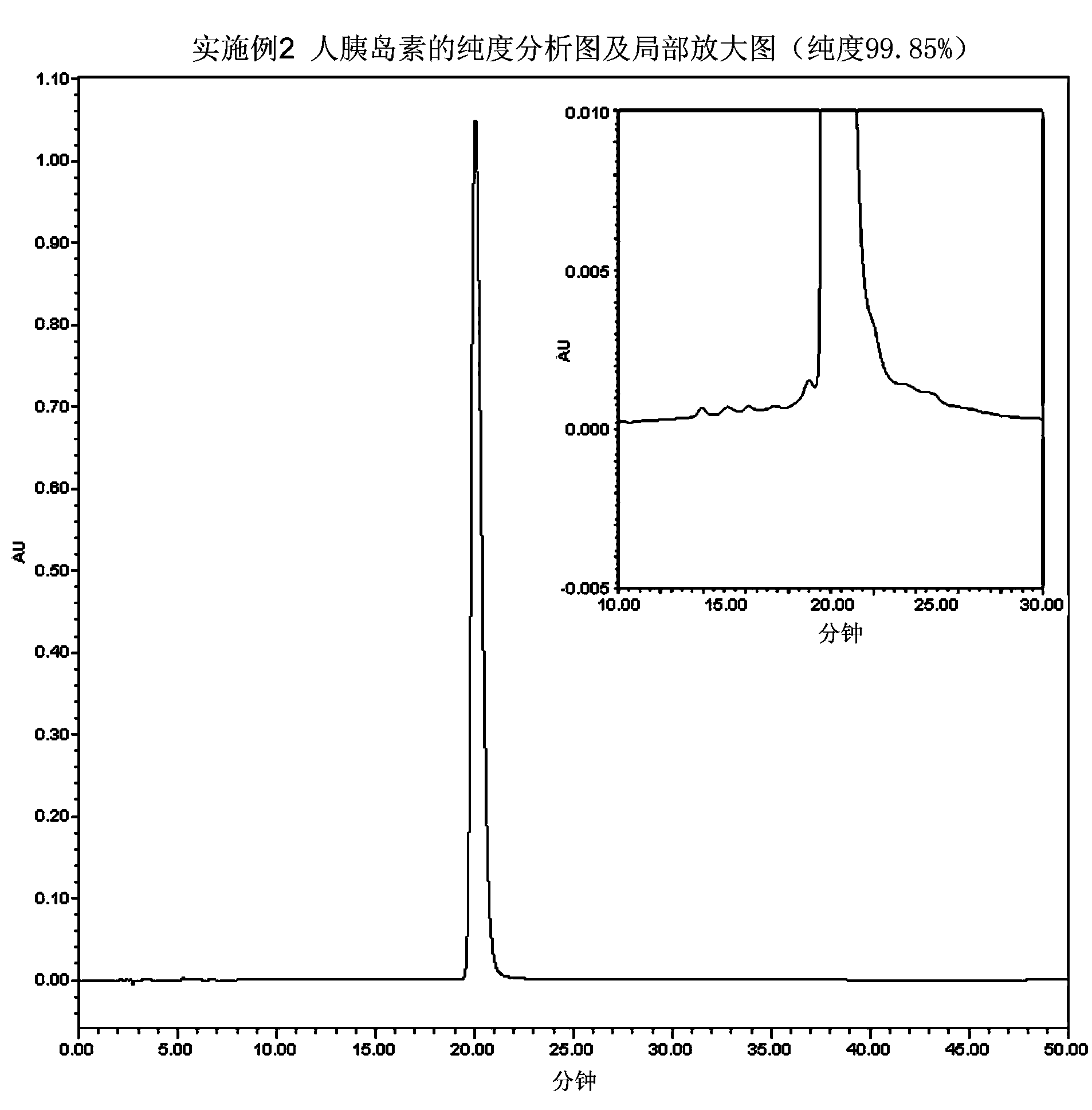
The invention relates to a preparation method of insulin. The method which comprises two steps of chromatography purification can improve the enzymatic digestion efficiency, and the controllability in an enzymatic digestion process, so a complete reaction of trypsin and carboxypeptidase B is realized, and insulin precursors not reacted with the carboxypeptidase B can be thoroughly removed, so the purity and the quality of final insulin products are improved, the purity of the final insulin products can reach above 99.7%, and the recovery rate is high, thereby industrialized production can be carried out.
Owner:GAN&LEE PHARMA
Preparation method of active carboxypeptidase B
InactiveCN1990861AOvercome the defects of cumbersome stepsBacteriaHydrolasesCarboxypeptidase BBiology
The invention relates to a method for preparing active carboxypeptidase B. It comprises following steps: expressing the recombination bacteria carrying with CPB in the form ofinclusion bodies; and separating and getting active CPB. It is characterized in that the plasmid of said recombiantino bacteria is pT7- 473- CPB, and the host is E coli Bl21 (DE3). The invention realizes the active CPB preparation by direct expression of CPB, and overcomes complicate steps in current methods.
Owner:TIBET JINKE GRP +1
Preparation method of recombinant carboxypeptidase B
The invention relates to a preparation method of recombinant carboxypeptidase B. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: firstly introducing plasmids with recombinant carboxypeptidase B protogene sequence into Escherichia coli cells to construct a recombinant engineering strain, fermenting for inducing and expressing recombinant carboxypeptidase B protogene, and carrying out renaturation, pancreatin conversion as well as separation and purification to obtain carboxypeptidase B with activity. The preparation method provided by the invention has the characteristic that the expressed carboxypeptidase B gene has completely identical sequence with human carboxypeptidase B.
Owner:JIANGSU WANBANG BIOPHARMLS
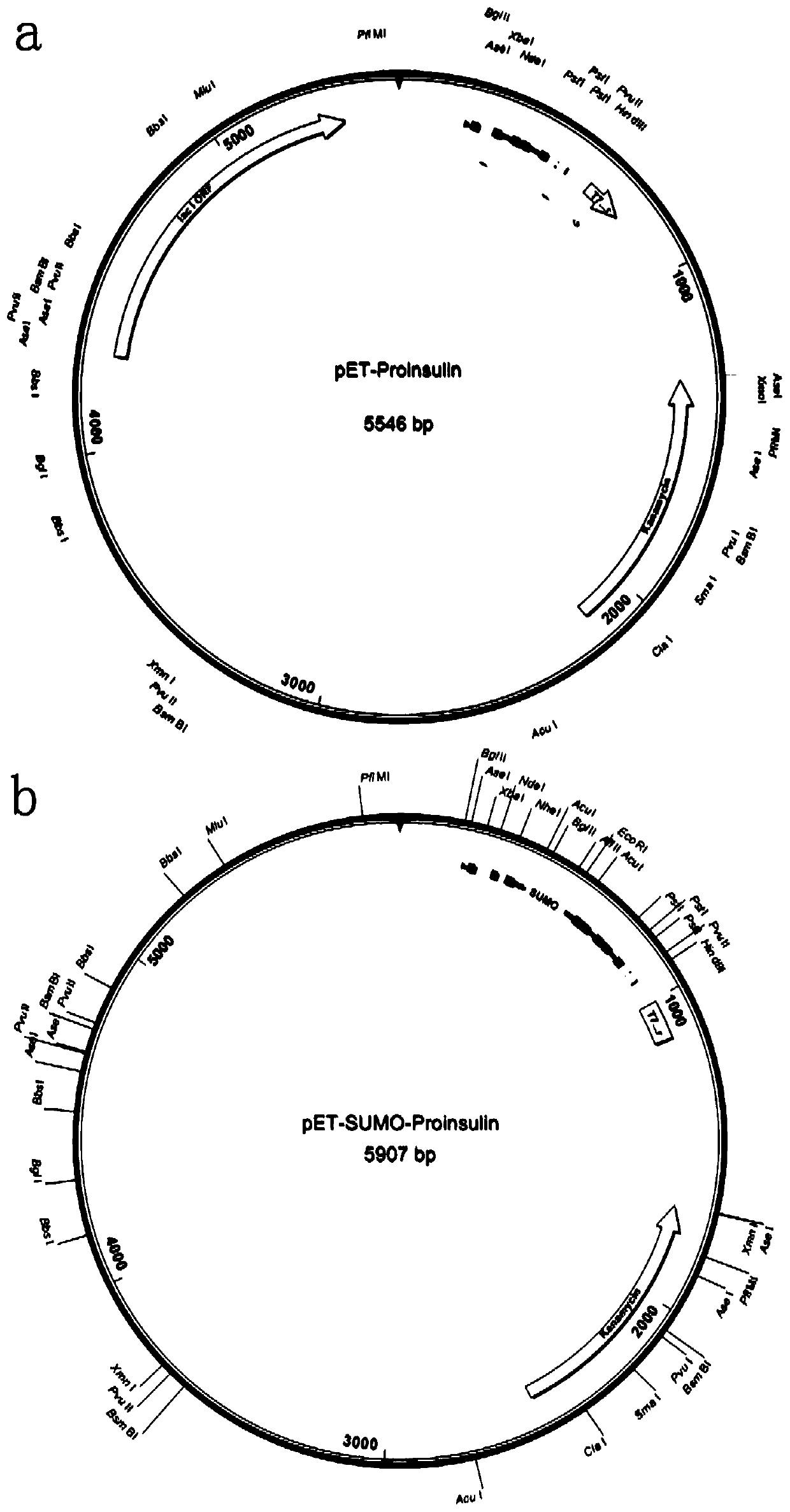
Preparation method of recombinant human insulin
ActiveCN108998458APromote efficient expressionPromote denaturation and refolding efficiencyAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsInsulinsInclusion bodiesNucleotide
The invention relates to a preparation method of recombinant human insulin. The preparation method comprises: inserting a nucleotide sequence shown in the formula of SEQ ID No. 2 into a position between EcoRI and HindIII enzyme sites of a pET-SUMO vector to obtain a recombinant plasmid, transferring the recombinant plasmid into a host strain, culturing the host strain in a medium at 18 to 37 DEG Cuntil OD600 of 0.5-0.7, carrying out induced expression, separating a Sumo-proinsulin fusion protein inclusion body, washing the Sumo-proinsulin fusion protein inclusion body through a buffer solution containing urea, carrying out centrifugation, taking precipitates, carrying out denaturation and gradient renaturation to obtain a renatured Sumo-proinsulin fusion protein, and carrying out one-stepdigestion renaturation on the Sumo-proinsulin fusion protein through Sumo protease, trypsin and carboxypeptidase B at pH of 6.0-8.0 at a digestion temperature of 16-37 DEG C for digestion time of 3-6h to obtain the recombinant human insulin.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
Preparation method of protaminase B and its composition
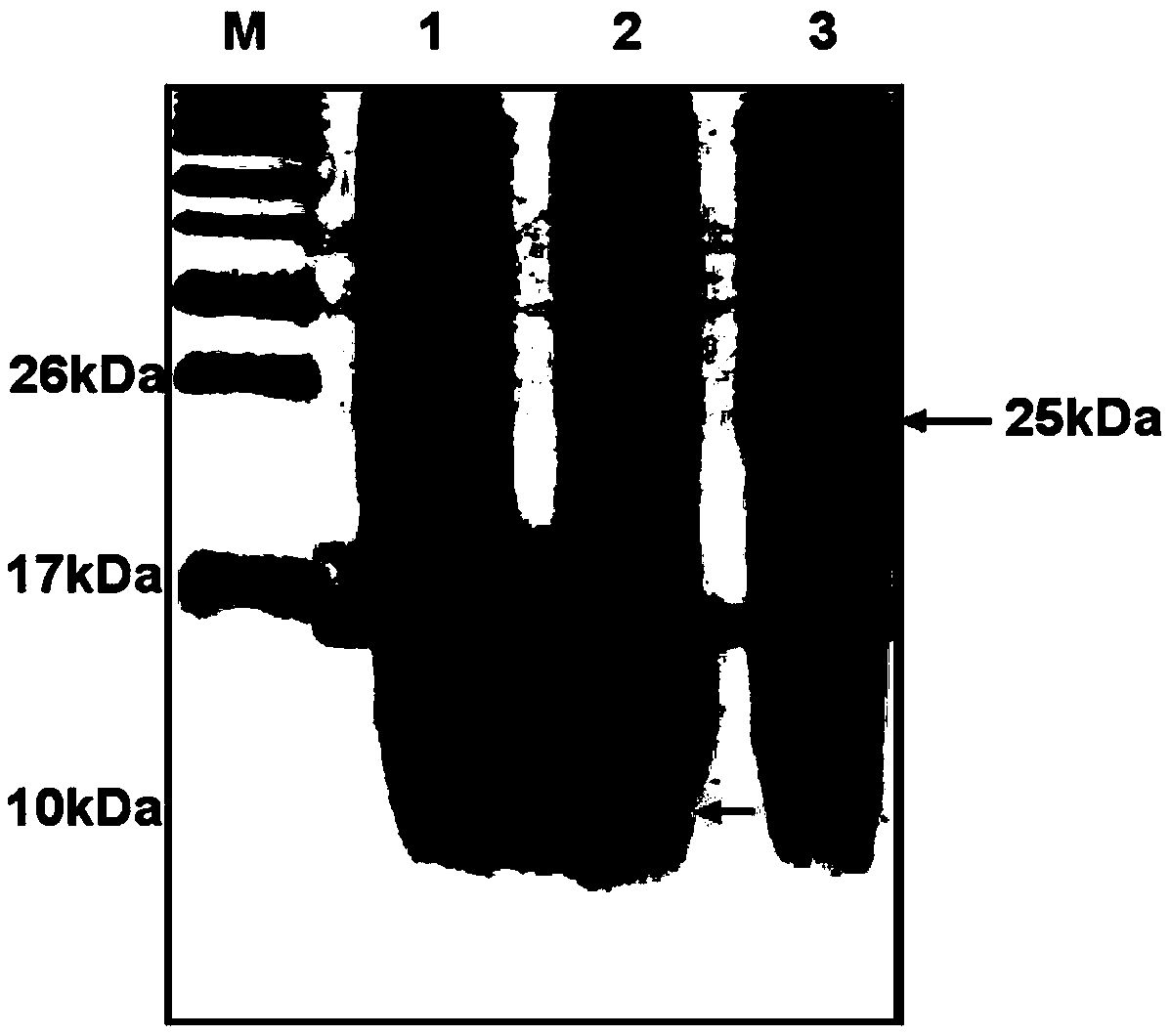
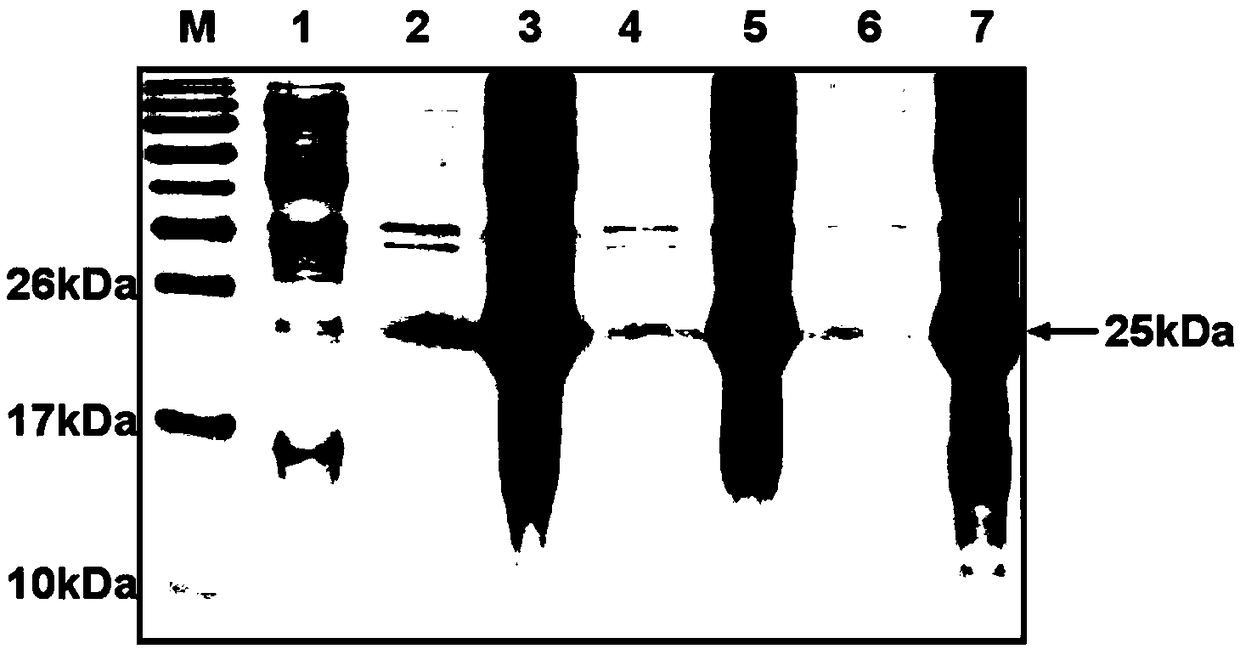
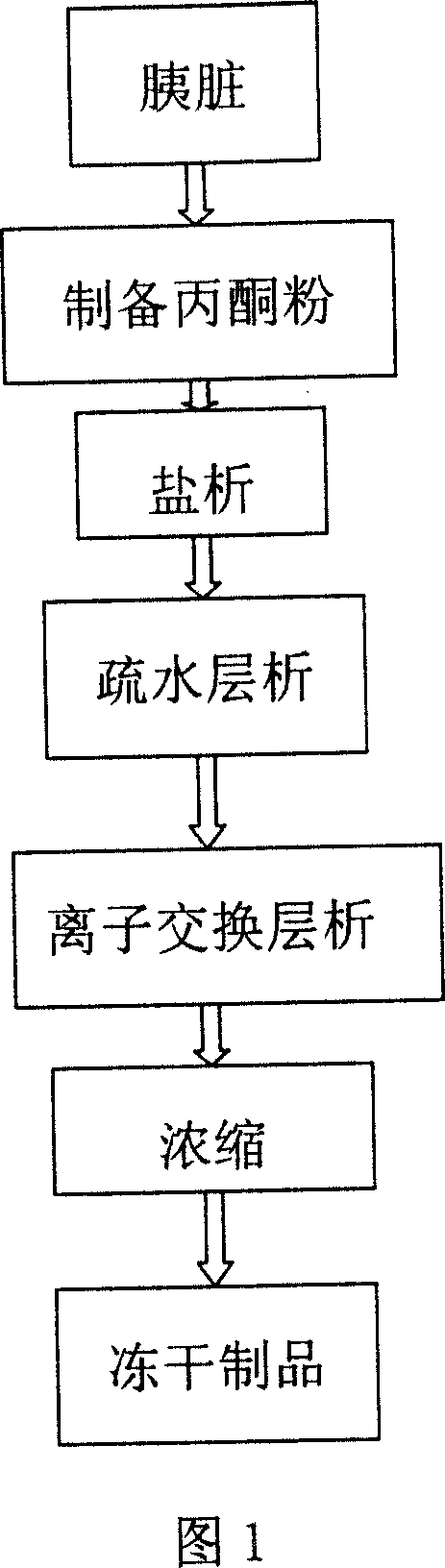
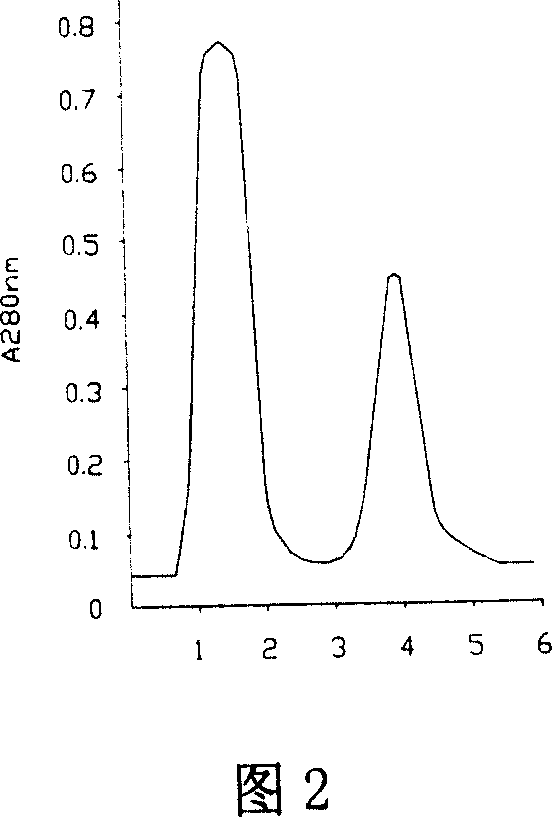
This invention discloses a preparation of carboxyl peptidase B and its combination relating to enzymology, combination containing enzyme and technology field of disconnecting and depurating method. The technology problem which needs to be solved by this invention is that providing a preparation of carboxyl peptidase B and its combination to solve the yield of carboxyl peptidase B preparation is low and carboxyl peptidase B is astable in present technology. Disclosing a preparation of carboxyl peptidase B, including the steps: salting out, hydrophobic chromatography, anion-exchange chromatography, its characteristic is that using 1-5 times of acetone to process 2-3 times, producing acetone powder; it also discloses a carboxyl peptidase B combination which contains 3-5%(w / v, g / 100ml) manicol. The yield of the invented carboxyl peptidase B achieves more than 60U / g pancreas, raising more than 20%, specific activity of carboxyl peptidase B exceeds 200U / mg, stability of carboxyl peptidase B is 2 years.
Owner:JIANGSU WANBANG BIOPHARMLS +1
Purification process for expressing tandem protein by pichia pastoris
The invention relates to a purification process for expressing tandem protein by pichia pastoris, and particularly provides a purification method for recombinant human proinsulin C peptide tandem protein. The purification method comprises the following steps of: (1) centrifuging fermentation liquor to obtain fermentation centrifugal supernatant; (2) adding electrolyte for salting out to obtain precipitated protein; (3) adding a cosolvent to obtain a precipitated protein complex solution; (4) purifying the precipitated protein complex solution through first column chromatography; (5) adding trypsin and carboxypeptidase B for double enzyme digestion to obtain enzyme digestion liquor; (6) sequentially performing reverse-phase ultrafiltration and normal-phase ultrafiltration on the enzyme digestion liquor to obtain ultrafiltrate; (7) purifying the ultrafiltrate through second column chromatography; and (8) performing normal-phase ultrafiltration to obtain recombinant human proinsulin C peptide stock solution. The method can be used for preparing recombinant human proinsulin C peptide with high purity and high yield.
Owner:SHANGHAI XINSHENGYUAN BIOLOGICAL MEDICAL +1
Method of producing mutation procarboxypeptidase B and mutation carboxypeptidase B
The invention discloses a saltatory carboxypeptidase B or corresponding procarboxypeptidase B as well as its coded recombinant generating method of polynucleotide, expressive carrier, host cell and carboxypeptidase B or procarboxypeptidase B, wherein the 288th cysteine at natural procarboxypeptidase B is substituted by natural amino acids expect the cysteine, which keeps the activity of natural carboxypeptidase B; the invention also provides an instrument enzyme to prepare saltatory carboxypeptidase B or corresponding procarboxypeptidase B from insulinogen or agent or agent box to test protein and diagnose pancreatic disease.
Owner:BEIJING GUANHONG TECH +1
Preparation method of recombinant carboxypeptidase b
InactiveCN102286502AReduce volumeNo subsequent concentration steps requiredHydrolasesFermentationDigestionCarboxypeptidase B
The invention relates to a method for preparing recombinant carboxypeptidase B (CPB) in Pichia pastoris. This method has a high expression level, and the expression product CPB zymogen does not need to undergo denaturation and renaturation, and active CPB can be obtained after direct enzymatic digestion to remove the propeptide, and the subsequent purification steps are also simple and convenient. The prepared recombinant carboxypeptidase B can be used for industrial production of recombinant human insulin.
Owner:GAN&LEE PHARMA
Carboxypeptidases B from anopheles gambiae. compositions comprising them, vaccine applications and use as therapeutical targets
The present invention provides two carboxypeptidase B enzymes from Anopheles gambiae and homologs thereof. The present invention also provides compositions and vaccines containing the carboxypeptidase B enzymes, as well as antibodies directed thereto and various methods of using the same. The methods of the present invention include a method of blocking Plasmodium development and a method of identifying compounds that inhibit carboxypeptidase B activity.
Owner:INST PASTEUR
Method for obtaining insulin or insulin derivatives with correctly bonded cystine bonds
A process for obtaining insulin or insulin derivatives with properly bonded cystine bonds from a precursor of insulin or insulin derivatives in the presence of cysteine or cysteine hydrochloride and a chaotropic agent undergoes a folding process in the presence of , after which insulin or insulin derivatives are obtained from said precursor by enzymatic cleavage with trypsin or tryptase and optionally additionally with carboxypeptidase B, followed by Purification is carried out on adsorbent resins.
Owner:SANOFI AVENTIS DEUT GMBH
Recombinant Carboxypeptidase B
ActiveUS20080311619A1Improve purification effectImprove high temperature stabilityFungiBacteriaBiologyCarboxypeptidase B
A nucleic acid coding for pro-carboxypeptidase B (Pro-CPB), comprising three segments A, B and C, wherein at least one of the segments has one of the sequences according to SEQ ID No. 1, 2 or 3.
Owner:SANOFI AVENTIS DEUT GMBH
Plasma carboxypeptidase b inhibitors
InactiveUS20090093520A1Mercapto/sulfide group formation/introductionBiocideAntithrombotic AgentCarboxypeptidase B
Compounds of the following formula (I), for example:wherein R1, R2, R3, and R4 are described herein, are useful as inhibitors of plasma carboxypeptidase B. Pharmaceutical compositions containing these compounds, methods of using these compounds as antithrombotic agents and processes for synthesizing these compounds are also described herein.
Owner:BAYER SCHERING PHARMA AG
Plasma Carboxypeptidase B as a Predictor for Disease Severity and Response
InactiveUS20130052186A1Reduced propensity for developingDecrease C activityNucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementAlleleDisease severity
Compositions and methods are provided for prognostic classification of individuals into groups that are informative of the individual's likelihood of developing severe disease associated with undesirable complement activation. Individuals having one or both alleles for a more stable or active carboxypeptidase B variant have a reduced propensity for developing severe disease. The presence of the protective variant may be identified through any suitable method.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV +1
Recombinant carboxypeptidase B
ActiveUS7977081B2Improve purification effectImprove high temperature stabilityBacteriaHydrolasesBiologyCarboxypeptidase B
Owner:SANOFI AVENTIS DEUT GMBH
Soluble expression system and application thereof in soluble expression of protein
PendingCN114317577ALow costSoluble expression achievedHydrolasesMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliDisulfide bonding
The invention discloses a soluble expression system and application thereof in soluble expression of protein. The inventor screens protein disulfide bond isomerase from different sources, and constructs the protein disulfide bond isomerase and sulfydryl oxidase under the control of the same promoter. The expression of the two proteins is optimized through a strategy of adding a nitrogen terminal tag, and a soluble expression system is constructed. In escherichia coli, after co-expression of the system and target protein recombinant porcine carboxypeptidase B, soluble expression of the porcine carboxypeptidase B can be realized, and formation of inclusion bodies is greatly reduced. The soluble expression system can also be used for soluble expression of other target proteins, such as trypsinogen, and has universality of promoting soluble expression of the target proteins. The method has application prospects in the fields of recombinant protein production, new enzyme original screening and the like.
Owner:江苏万邦医药科技有限公司 +2
Preparation method of recombinant human insulin
ActiveCN108998458BPromote efficient expressionPromote denaturation and refolding efficiencyAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsInsulinsInclusion bodiesNucleotide
The invention relates to a preparation method of recombinant human insulin. The preparation method comprises: inserting a nucleotide sequence shown in the formula of SEQ ID No. 2 into a position between EcoRI and HindIII enzyme sites of a pET-SUMO vector to obtain a recombinant plasmid, transferring the recombinant plasmid into a host strain, culturing the host strain in a medium at 18 to 37 DEG Cuntil OD600 of 0.5-0.7, carrying out induced expression, separating a Sumo-proinsulin fusion protein inclusion body, washing the Sumo-proinsulin fusion protein inclusion body through a buffer solution containing urea, carrying out centrifugation, taking precipitates, carrying out denaturation and gradient renaturation to obtain a renatured Sumo-proinsulin fusion protein, and carrying out one-stepdigestion renaturation on the Sumo-proinsulin fusion protein through Sumo protease, trypsin and carboxypeptidase B at pH of 6.0-8.0 at a digestion temperature of 16-37 DEG C for digestion time of 3-6h to obtain the recombinant human insulin.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
Preparation method of protaminase B and its composition
This invention discloses a preparation of carboxyl peptidase B and its combination relating to enzymology, combination containing enzyme and technology field of disconnecting and depurating method. The technology problem which needs to be solved by this invention is that providing a preparation of carboxyl peptidase B and its combination to solve the yield of carboxyl peptidase B preparation is low and carboxyl peptidase B is astable in present technology. Disclosing a preparation of carboxyl peptidase B, including the steps: salting out, hydrophobic chromatography, anion-exchange chromatography, its characteristic is that using 1-5 times of acetone to process 2-3 times, producing acetone powder; it also discloses a carboxyl peptidase B combination which contains 3-5%(w / v, g / 100ml) manicol. The yield of the invented carboxyl peptidase B achieves more than 60U / g pancreas, raising more than 20%, specific activity of carboxyl peptidase B exceeds 200U / mg, stability of carboxyl peptidase Bis 2 years.
Owner:JIANGSU WANBANG BIOPHARMLS +1
A method for determining the glycosylation and terminal modification of immunoglobulin charge variants
ActiveCN103217499BImprove compatibilityReduce resolutionComponent separationChromatographic separationImmunglobulin e
The invention provides a method for determining immunoglobulin charge isomer glycosylation and terminal modification states. With the method, immunoglobulin glycosylation, N-terminal pyroglutamic acidification, and C-terminal de-lysine can be simultaneously determined rapidly. The method comprises the steps that: (1) immunoglobulin before and after carboxypeptidase B digestion are analyzed by using cation exchange chromatography (CEX-HPLC), and different immunoglobulin charge isomers are collected according to retention times after the column; (2) the immunoglobulin component in the step (1) is denatured by using a denaturant, and is reduced by using a reducing agent, such that light chain and heavy chain are split; (3) the light chain and heavy chain in the step (2) are separated with reversed-phase ultrahigh-pressure liquid chromatography; (4) molecular weights of the light chain and heavy chain obtained in the step (3) are determined by using mass spectrometry; and (5) the chromatographic data in the step (3) and the mass spectral data in the step (4) are analyzed, such that the glycosylation and terminal modification states of the immunoglobulin are determined.
Owner:LIVZON MABPHARM
Production and application of high-stability recombination carboxypeptidase B
The invention relates to production and application of high-stability recombination carboxypeptidase B. The invention also discloses a method for producing recombination carboxypeptidase B, which comprises the following steps: (1) carrying out recombinant expression on carboxypeptidase B with a mutated leading sequence at the N terminus to obtain a recombination protein in an inclusion body form;(2) denaturing and renaturing the recombination protein in an inclusion body form to obtain a soluble recombination protein; and (3) removing leading sequences of the carboxypeptidase B with a leading sequence at the N terminus of the soluble recombination protein to obtain the recombination carboxypeptidase B. The invention uses an intramolecular chaperone to enhance the in vitro refolding of the carboxypeptidase B, and the obtained recombination carboxypeptidase B has high stability and can well resist the enzymolysis of trypsase.
Owner:上海雅心生物技术有限公司
Preparation method of insulin
InactiveCN102628072BFull effectImprove digestion efficiencyPeptide preparation methodsInsulinsEnzymatic digestionInsulin products
The invention relates to a preparation method of insulin. The method which comprises two steps of chromatography purification can improve the enzymatic digestion efficiency, and the controllability in an enzymatic digestion process, so a complete reaction of trypsin and carboxypeptidase B is realized, and insulin precursors not reacted with the carboxypeptidase B can be thoroughly removed, so the purity and the quality of final insulin products are improved, the purity of the final insulin products can reach above 99.7%, and the recovery rate is high, thereby industrialized production can be carried out.
Owner:GAN&LEE PHARMA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com