Preparation method of recombinant human insulin
A technology for recombining human insulin and proinsulin, applied in insulin, chemical instruments and methods, recombinant DNA technology, etc., can solve the problems of amino acid residues at enzyme cleavage sites, low production efficiency, poor stability, etc., and achieve simple and convenient conversion process, The effect of saving production cost and simplifying the process flow
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0042] Example 1 Design of Sumo-proinsulin fusion gene
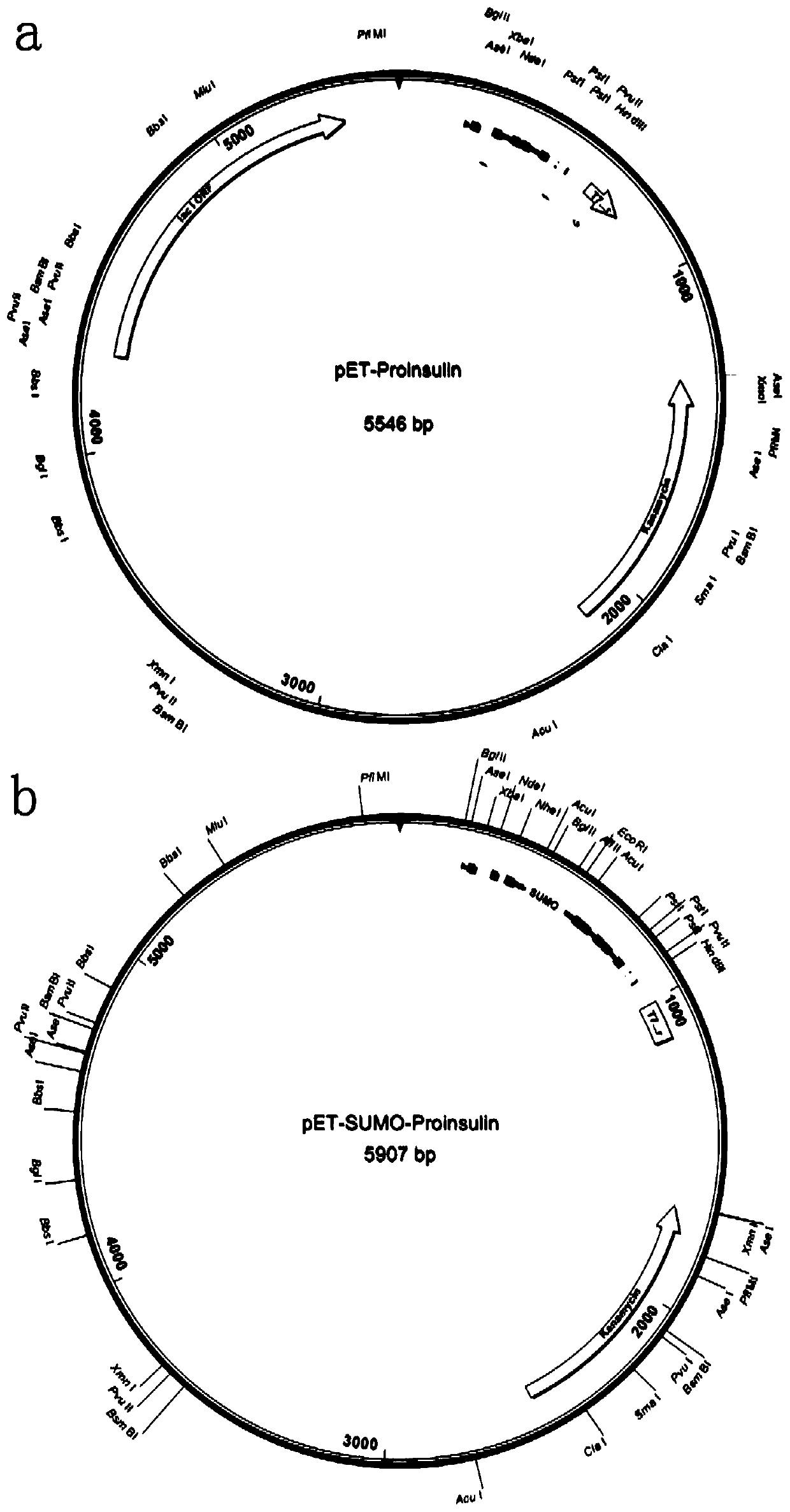
[0043] Based on the pET-SUMO vector, the pET-SUMO-Proinsulin recombinant plasmid with the Sumo tag was designed and constructed ( figure 1 a), the plasmid includes T7 promoter, Lac control element, proinsulin gene and Sumo gene coding region (SEQ ID No.1).
[0044] In order to test the effect of Sumo fusion tag on the expression of proinsulin in Escherichia coli, the pET-Proinsulin (proinsulin) plasmid without Sumo tag was constructed in addition ( figure 1 b), the plasmid includes T7 promoter, Lac control element, proinsulin gene coding region (SEQ ID No.3). The specific method is as follows:
[0045] A DNA fragment (SEQ ID No.2) with a full length of 357 bases was obtained by chemical synthesis. This fragment has two endonuclease sites, EcoRI and HindIII, at the 5' and 3' ends, respectively, and the middle sequence contains 28 amino acids at the C-terminal of the compiled Sumo and the full length of human proinsul...
Embodiment 2
[0046] Induced expression of embodiment 2 recombinant Sumo-proinsulin protein
[0047] The pET-Proinsulin and pET-SUMO-Proinsulin recombinant plasmids constructed and confirmed by DNA sequencing were transferred into BL21(DE3) cells by the traditional heat shock method, single clones were selected, and grown in LB medium at 37°C to OD 600 =0.5, then add 1 mM IPTG to induce expression for 6 hours.
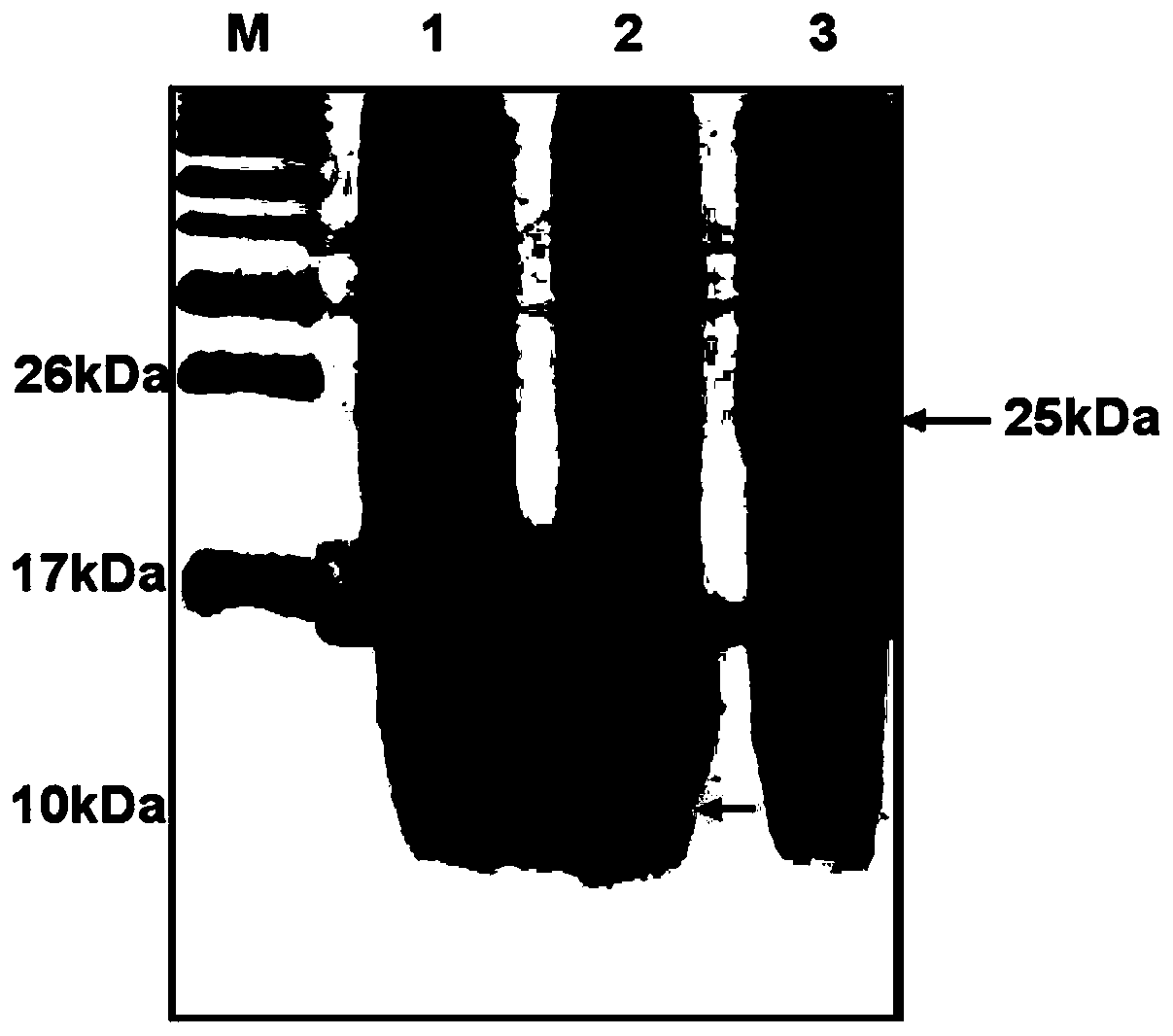
[0048] In order to compare the effect of the Sumo fusion tag on the expression of proinsulin protein in Escherichia coli, after the induction, the bacterial solution was centrifuged and the obtained large intestine was lysed, and then analyzed by gel electrophoresis. The results are shown in figure 2 . figure 2 Among them, lane M represents the marker; lane 1 represents Pet-Sumo (positive control), with a relative molecular mass of 17kDa; lane 2 represents Pet-Insulin (C peptide), with a theoretical relative molecular mass of 9kDa, and the arrow shows an ideal situation The pos...
Embodiment 3
[0049] Example 3 Denaturation and renaturation of recombinant Sumo-proinsulin
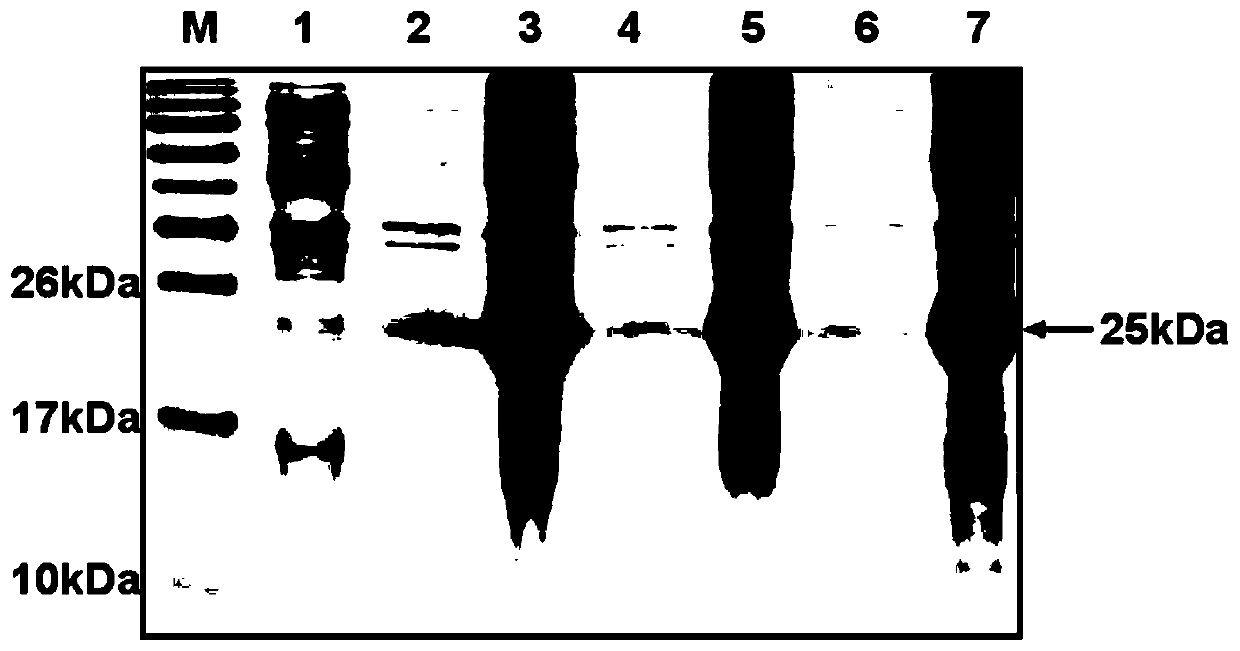
[0050] After the induction in Example 2, the Escherichia coli expressing the recombinant Sumo-proinsulin protein was lysed, and the precipitate was collected to obtain insoluble inclusion bodies. At the same time, polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis analysis was performed on the supernatant and the precipitate, and the results were as follows: image 3 shown. image 3 Among them, lane M represents the marker; lane 1 represents the uninduced E. coli lysate after plasmid transfer; lane 2 represents the supernatant after the first wash with 1×PBS; lane 3 represents the first wash with 1×PBS Precipitate after washing; Lane 4 indicates the supernatant after the second wash with 1×PBS; Lane 5 indicates the precipitate after the second wash with 1×PBS; Lane 6 indicates the supernatant after washing with washing solution; Lane 7 indicates the supernatant after washing with washing solution precipitation. ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com