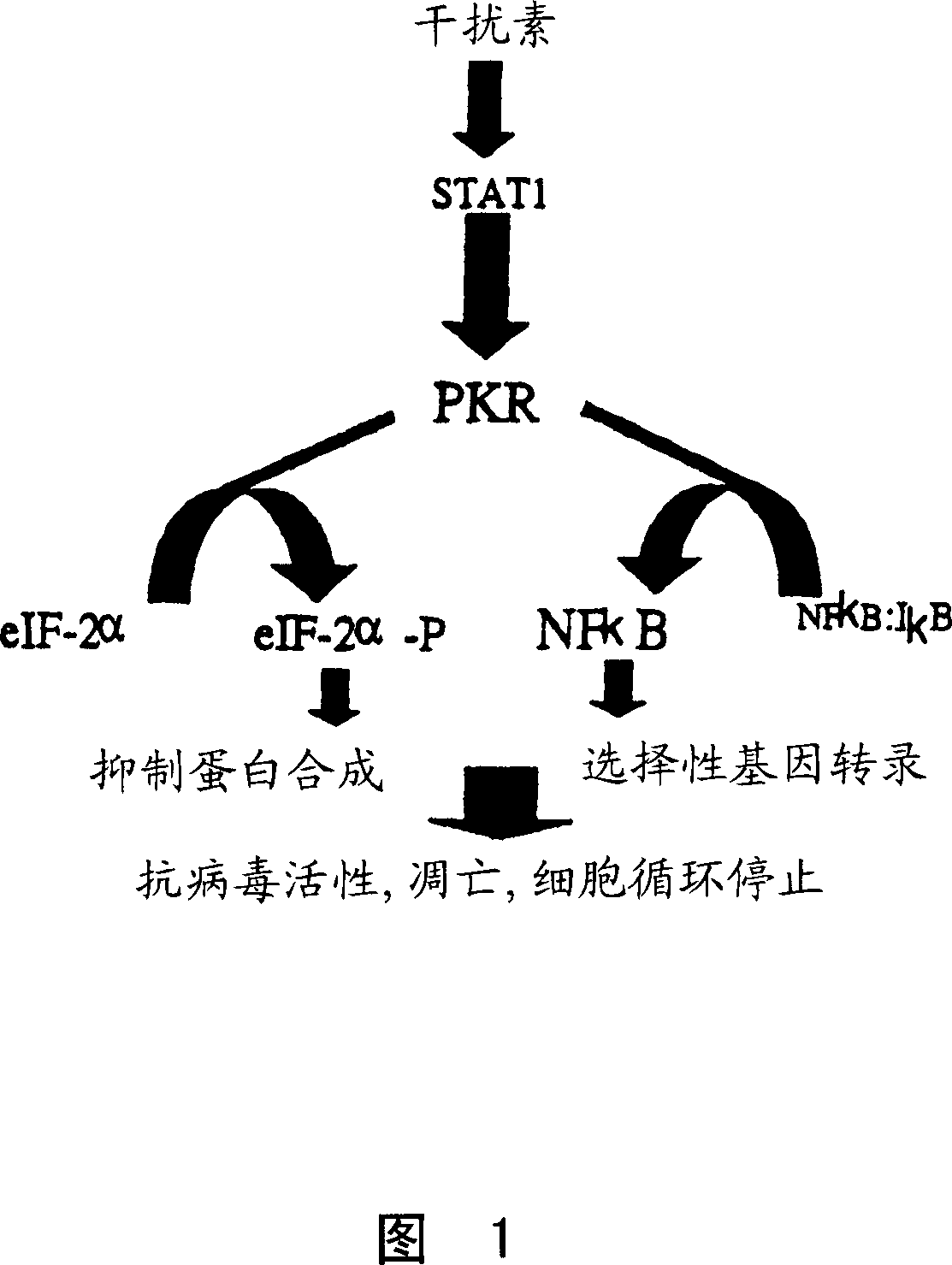
Vesicular stromatitis virus (VSV)
A virus and tumor technology, applied in the direction of viruses, viral peptides, viruses/phages, etc., can solve the problem of not testing the anti-VSV cytotoxic activity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0117] Example 1: PKR negative cells are susceptible to VSV infection.
[0118] in vivo experiment
[0119] Initial experiments are aimed at identifying viruses capable of infecting PKR- / - animals and cells. A PKR-deficient mouse strain (35, incorporated herein by reference) was generated using a homologous recombination strategy and tested for their ability to resist viral infection. Since these mice are PKR- / -, they should be susceptible to virus infection. Several virus species were administered to PKR null animals at a range of concentrations.
[0120] Infection of PKR-deficient mice
[0121] PKR-null mice were generated using conventional knockout techniques (Abraham, N., et al., J Biol Chem, 1999. 274:5953-5962). Groups of 5 female mice, three months old or older, were infected intranasally with varying amounts of herpetic stomatitis virus (Indiana strain). Age-matched wild-type animals were infected in parallel and both series of animals were monitored daily for si...
Embodiment 2
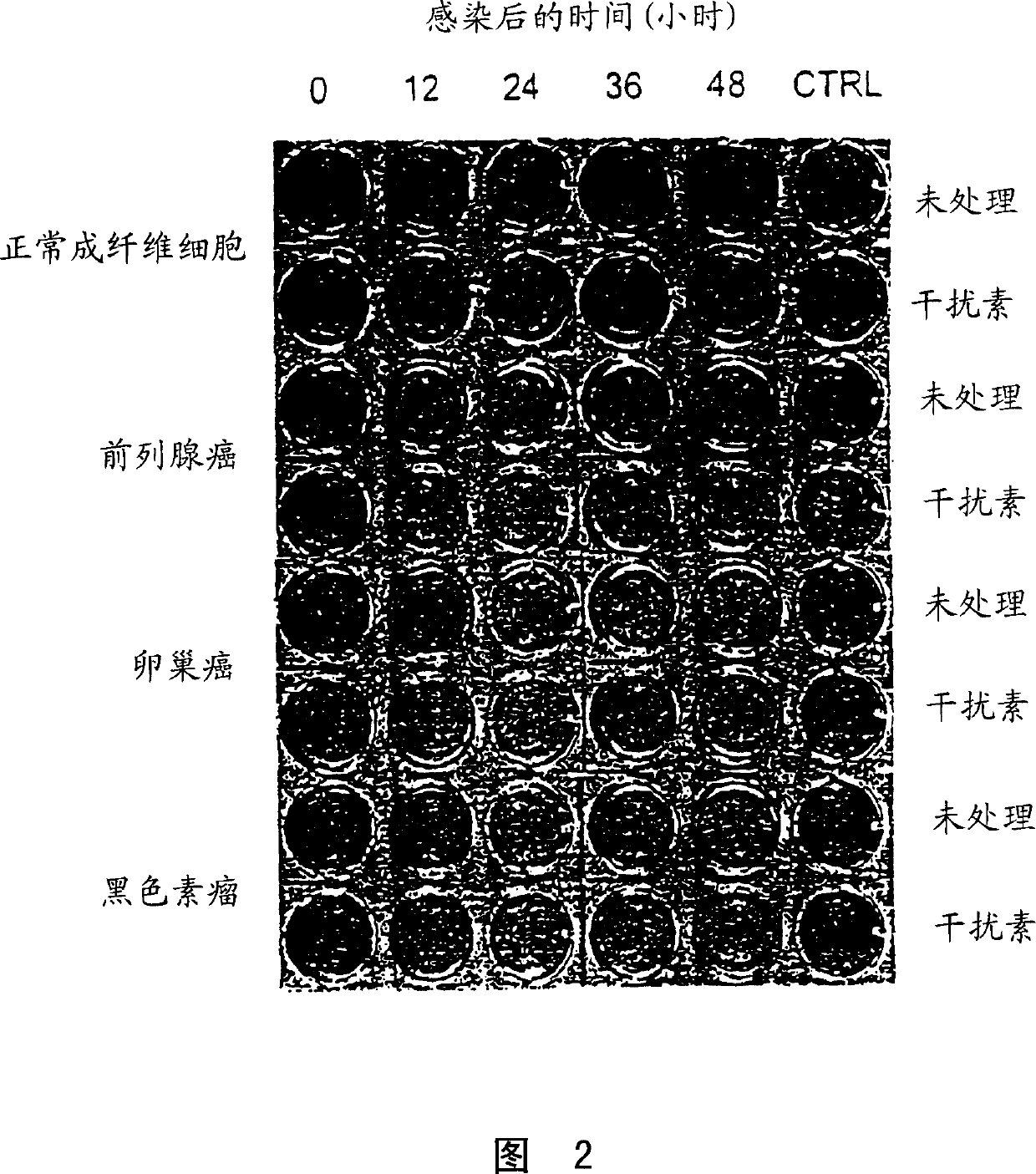
[0124] Example 2: Selective killing of tumor cells with VSV
[0125] In vitro experiments
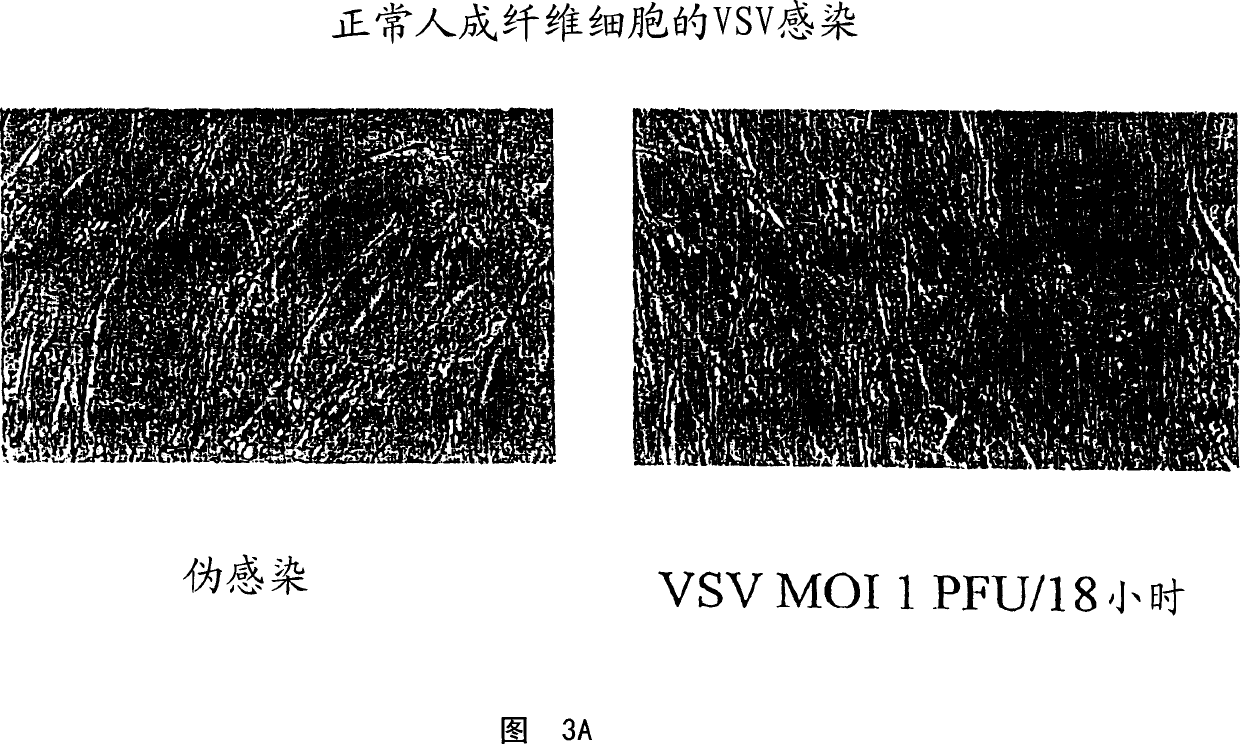
[0126] Several tumor cell lines were randomly selected at the Ottawa Regional Cancer Center and tested for their susceptibility to VSV infection. Primary fibroblast cultures from healthy adult volunteers or primary bone marrow samples from healthy donors were used as control cells.
[0127] Infection of tumor cells with VSV
[0128] As a first test of the oncolytic properties of VSV, virus yield and cytopathic effect after overnight incubation with VSV were assessed. Cell monolayers were incubated with Indiana strain VSV at a multiplicity of infection (moi) of 0.1 plaque forming units (pfu). After allowing the virus to adsorb for 30 minutes at 37 degrees, the culture was rinsed thoroughly with phosphate buffered saline (PBS) and incubated for an additional 18 hours at 37 degrees. At this point, cytopathic effects (cpe) were examined under a microscope and photographed. The 18-hour ...
Embodiment 3
[0139] Example 3: Killing Tumor Cells in Mixed Cultures
[0140] Human fibroblasts and 293T tumor cells were co-cultured at a ratio of 50:50. Since 293T cells express a macromolecular T antigen that is not present in normal cells, the two cell types can be distinguished by immunofluorescence.
[0141] Cultures were infected in this experiment at a moi of 0.1 pfu / cell and infection was allowed in the presence or absence of interferon. At 0, 18 and 24 hours (Figure 4) the cultures were fixed and stained with an antibody to the macromolecular T antigen (red nuclei) to detect 293T cells and DAPI (blue nuclei) to stain all cell types. Both cell types initially exhibit a spindle-shaped morphology with large oval nuclei. After 18 hours the number of 293T cells (red nuclei) decreased and many remaining 293T cells showed altered nuclear morphology. At 24 hours after infection, very few 293T cells were detected, and the few remaining 293T cells showed the characteristics of condensed...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com