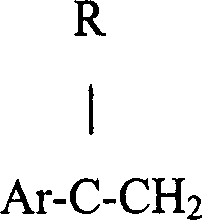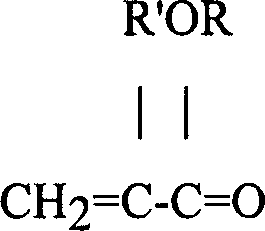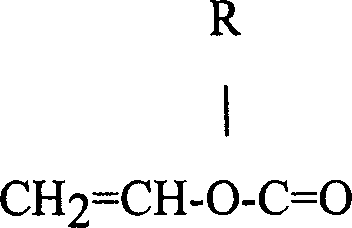Microbeam and unmixed polyester for thermal imaging media
A technology of polymer particles, polyester, used in transportation and packaging, thermography, coating, etc., can solve problems such as inability to provide solutions, tearing, poor contact of inorganic pore initiator dye-donor elements, etc. Achieve improved image quality, reduced production costs, and improved grain appearance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0110] Example 1 - Porous layer prepared from cross-linked microbeads only (comparative)
[0111] A monolayer film comprising an apertured polyester layer was prepared by the method described below. The material used to make the film was a complex mixture consisting of 35 wt% PETG 6763 resin (IV = 0.73 dl / g) (amorphous polyester resin commercially available from Eastman Chemical Co.), 35 wt% polyparaphenylene Ethylene glycol diformate (commercially available as PET #7352 from Eastman Chemicals) and 30 wt% cross-linked spherical polymethyl methacrylate, (PMMA), 1.7 μm diameter beads. Cross-linked organic beads were prepared by the previously described method of limited coalescence. The beaded poly(methyl methacrylate) was compounded with the polyester resin by mixing in a counter-rotating twin-screw extruder connected to a pelletizing die that formed pellets of the resin mixture.
[0112] The obtained resin was dried at 65°C. The resin melts at 275°C and is fed through a m...
Embodiment 2
[0114] Example 2 - Preparation of a porous layer using only non-crosslinked polymer particles immiscible with the polyester matrix (comparative)
[0115] A monolayer film comprising an absorbent polyester layer was prepared by the method hereinafter described. Polyethylene terephthalate (commercially available as PET #7352 from Eastman Chemicals) was dry blended with 20% by weight polypropylene ("PP", Huntsman P4G2Z-073AX), based on the total weight of the mixture, and at 65 C in a desiccator for 12 hours.
[0116] The resin is then melted at 275°C and fed through a masticating screw extruder into the extrusion die manifold to create a melt stream that exits the die and is rapidly quenched on chill rolls . By controlling the throughput of the extruder, the thickness of the final cast sheet can be adjusted. In this case, the thickness of the cast sheet was about 420 μm. The cast sheet was first oriented in the machine direction at a draw ratio of 3.3 and a temperature of ...
Embodiment 3
[0117] Embodiment 3 (invention)
[0118] Monolayer films comprising a voided polyester matrix layer were prepared using the method described below. The material used to make the film was a complex mixture consisting of: 35 wt% PETG 6763 resin resin (IV = 0.73 dl / g) (amorphous polyester resin commercially available from Eastman Chemical Company), 35 wt% polyparaffin Ethylene phthalate (commercially available as PET #7352 from Eastman Chemicals) and 30 wt% cross-linked spherical polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA), 1.7 μm diameter cross-linked organic beads. Cross-linked organic beads were prepared by the previously described method of limited coalescence. The beaded polymethyl methacrylate was compounded with PETG resin by mixing in a counter-rotating twin-screw extruder attached with pelletizing dies forming pellets of the resin mixture. Then, 20 wt% of polypropylene ("PP", Huntsman P4G2Z-073AX) was dry blended with polyethylene terephthalate (PET #7352 commercially available f...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com