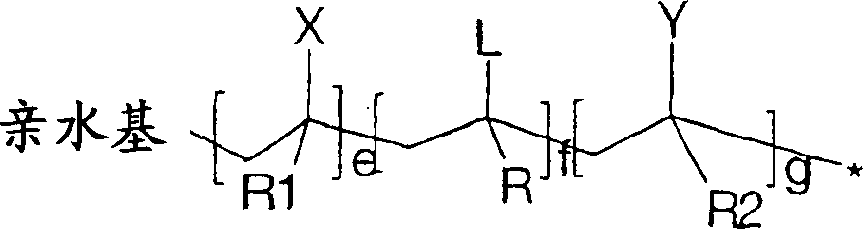
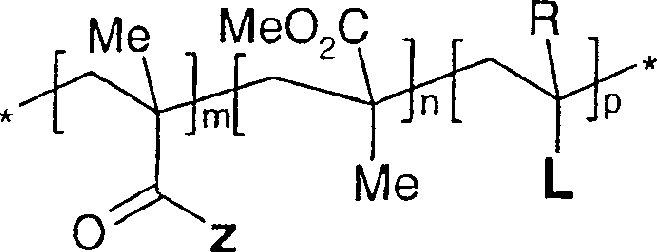
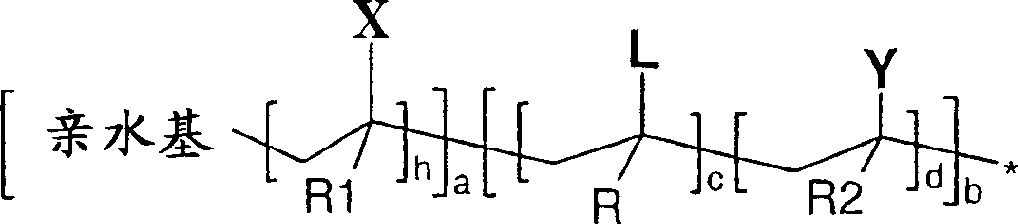
Use of reactive polymeric surfactants in formation of emulsions
A polymer and emulsion technology, applied in animal repellents, plant growth regulators, applications, etc., can solve the problems of capsule processing and adverse effects on performance, environmental pollution, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0197] Synthesis of living polymer surfactants by atom transfer radical polymerization (ATRP).
[0198] General synthesis steps:
[0199] In a typical polymerization reaction, the monomers in the desired molar ratio are dissolved in a suitable solvent or solvent mixture. When all the components in the reaction are soluble in toluene, toluene is generally used. Some components such as AEMA·HCl, QuatDMAEMA, SSA, DMMAPSA betaine and DMMAEA betaine have poor solubility in organic solvents, so use methanol-water mixtures for their mixture (volume ratio 1:1~3:1) .
[0200] Add the appropriate initiator. In order to prepare non-ionic block copolymers, it is a polymer macroinitiator, such as mono-2-bromoisobutyryl monomethoxy poly(ethylene glycol), abbreviated as PEG-Br(#), where # Is the number of ethylene glycol units, which is prepared by literature methods (Jankova et al., Macromolecules, 1998, 31, 538-541). In order to prepare graft copolymers or ionic block copolymers, the initiator...
Embodiment 5a-6l
[0219] The function of the following examples is to illustrate that the active polymer surfactant of the present invention can utilize isocyanate and carbodiimide to crosslink at the oil / water interface to prepare a stable emulsion.
Embodiment 5a-5k
[0220] Examples 5a-5k. Isocyanate method.
[0221] A reactive polymer surfactant containing amino groups is used to emulsify a water-immiscible phase containing a small amount of hydrophobic polyfunctional isocyanate, such as PMPPI or HDIT. If necessary, adjust the pH of the emulsion to 7-9, and then stir at 20-50°C for 1-24h for cross-linking.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com