Method of detecting inorganic phosphoric acid, pyrophosphate and nucleic acid, and method of typing snp sequence of DNA
A technology of inorganic phosphoric acid and detection method, which is used in biochemical equipment and methods, determination/inspection of microorganisms, material analysis by electromagnetic means, etc., and can solve problems such as inability to detect target nucleic acid molecules.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach 1
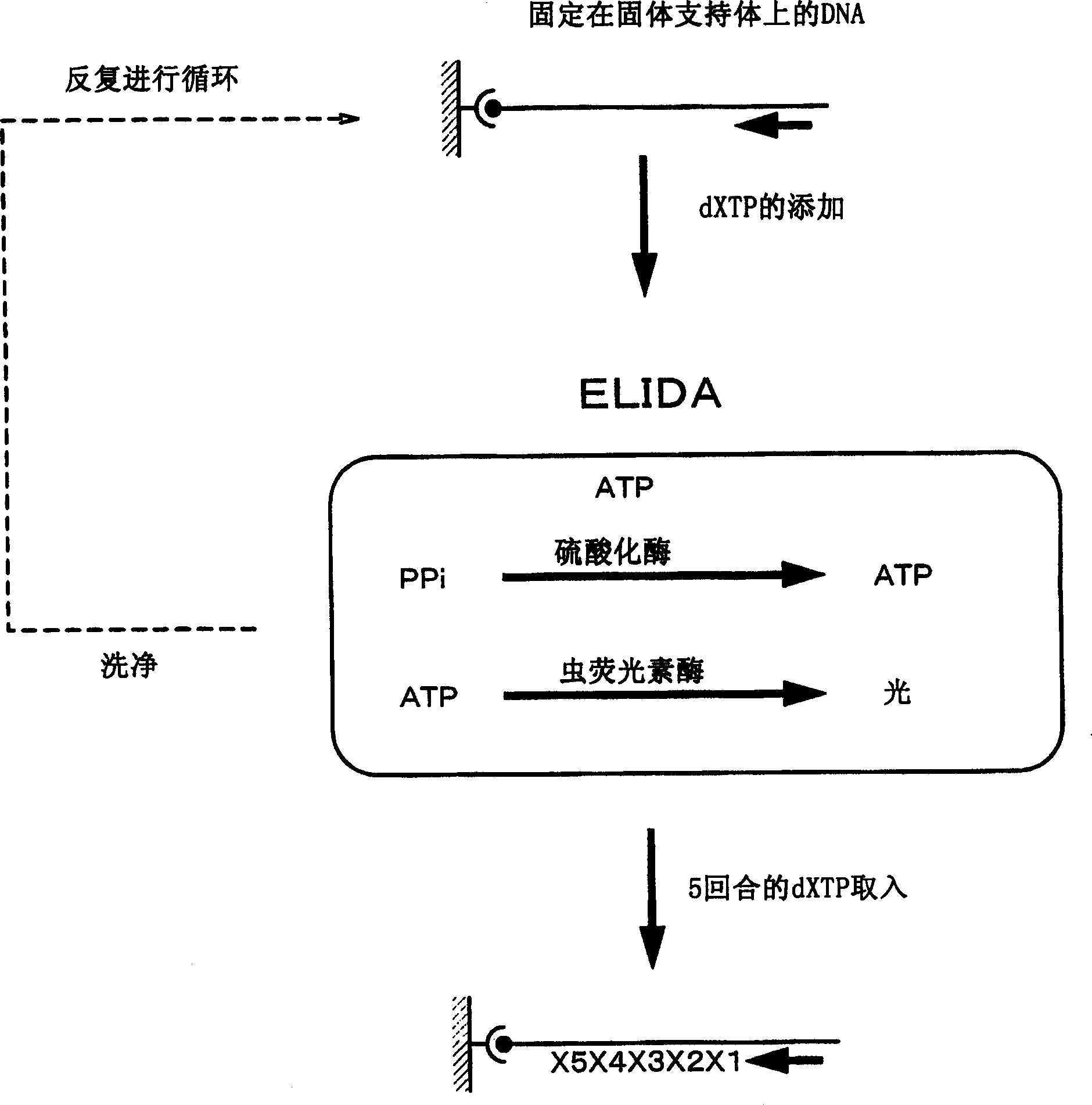
[0037] In Embodiment 1 of the present invention, simple quantitative detection of inorganic phosphate is performed using an enzyme reaction. Embodiment 1 of the present invention relates to a method for detecting inorganic phosphoric acid, the method comprising: supplying a sample to a sample containing glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate, oxidized nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD + ) or oxidized nicotinamide phosphate adenine dinucleotide (NADP + ), a step in the measurement system of glyceraldehyde phosphate dehydrogenase and an electron transport mediator; and, a step in which the current value is measured in the system. In the present specification, "measurement system" refers to the whole of a series of reactions of the mechanism involved in the detection of inorganic phosphate and the place where such a series of reactions are carried out. Components necessary for carrying out a series of reactions exist in the "measurement system". The "measurement system" is usually obt...
Embodiment approach 2
[0062] In Embodiment 2 of the present invention, pyrophosphate is simply and quantitatively detected using an enzymatic reaction.
[0063] Embodiment 2 of the present invention will be described using the reaction formula (V).
[0064] First, as shown in the reaction formula (V), pyrophosphoric acid (PPi in the reaction formula (V)) is hydrolyzed to become inorganic phosphoric acid (Pi in the reaction formula (V)).
[0065] Reaction formula (V)
[0066]
[0067] This hydrolysis reaction may be carried out at a high temperature, or may be carried out using pyrophosphatase, which is an enzyme that catalyzes the reaction.
[0068] Next, pyrophosphoric acid can be quantitatively detected by detecting the inorganic phosphoric acid produced by the reaction of the reaction formula (V) in the same manner as in the first embodiment.
[0069] In this embodiment, the reaction of the reaction formula (V) does not need to be performed separately in the reaction in the detection of...
Embodiment approach 3
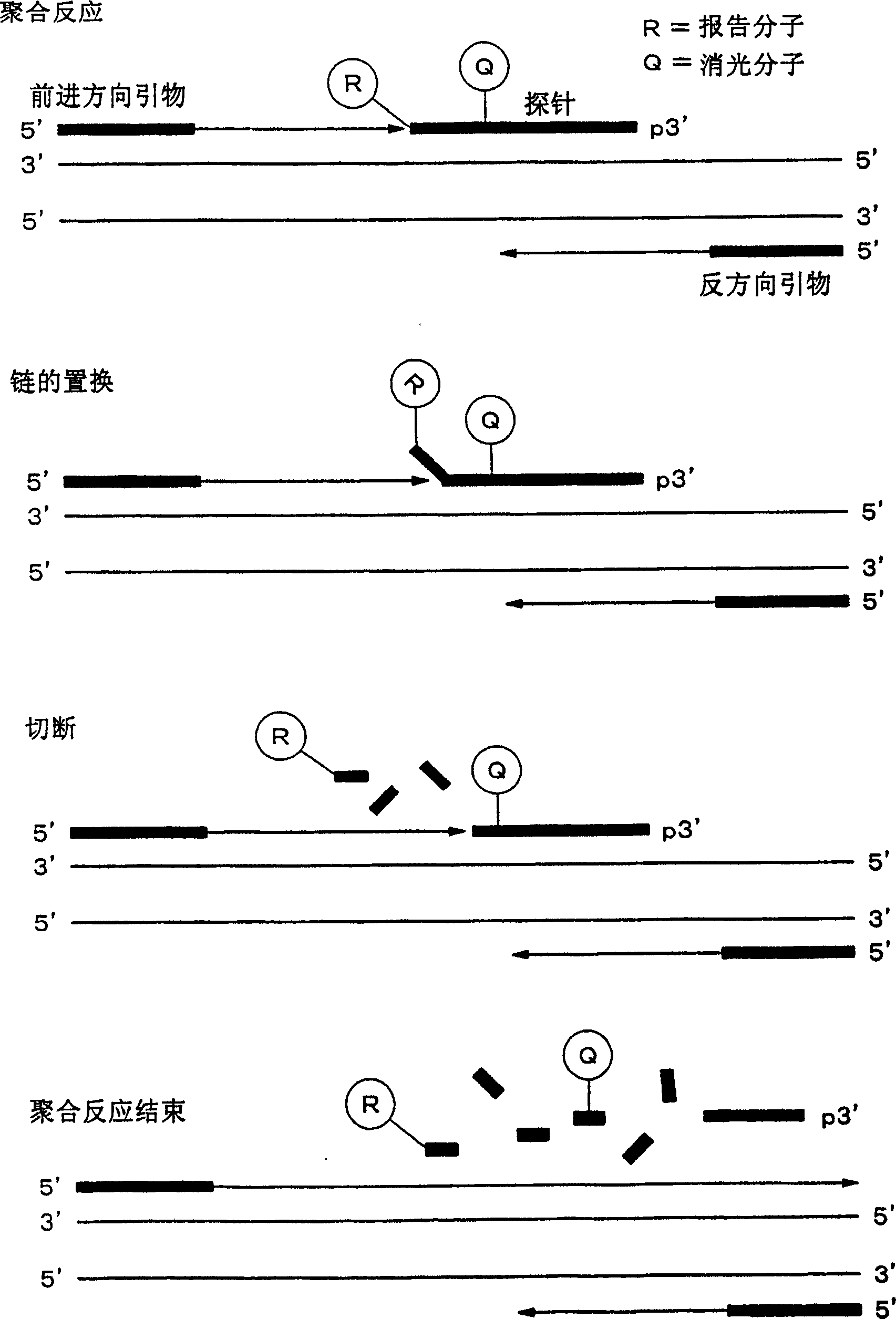
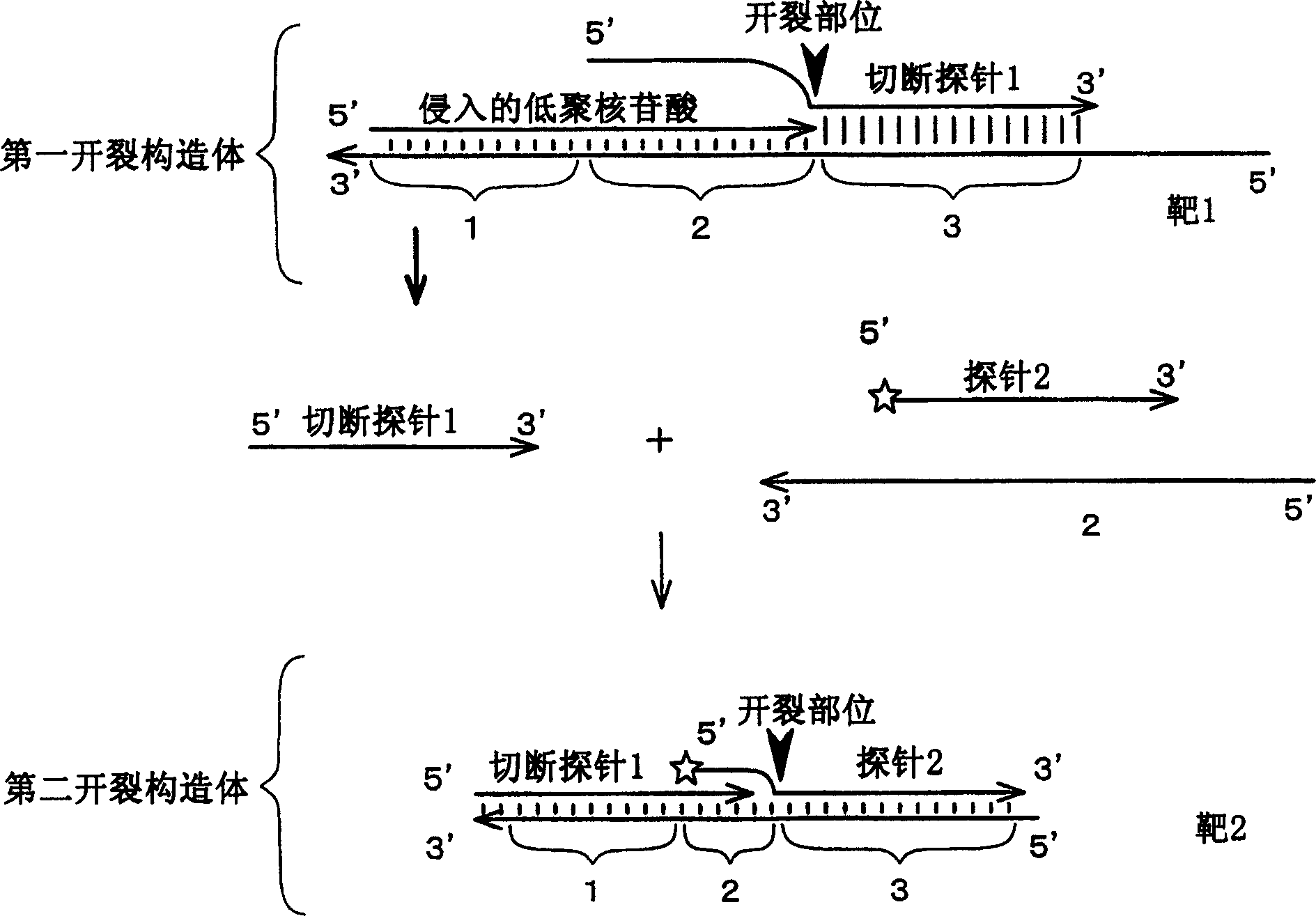
[0071] In Embodiment 3 of the present invention, a method for detecting DNA having a specific sequence with high sensitivity is implemented.
[0072] In the present embodiment, first, a sample is supplied to a reaction system containing a DNA probe having a sequence complementary to a target DNA sequence, a DNA polymerase, and a deoxynucleotide. The "reaction system" as used herein refers to a series of nucleic acid extension reactions as described below and a place where such reactions are carried out. In a "reaction system", there are components necessary to carry out a series of reactions. A "reaction system" typically dissolves the above components in a suitable solvent (eg, Tris-HCl buffer, any buffer commonly used in nucleic acid elongation reactions or nucleic acid propagation reactions (including those in commercially available kits). buffer)), provided as a solution. The DNA polymerase may be any DNA polymerase that is commercially available or prepared by those ski...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com