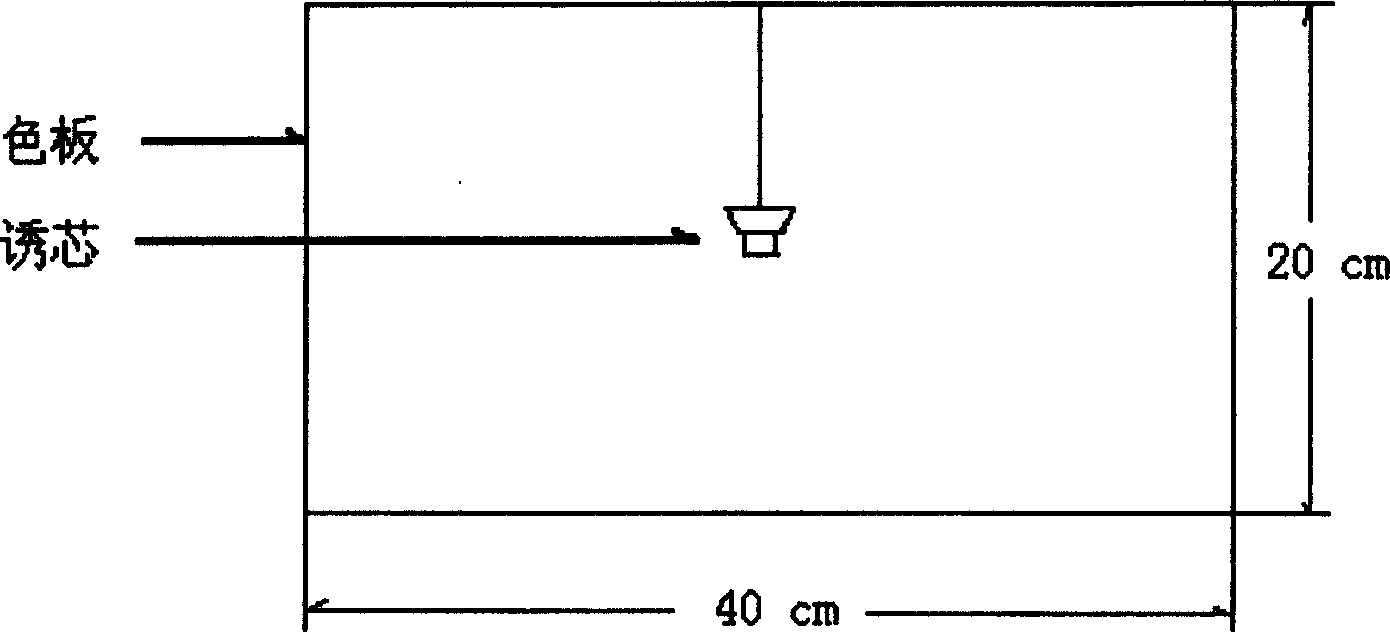
Tea garden insect trapping method
A technology for natural enemy insects and tea gardens, which can be used in the device, application, and animal husbandry of catching or killing insects. It can solve the problems of natural enemies in tea gardens that have not yet been seen, and achieve the effects of low cost, easy transportation, and stable performance.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0047] Embodiment 1 adopts adsorption method to separate and identify 10 kinds of volatiles of tea shoots infested by insects, namely benzaldehyde, trans-2-hexenal, indole, methyl salicylate, ocimene, cis-3-hexenyl acetate, cis-3-hexen-1-ol, linalool, geraniol and trans-2-hexenoic acid
[0048] Make a hollow glass column with a small opening of 7 mm in diameter at both ends, with a volume of 5 liters. The inlet is connected to a compressed air bottle, and the outlet is connected to a Tenax TA adsorption column and a vacuum pump in turn. The TenaxTA column was activated with nitrogen at 275°C for 4 hours prior to adsorption of volatiles. Add 200 grams of tea aphids to harm tea shoots in a glass container, blow in air, and simultaneously draw air from behind the adsorption column. Before the inlet and behind the Tenax TA column, use a flow meter to control the flow rate. The air inlet and outlet flow rates are both 300 ml / min.
[0049] After 12 hours, the adsorption column was ...
Embodiment 2
[0051] Example 2 Determining that benzaldehyde, trans-2-hexenal, indole, and methyl salicylate are volatile components with attractant activity by biological assay method
[0052] According to Embodiment 2, the behavioral responses of 9 kinds of natural enemy insects to 10 kinds of pest volatiles in the olfactometer were measured with a taste source with a concentration of 1 μg / ml. Count the number of natural enemy insects that select the taste source and n-hexane. use χ 2 The method was used to detect the difference between the number of insects that chose the odor source and the number of insects that chose n-hexane. It was found that 9 kinds of tested insects showed obvious tropism to benzaldehyde, trans-2-hexenal, indole, and methyl salicylate, and tended to trans-2-hexenal, benzaldehyde, and methyl salicylate The difference between the number of insects and the number of insects tending to the control (n-hexane) reached a significant level (P<0.05).
[0053] According ...
Embodiment 3
[0054] Example 3: Benzaldehyde, trans-2-hexenal, indole, and methyl salicylate were made into flavor sources with a concentration of 0.01-20 μg / ml respectively, and then the four flavor sources were mixed in a ratio of 1: 0.5- 1.5∶0.2-1.2∶0.3-1.5 combination to prepare an attractant for attracting natural enemy insects
[0055] Using n-hexane as solvent, make benzaldehyde, trans-2-hexenal, indole, and methyl salicylate respectively into odorants with a concentration of 1 μg / ml, and then press 1: 1:1:1 combination. Soak rubber tips made of natural rubber in absolute ethanol for 24 hours and let dry. Soak the rubber head with the attractant for 24 hours and dry it to make the natural enemy attractant.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com