Method of removing solvent from polymer solution and solventremoving apparatus
A polymer solution and desolventization technology, applied in separation methods, chemical instruments and methods, evaporation, etc., can solve problems such as difficult desolventization
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
experiment example 1( Embodiment 1~4 and comparative example 1~2
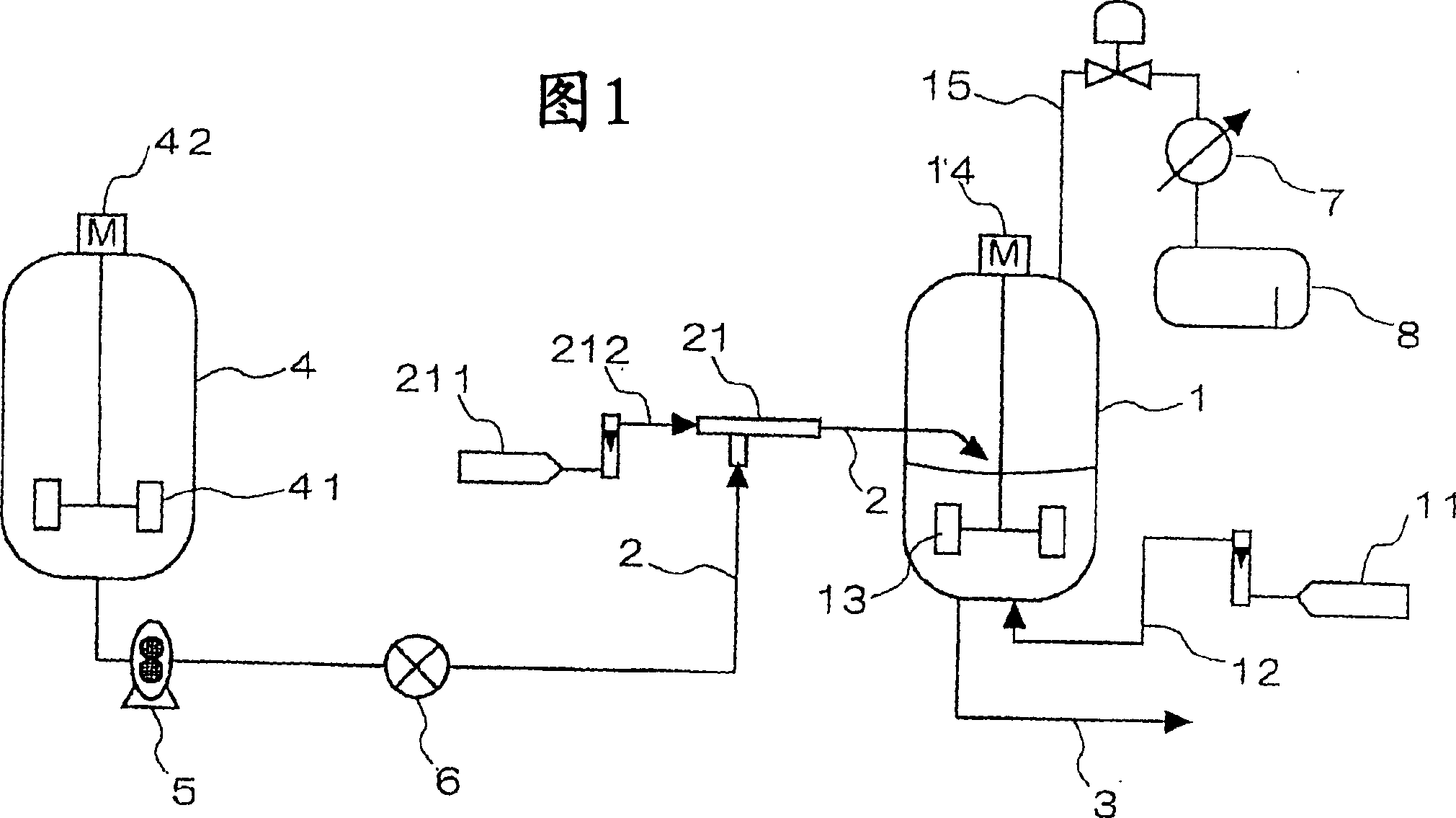
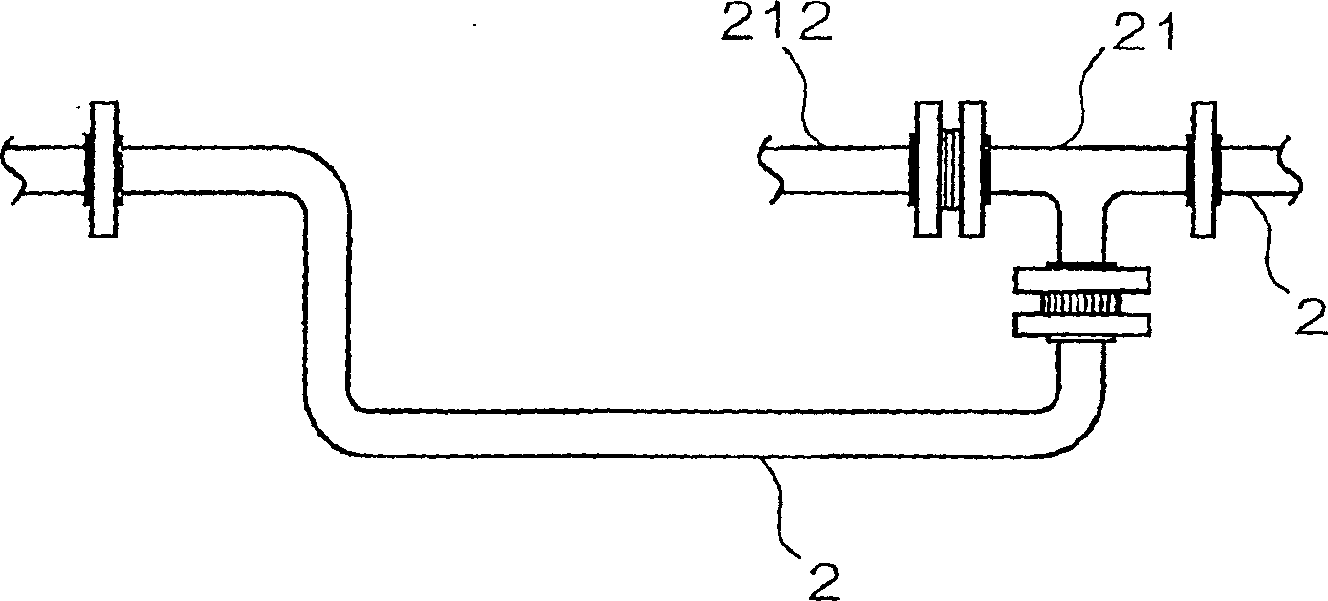
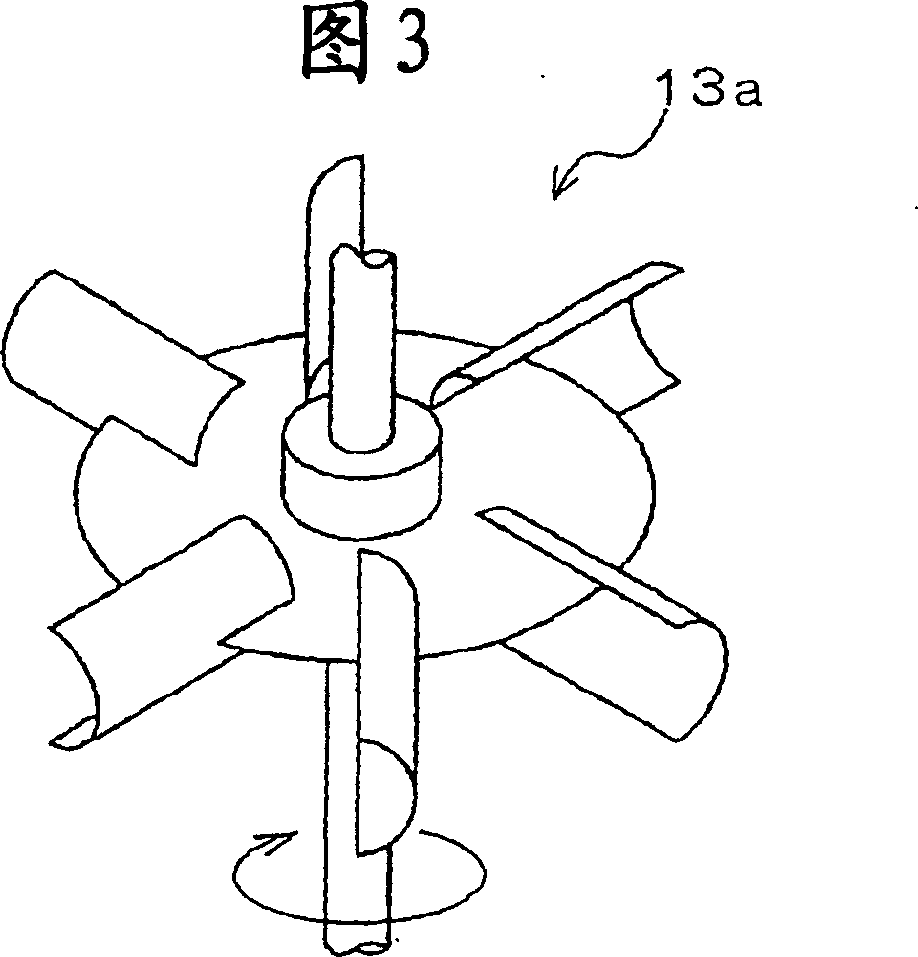
[0148] Use the mixed solvent that 90 mass % hexanaphthene and 10 mass % n-heptane forms as reaction solvent, use the device shown in Figure 1 to carry out desolvation to polymer solution (temperature 60 ℃), this polymer solution contains 20 mass % A styrene-butadiene copolymer (styrene content: 10% by mass) obtained by copolymerizing styrene and butadiene using n-butyllithium as a polymerization initiator. That is, while stirring the polymer tank 4 (made of stainless steel, with an internal volume of 3 m 3 ) in the styrene-butadiene copolymer solution is sent out by the pump 5 (plunger pump), transferred through the polymer solution transfer pipe 2, and supplied to the built-in polymer solution at a speed of 130 liters / hour. In the in-line mixer 21 as a gas-liquid mixer in the pipe 2 for solution transfer. Simultaneously, steam [pressure (gauge pressure) 1.2 MPa, temperature 220° C. (the pressure and temperature of steam are the same below)] was supplied from the steam source...
experiment example 2( Embodiment 5~6 and comparative example 3~4
[0152] When the solvent contained in the polymer solution is expressed as 100 parts by mass, the total amount of steam supplied to the gas-liquid mixer and the amount of steam supplied to the desolventizing tank is 150 parts by mass, and is changed as shown in Table 1. Except for the respective supply amounts, solvent removal was performed in the same manner as in Example 1.
experiment example 3( Embodiment 7~9 and comparative example 5~6
[0154] A mixed solvent composed of 90% by mass cyclohexane and 10% by mass of n-heptane was used as a reaction solvent, and a polymer solution (temperature 60°C) containing 15% by mass of n-butyllithium as a polymerization initiator was used. Styrene-butadiene rubber (styrene content: 35% by mass) obtained by copolymerization of styrene and butadiene was supplied to a gas-liquid mixer when the solvent contained in the polymer solution was calculated as 100 parts by mass. Desolvation was performed in the same manner as in Example 1, except that the total amount of steam in and the amount of steam supplied to the desolventization tank was 70 parts by mass, and the respective supply amounts were changed as shown in Table 1.
[0155] In addition, in these Experimental Examples 1 to 3, the residual solvent concentration of the polymer after desolventization refers to the solvent concentration in the dry polymer, which was obtained by a gas chromatograph (apparatus equipped with an F...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| boiling point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com