Optic micro distance correcting method
A correction method and macro-distance technology, applied in optics, optomechanical equipment, and originals for optomechanical processing, etc., can solve problems such as unprovided, difficult operation, and reduced optical process margins
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0036] This disclosure describes an improved OPC technique for correcting end-of-line distortion / offset due to optical macro effects in semiconductor manufacturing. This disclosed method uses an asymmetric structure as the serif of OPC to improve the general method, and the serif has no or little damage to the margin of the optical photolithography and line etching process, so as to avoid the connection between the line end and the line end. shortened problem.
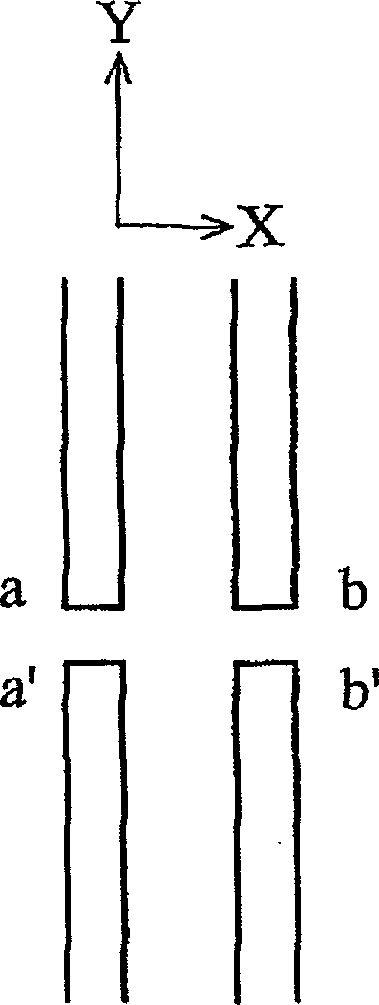
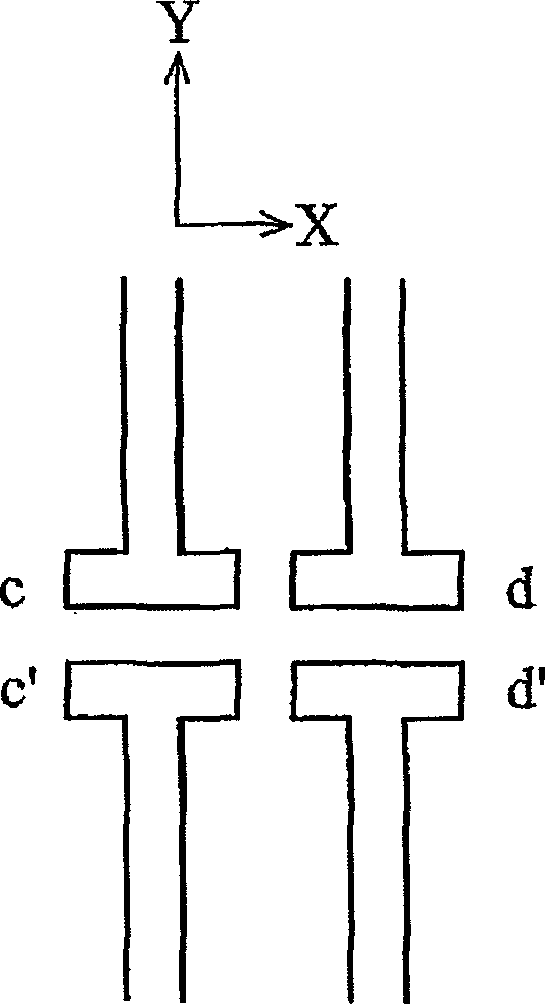
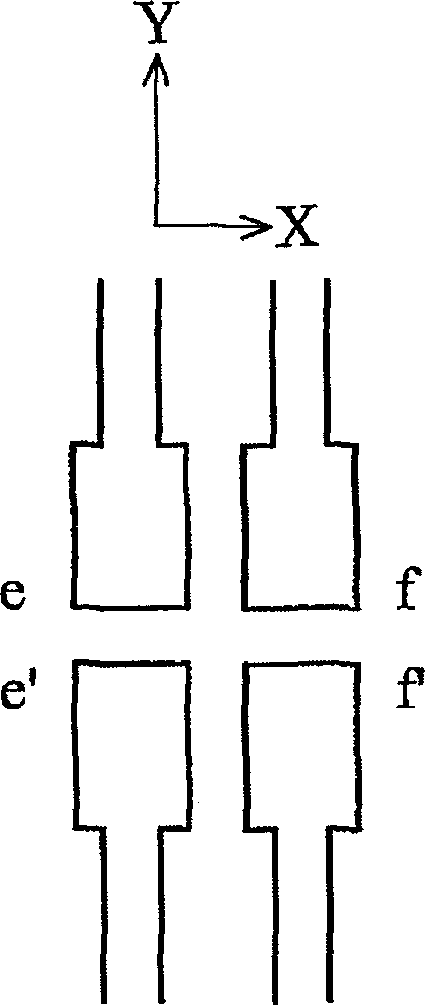
[0037] Figure 2A to Figure 2D Describe how this disclosure uses an asymmetric OPC structure for OPC processing. The size and shape of the OPC structure disclosed in the present disclosure do not have to be symmetrical to effectively correct the line distortion / offset, but some better orientations and asymmetrical OPC structures are used to correct the line distortion / offset.
[0038] Figure 2A It is an example of an asymmetrical OPC structure. Part of the mask pattern includes 4-line ends. The 4-line ends are a pa...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com