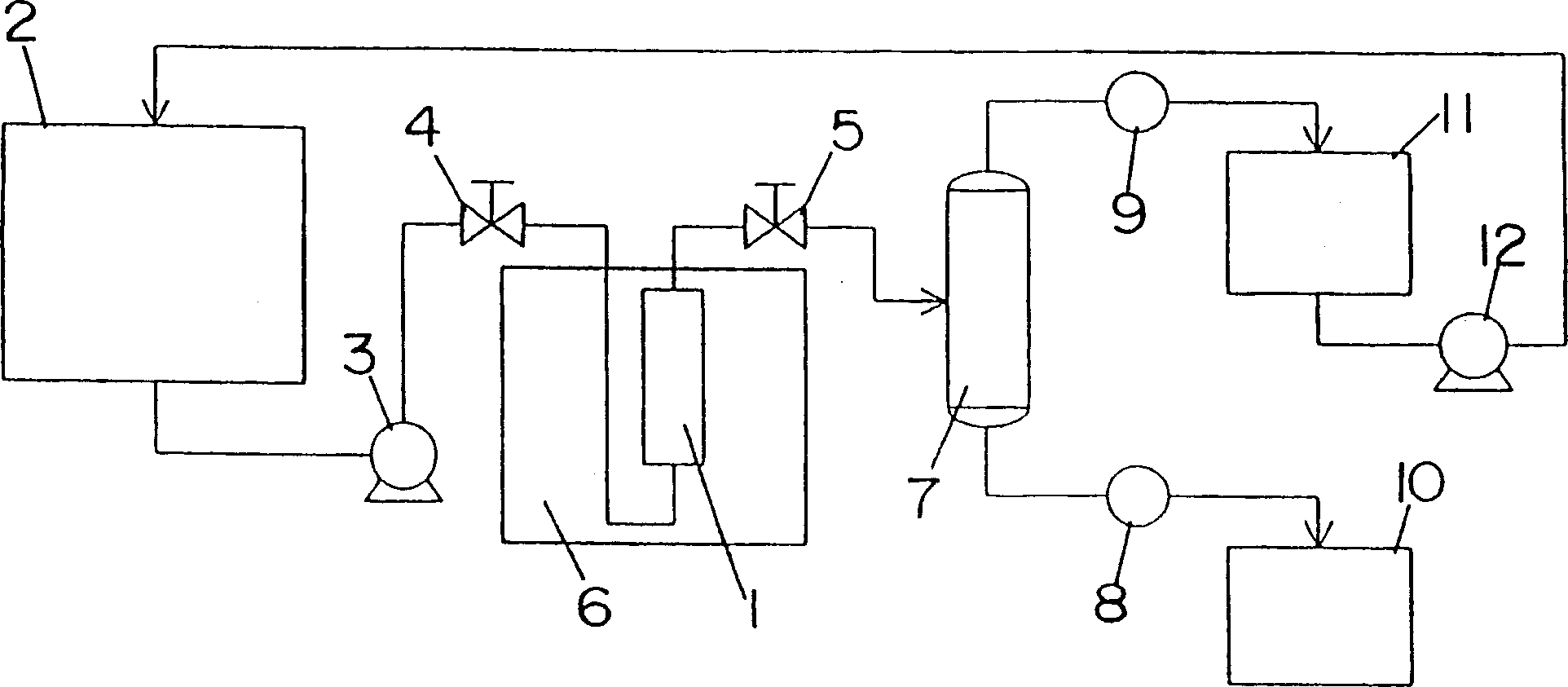
Depolymerization process
A technology of polymers and compounds, applied in recycling technology, plastic recycling, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
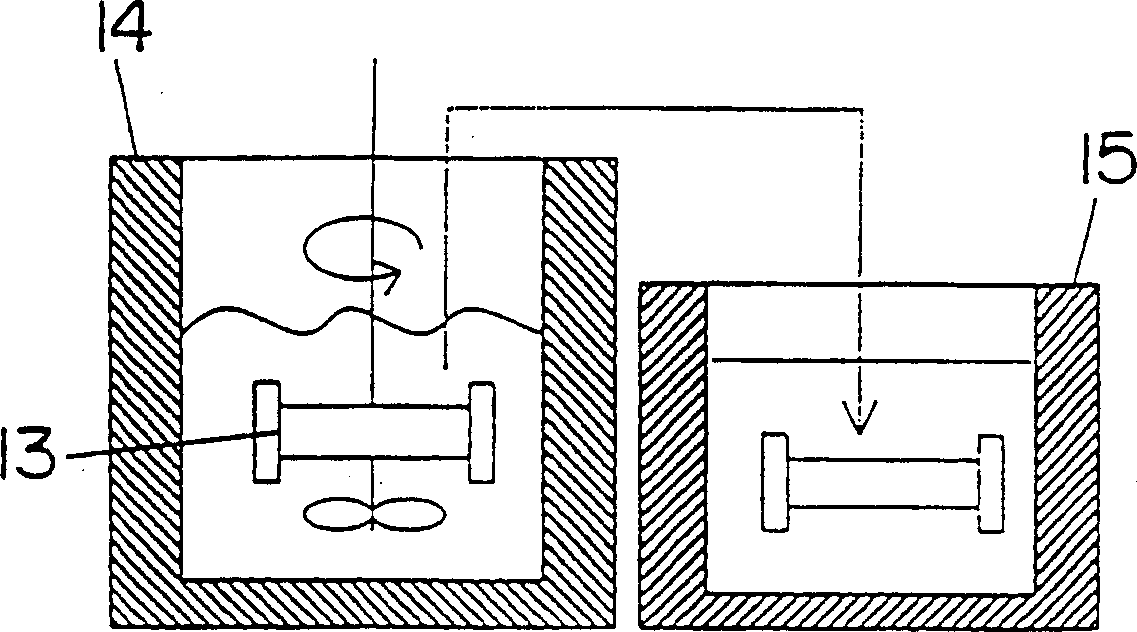
[0041] 2 g of cured product of unsaturated polyester resin (manufactured by Showa Polymer "RIGOLAC M-580"), 10 g of pure water, and 2 g of calcium carbonate were added to the reaction tube 13, and the atmosphere in the reaction tube 13 was replaced with argon gas and sealed. The reaction tube 13 was immersed in a constant temperature tank 14 at 360° C., so that the water in the reaction tube 13 was in a subcritical state. The decomposition reaction was performed for 20 minutes while the reaction tube 13 was immersed in the thermostat 14 . Then, the reaction tube 13 was taken out from the constant temperature tank 14, immersed in the cooling tank 15, and rapidly cooled to room temperature. Although water, organic acid salts, glycols, by-products, and calcium carbonate are present in the contents of the reaction tube 13, there is no undecomposed resin at all, and the decomposition rate is approximately 100%.
[0042] After adding a sufficient amount of water to the content to d...
Embodiment 2
[0044] Except using barium carbonate 2g to replace calcium carbonate as water insoluble alkali, all the other steps are identical with embodiment 1. There was no undecomposed resin in the contents of the reaction tube 13, and the decomposition rate was approximately 100%. The results of Example 2 are shown in Table 1.
Embodiment 3
[0046] Except using calcium hydroxide 2g to replace calcium carbonate as water insoluble alkali, all the other steps are identical with embodiment 1. There was no undecomposed resin in the contents of the reaction tube 13, and the decomposition rate was approximately 100%. The results of Example 3 are shown in Table 1.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com