Auto-ip traffic optimization in mobile telecommunications systems
A mobile communication network and traffic technology, applied in the field of providing data services, can solve the problems of special and complex mapping, undefined connections, etc., and achieve the effect of simplifying design and operation and avoiding difficult problems.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
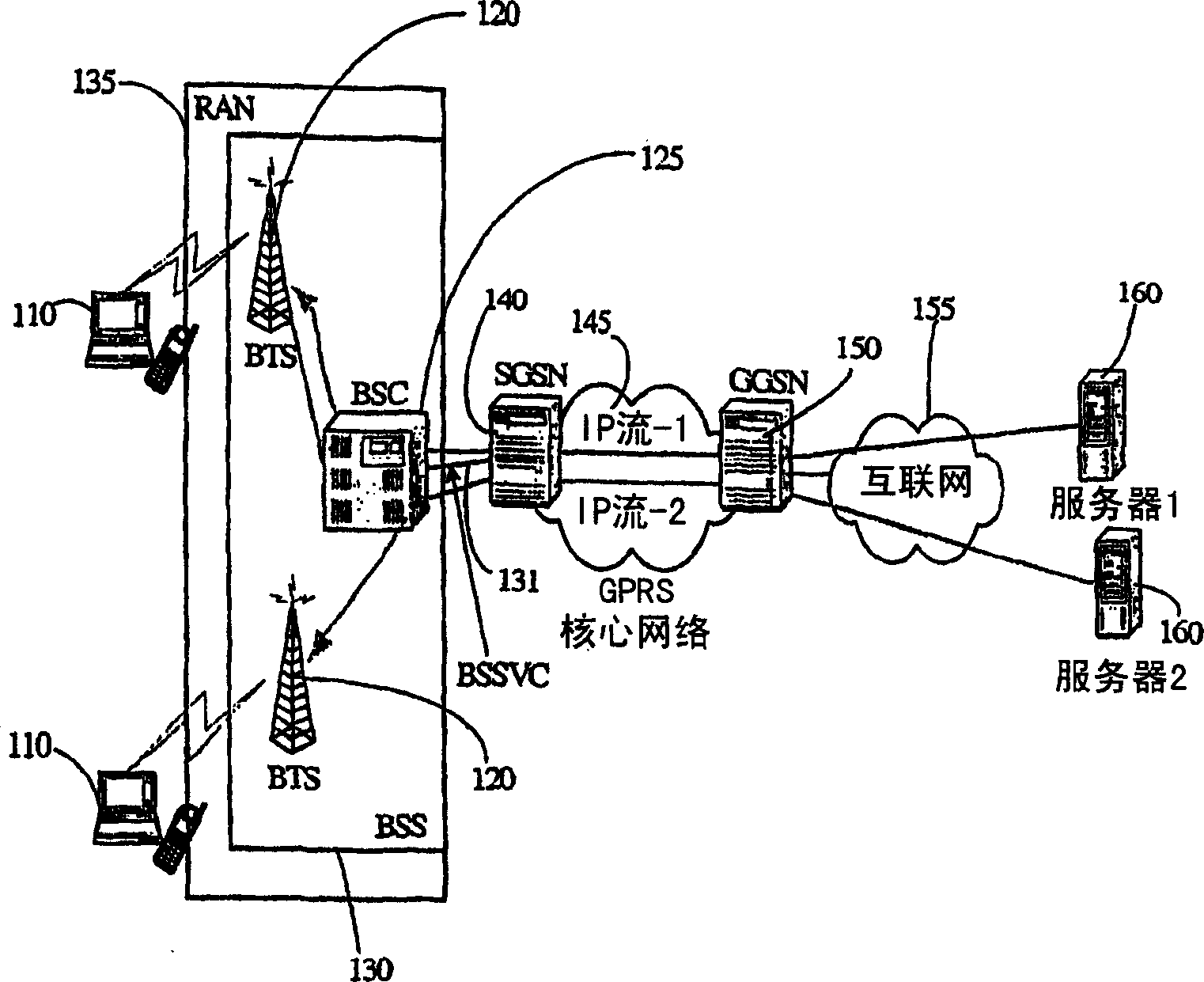
[0037] figure 1 A typical GPRS / UMTS mobile network is shown. Mobile station 110 communicates with the network by receiving and transmitting signals from / to base transceiver station (BTS) 120 . Each BTS 120 communicates with a Base Station Controller (BSC) 125 which controls one or more BTS devices. Multiple BTS devices and BSC devices are often collectively referred to as a base station system (BSS) 130 . In addition, a radio access network (RAN) 135 includes a BSS and transmits signals from / to the MS device 110 over the air.
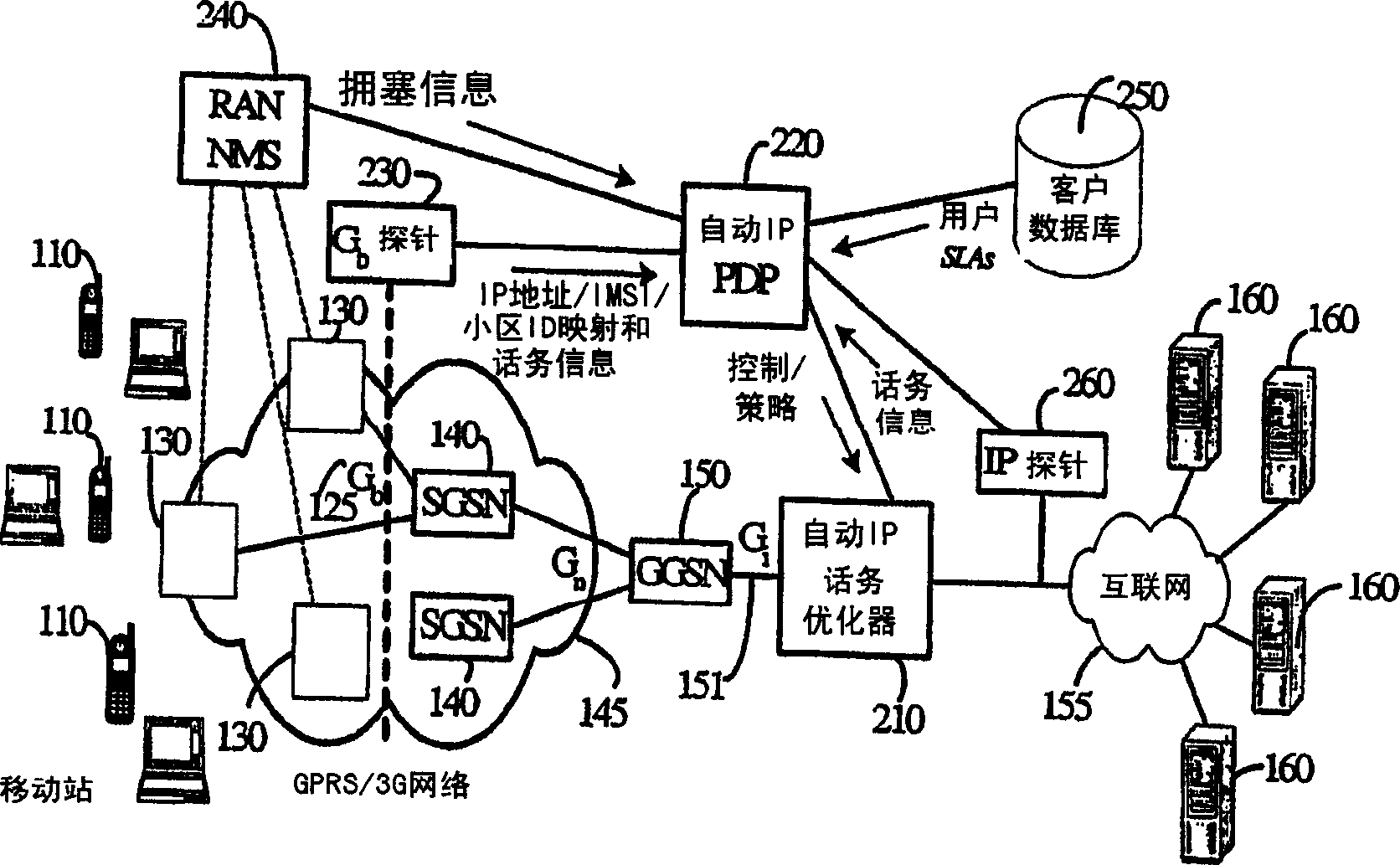
[0038] Through a BSS virtual circuit (BSSVC) 131 , the BSC 125 communicates with a Serving GPRS Support Node (SGSN) 140 that performs mobility and data session management for the mobile station 110 . SGSN 140 communicates with Gateway GPRS Support Node (GGSN) 150 through GPRS core network 145 . GGSN 150 acts as a gateway between GPRS core network 145 and external packet data networks, such as the Internet 155 . The GGSN 150 communicates with a plur...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com