Bonding wire and integrated circuit device using the same
A technology for bonding lead wires and coating layers, which is applied in the direction of circuits, electrical components, and electrical solid devices, and can solve problems such as poor drawability, difficult drawing of high melting point metals, and short mold life
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
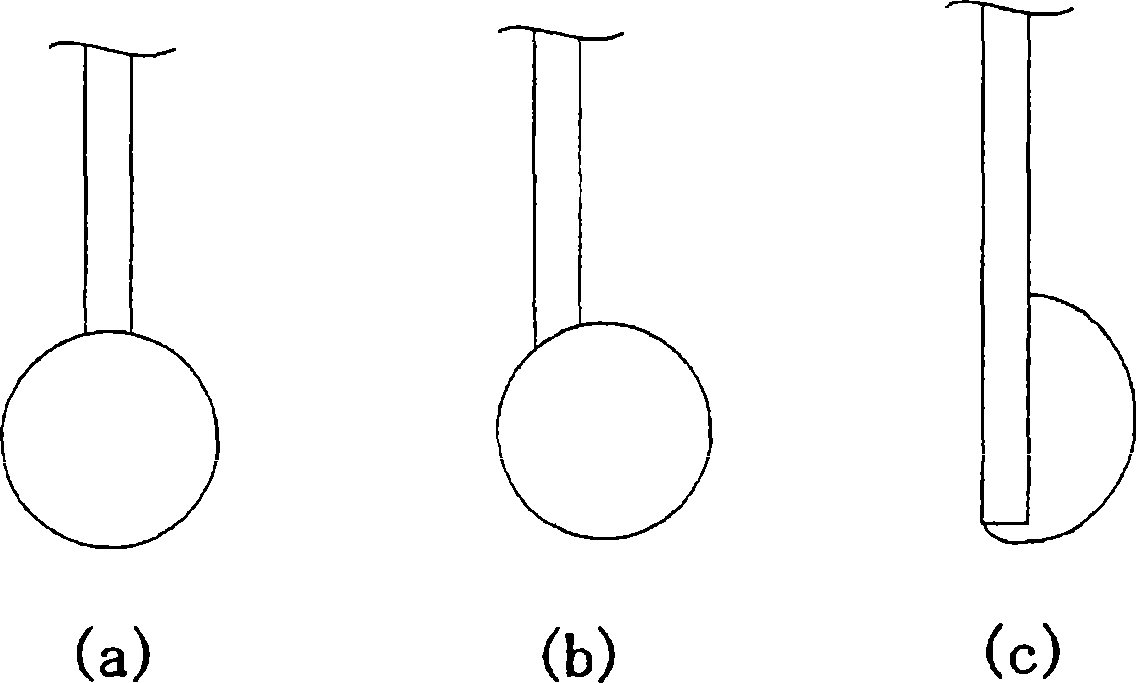
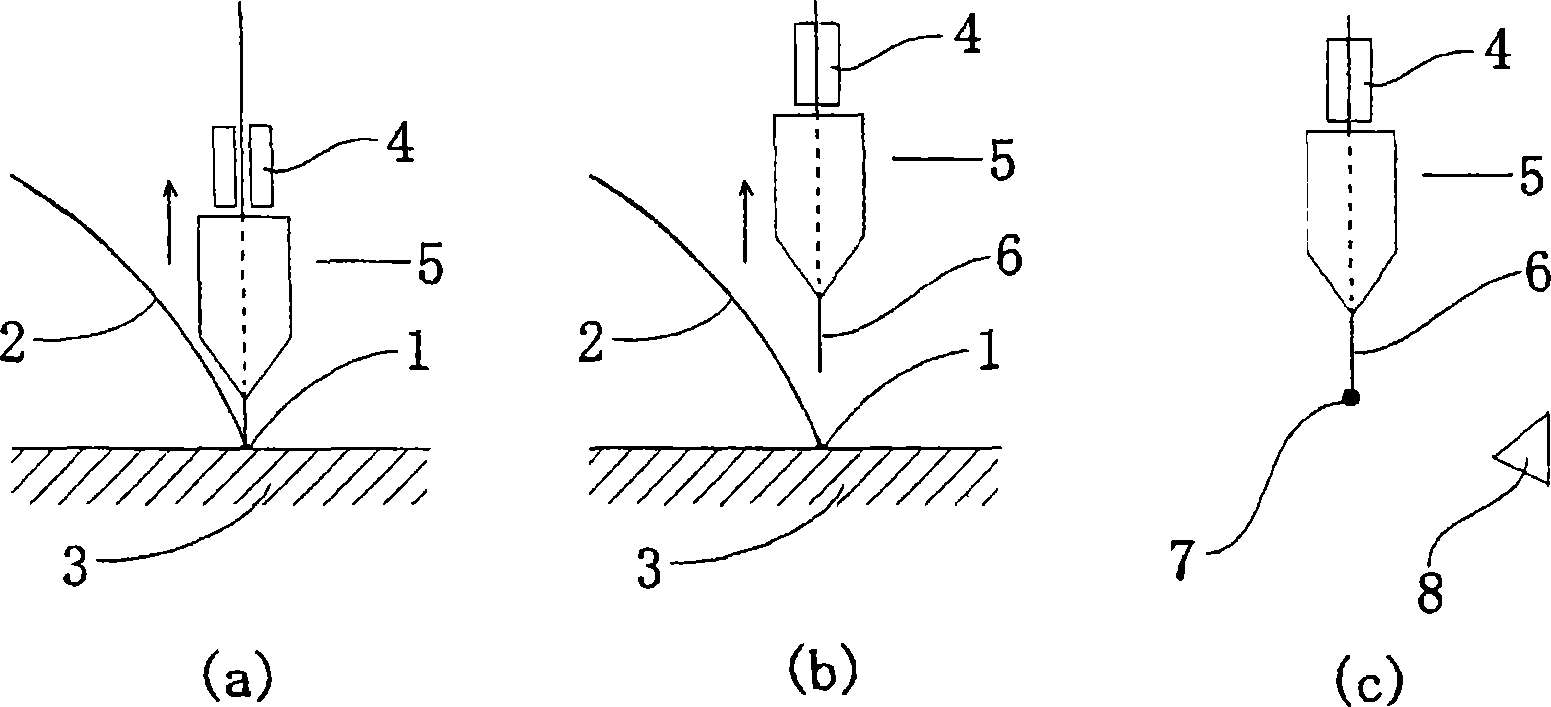
[0104] A 0.8 μm-thick coating layer was formed by electroplating on a core copper lead having a purity of 99.995% and a diameter of 200 μm. By drawing and annealing the wire, various types of bonding wires having a core diameter of 25.2 μm and a coating layer thickness of 0.1 μm were produced. Using various leads, 100 balls with a diameter of 60 μm were formed by using a bonding machine (model FB 137 manufactured by Kaijo Co., Ltd.), and the number of occurrences of shape defects in which the center of the ball was displaced from the center of the lead was checked. The results are shown in Table 1 together with the core and coating materials used.
[0105] The wet contact angle when the core material was melted was measured by using high temperature wettability test apparatus WET1200 manufactured by ULVAC-RIKO in the following manner.
[0106] A piece of material produced by compressing 2.5 mm sized balls of core material into an easily mountable shape was placed on a piece of ...
example 2
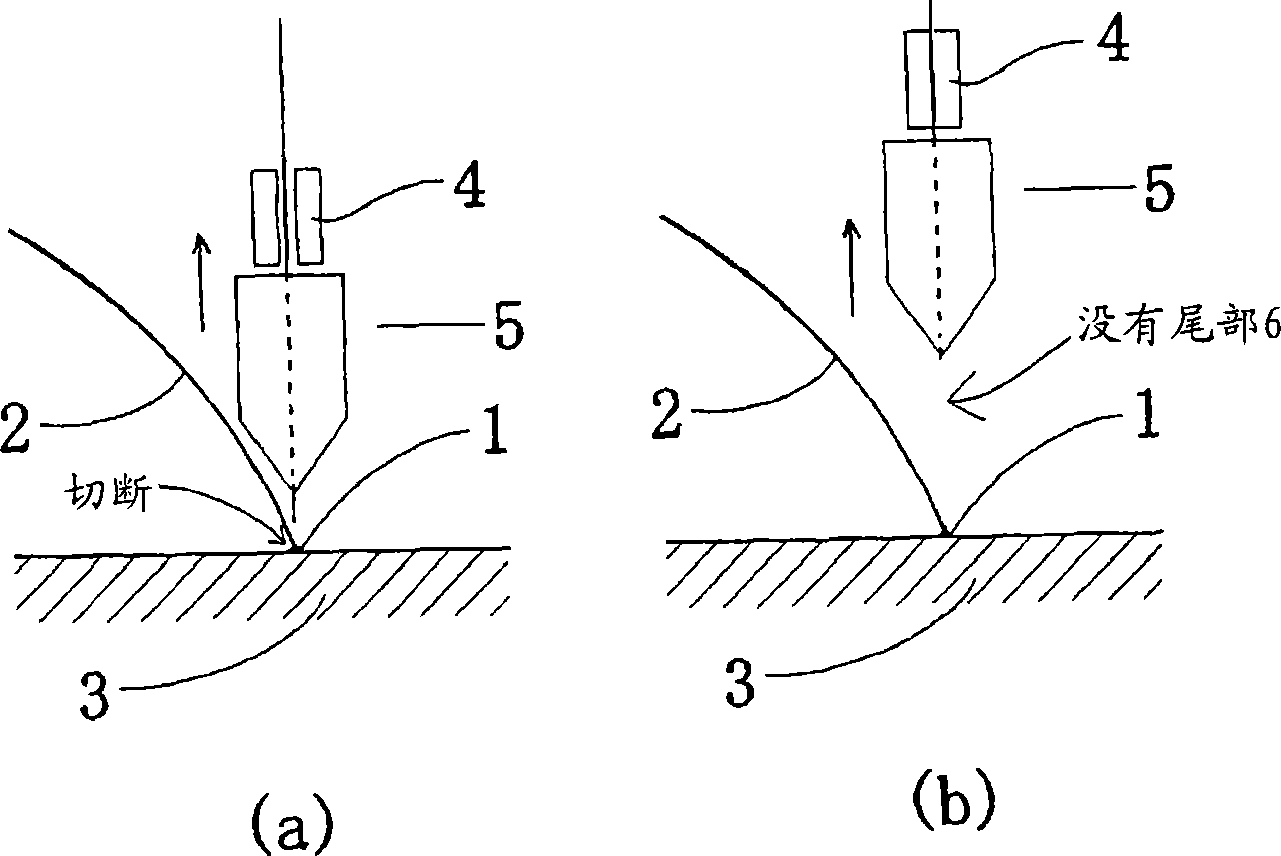
[0110] (1) An approximately 0.04 μm thick gold underplating film was formed by underplating on a copper lead having a purity of 99.995% and a diameter of 200 μm. After that, a 0.8 µm thick palladium plating film was formed. Copper bonding wires are produced by drawing and annealing the wires. Various bonding wires have a copper core diameter of 25.2 μm, a palladium layer (coating layer) thickness of 0.1 μm, and a gold layer (different metal layer) thickness of about 0.005 μm, the elongation is 15%. Samples with various radii of curvature were produced by adjusting the diameter of the guide roll and the tension used to wind the lead wire around the spool. Using various samples, a 208-pin QFP (copper lead frame, silver spot plating) with a loop length of about 4 mm was applied using a bonding machine (model EAGLE AB339 manufactured by ASM) by applying a load of 80 g and an ultrasonic energy of 160 Bonding is performed on the board and the defect rate is checked (ppm: the numbe...
example 3
[0115] A gold underplating film with a thickness of about 0.04 μm was formed by underplating on a copper lead having a purity of 99.995% and a diameter of 200 μm. After that, a 0.8 µm thick palladium plating film was formed. Copper bonding wires with various yield strength values were produced by drawing and annealing the wires. The copper core diameter of various bonding wires was 25.2 μm, the thickness of the palladium layer (coating layer) was 0.1 μm, and the gold layer (different metals) layer) has a thickness of about 0.005 μm. Various copper bonding leads have a radius of curvature of 40mm. Bonding was performed on a 208-pin QFP (copper leadframe, silver plating) with a loop length of approximately 4 mm using a bonding machine (model EAGLE AB339 manufactured by ASM) by applying a load of 80 g and varying ultrasonic energy and inspecting using various leads. The defect rate (ppm: the number of short-tail defects and no-stem defects occurring per million bonds) is belo...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com