Laminated microfluidic structures and method for making
A technology of microfluidic structure and microstructure, applied in the field of microfluidics, can solve problems such as inability to have high yield
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
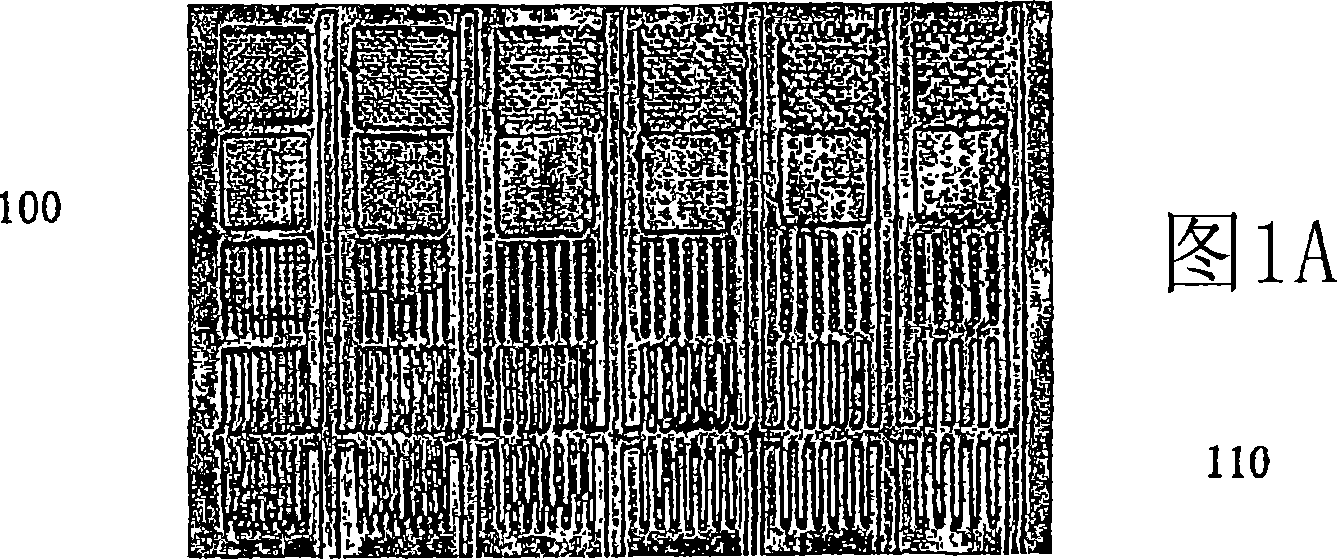
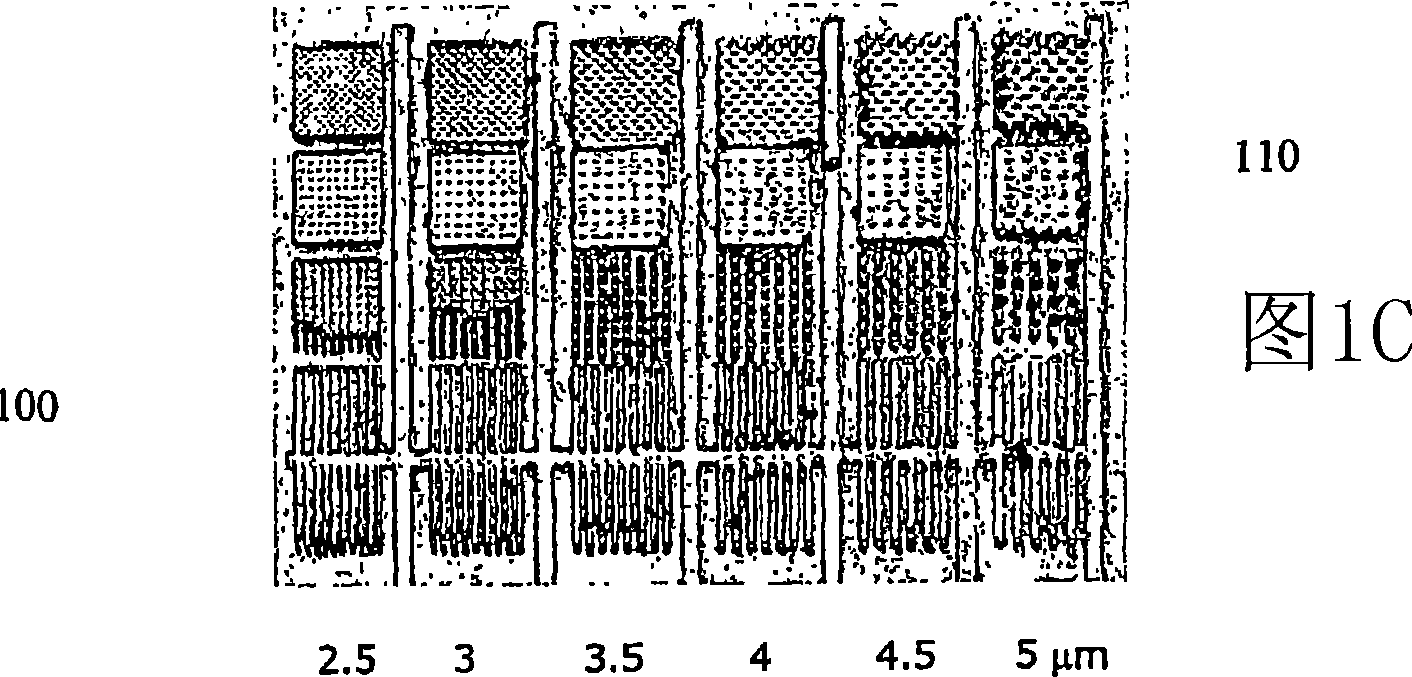
[0025] As used herein, the term "microstructure" generally refers to a structural feature on a microfluidic substrate element having a plurality of walls, the walls having at least one dimension ranging from about 0.1 microns to about 1000 microns. These features can be, but are not limited to, microchannels, microfluidic pathways, microreservoirs, microvalves, or microfilters. The term "polymeric" refers to a macromolecular structure or material having a molecular weight significantly higher than that of the constituent monomers and produced by polymerization. All materials generally and herein referred to as "plastic" materials are polymeric materials. The term "acrylic" means Acrylite 、Plexiglas , PMMA or other trade names for polymethyl methacrylate. "Two-dimensional microfluidic network" refers to the fluidic connectivity of at least two microfluidic pathways or channels co-existing within an element or in the plane of a planar element. "Three-dimensional microflu...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com