Parallel divided flow-type fluid supply apparatus, and fluid-switchable pressure-type flow control method and fluid-switchable pressure-type flow control system for the same fluid supply apparatus
a flow-type fluid supply and flow-type technology, applied in fluid pressure control, process and machine control, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of small transient effect on upstream pressure po, unpredictable problems, and semiconductor semiconductor defects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 2
Pressure Type Flow Controller
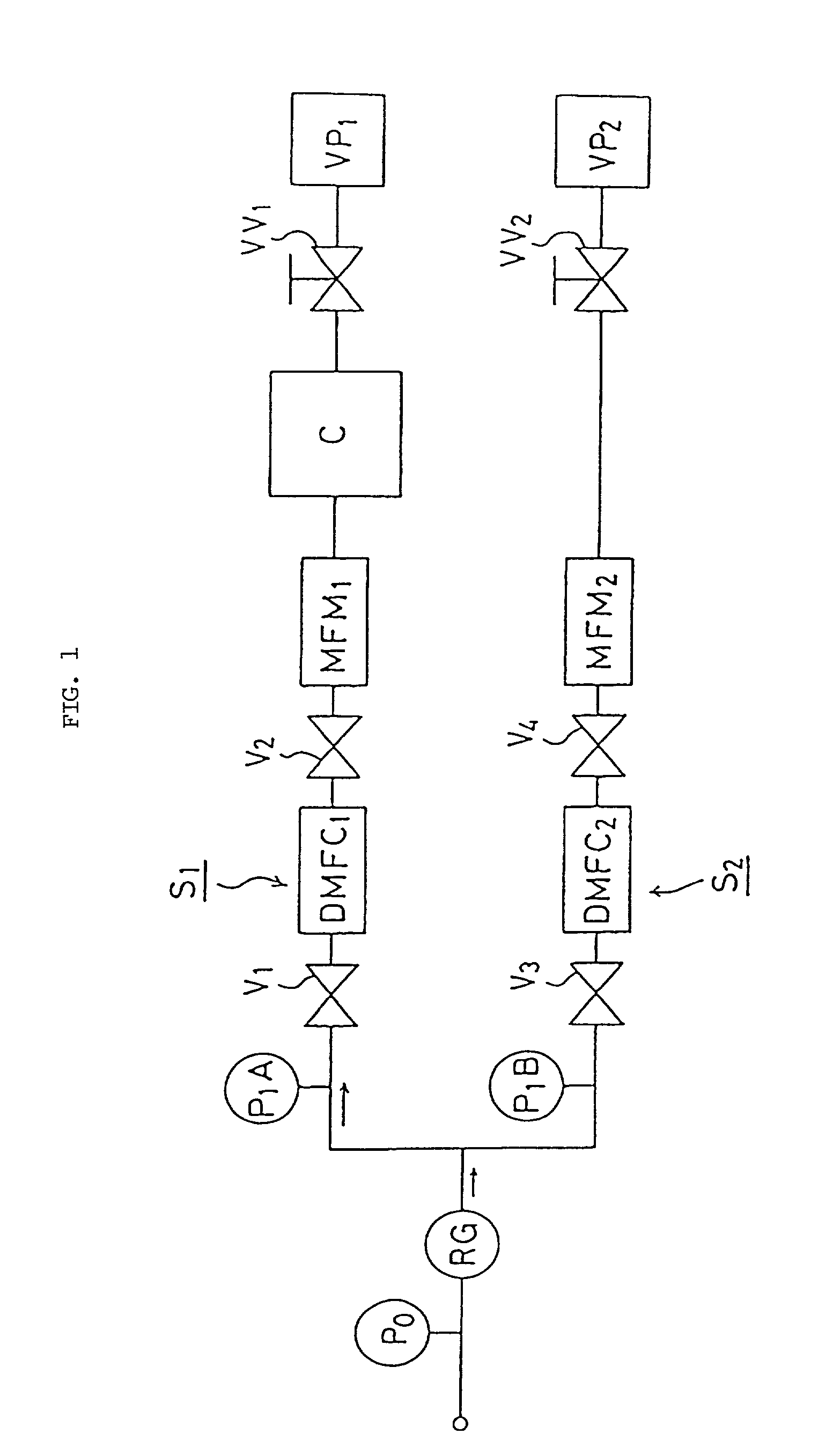
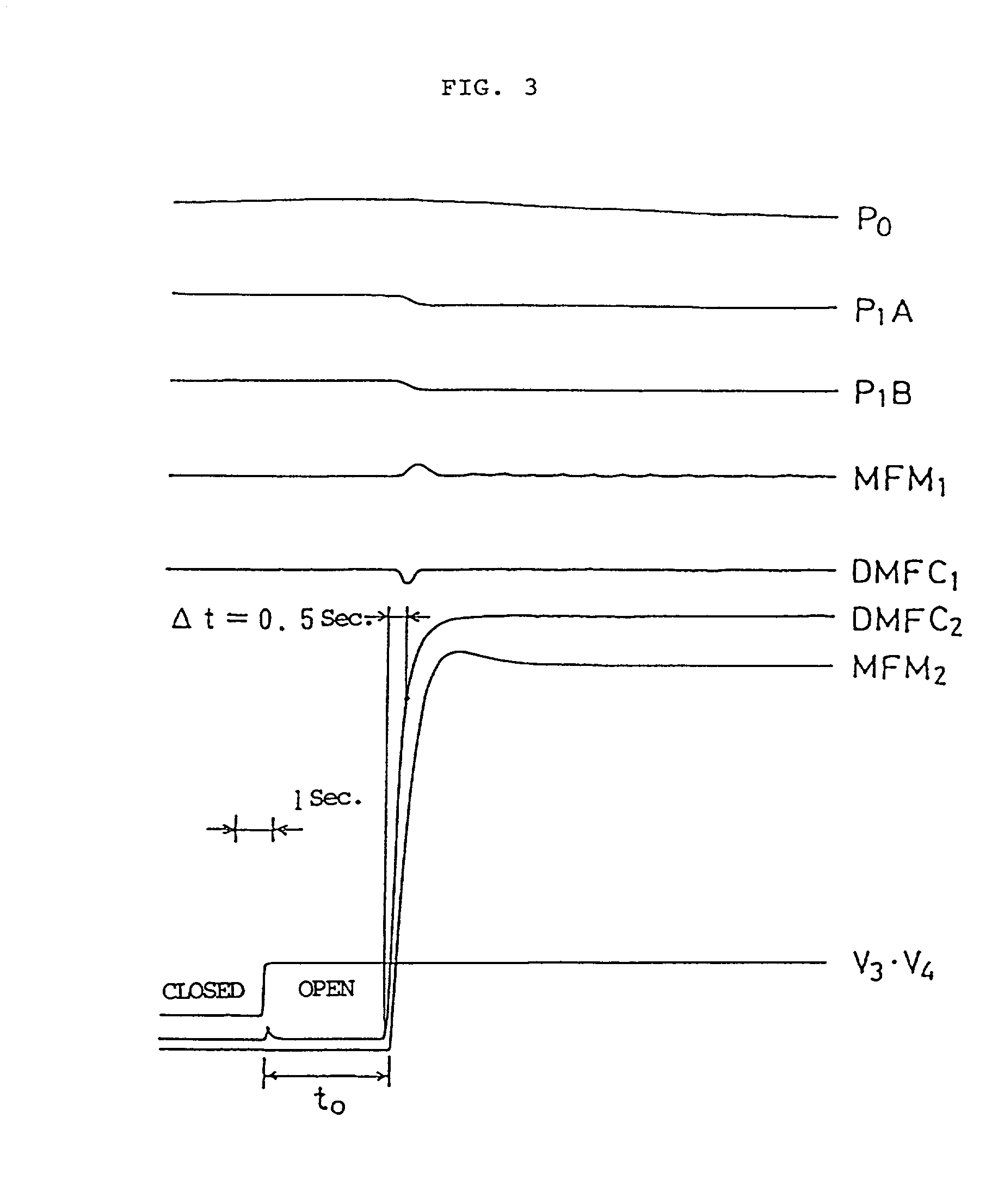
[0120] FIG. 7 is a schematic diagram of an embodiment of the parallel divided flow type fluid supply apparatus according to a further embodiment of the present invention in which pressure-type flow control systems are used. FIG. 7 is identical with FIG. 1 in arrangement except that pressure-type flow control systems FCS.sub.1, FCS.sub.2 are used in place of time delay type mass flow controllers DMFC.sub.1, DMFC.sub.2. No description of like components will be repeated.
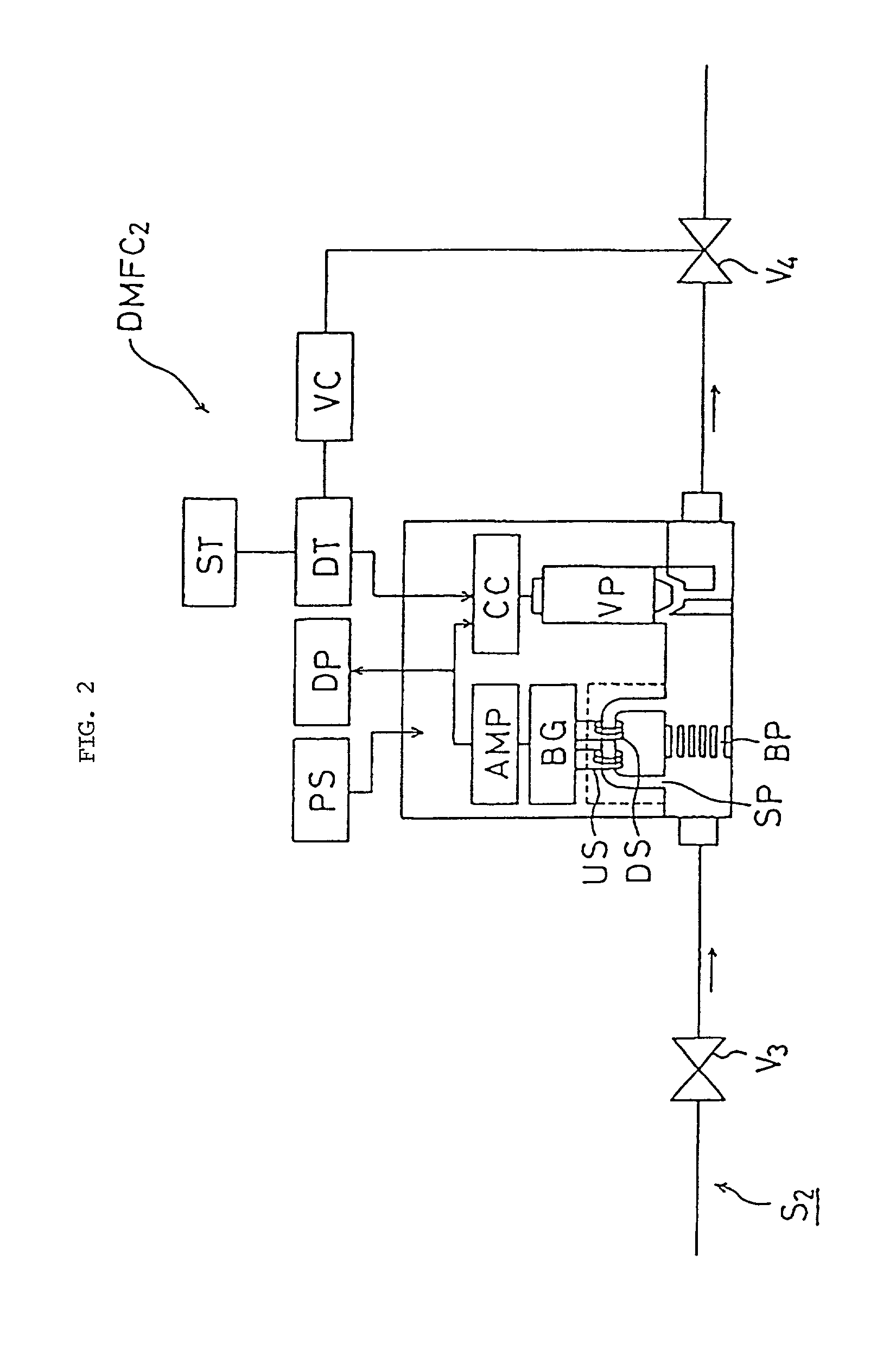
[0121] FIG. 8 is a schematic diagram of the pressure-type flow control system FCS.sub.1 in flow passage S.sub.1. The same is provided in flow passage S.sub.2. Referring to FIG. 8, OR indicates orifice; P.sub.1, pressure gauge on the upstream side of the orifice; AP.sub.1, amplifier; A / D, A-D converter; M, temperature compensator; SS, flow rate setter; CC, comparison circuit; AP.sub.2, amplifier; DV, drive; and CV, control valve. It is also understood that SS, CC, M and AP.sub.2 as a whole a...
example 3
Application Example of Fluid Switchable Pressure-type Flow Control System
[0130] FIG. 10 shows an application example of the fluid switchable pressure-type flow control system according to a still further embodiment of the present invention. This corresponds to the prior art using mass flow controllers shown in FIG. 18. The fluid s witchable pressure-type flow control system is indicated by FCS.sub.2a. That is, the flow rates of three kinds of gases--H.sub.2 gas, O.sub.2 gas and N.sub.2 gas--are controlled by two pressure-type flow control systems FCS.sub.1 and FCS.sub.2a.
[0131] In FIG. 10, two pressure-type flow control systems FCS.sub.1 and FCS.sub.2a are required to supply H.sub.2 and O.sub.2 simultaneously to the reactor RR. But O.sub.2 and N.sub.2 do not have to be fed to the reactor RR at the same time, and the fluid switchable pressure-type flow control system FCS.sub.2a can be used for control of the flow rates of both O.sub.2 and N.sub.2.
[0132] To generate moisture, the firs...
example 4
Another Application Example of Fluid Switchable Pressure-type Flow Control System
[0135] FIG. 11 shows another application example of the fluid switchable pressure-type flow control system FCS.sub.2a--an example where the fluid switchable pressure-type flow control system FCS.sub.2a is applied to the so-called single chamber multiple process in semiconductor manufacturing facilities.
[0136] If Si is going to be nitrided immediately after oxidation in FIG. 11, for example, the system is first purged with N.sub.2 gas and then H.sub.2 gas and O.sub.2 gas are supplied to the reactor RR to oxidize Si. Then, N.sub.2O gas is supplied to nitride the Si oxide film. Finally, N.sub.2 gas is supplied to purge the system.
[0137] That is why the application example of the flow control system in FIG. 11 uses one pressure-type flow control system FCS.sub.1 and one fluid switchable pressure-type flow control system FCS.sub.2a--a total of two units. But if this fluid supply apparatus is formed of the pr...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com