Component source interchange gantry
a technology of component source and gantry, which is applied in the direction of article separation, packaging, thin material processing, etc., can solve the problems of additional operation cost and not only labor
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0022] For a general understanding of the present invention, reference is made to the drawings. In the drawings, like reference numerals have been used throughout to designate identical elements.
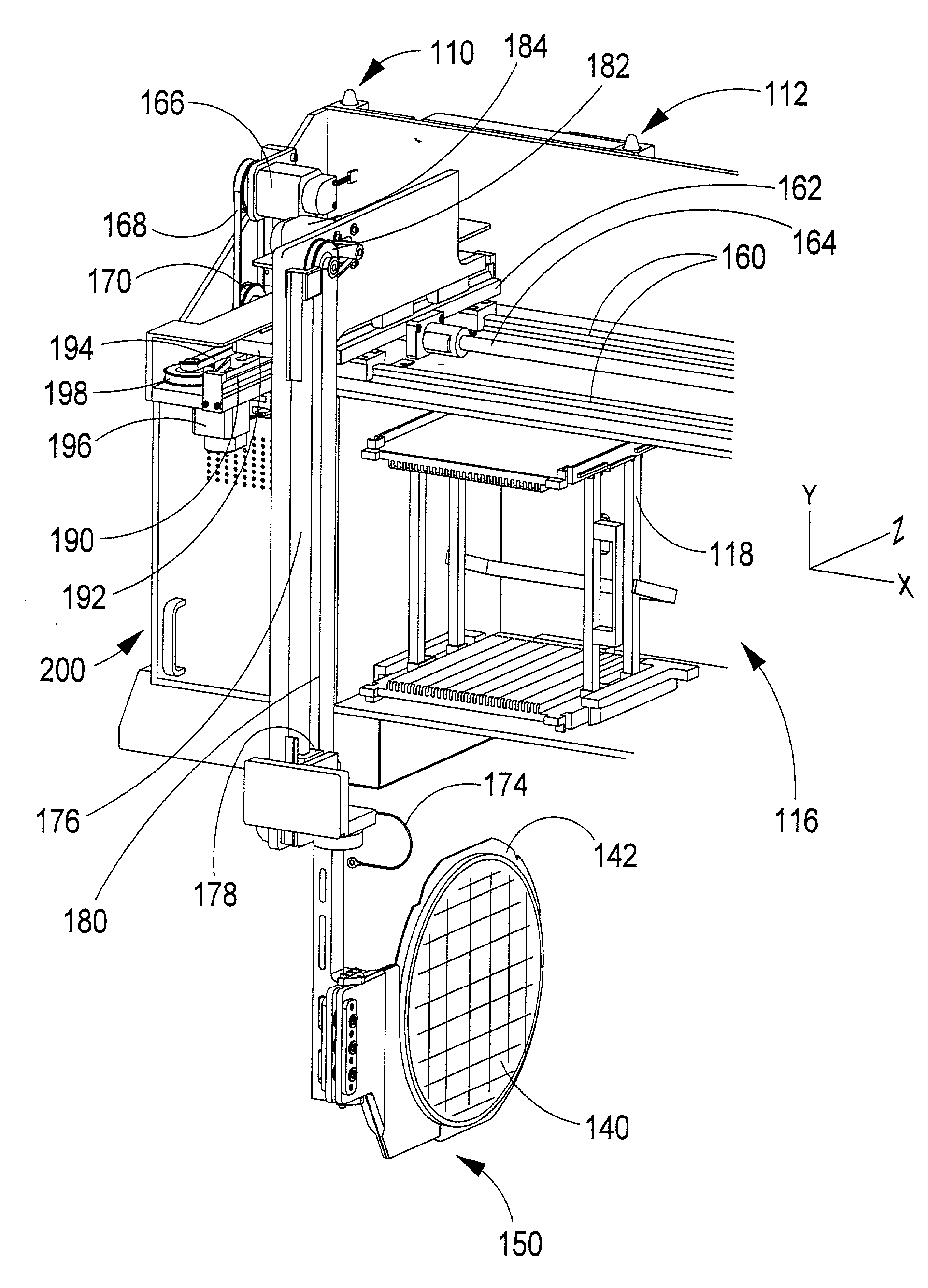
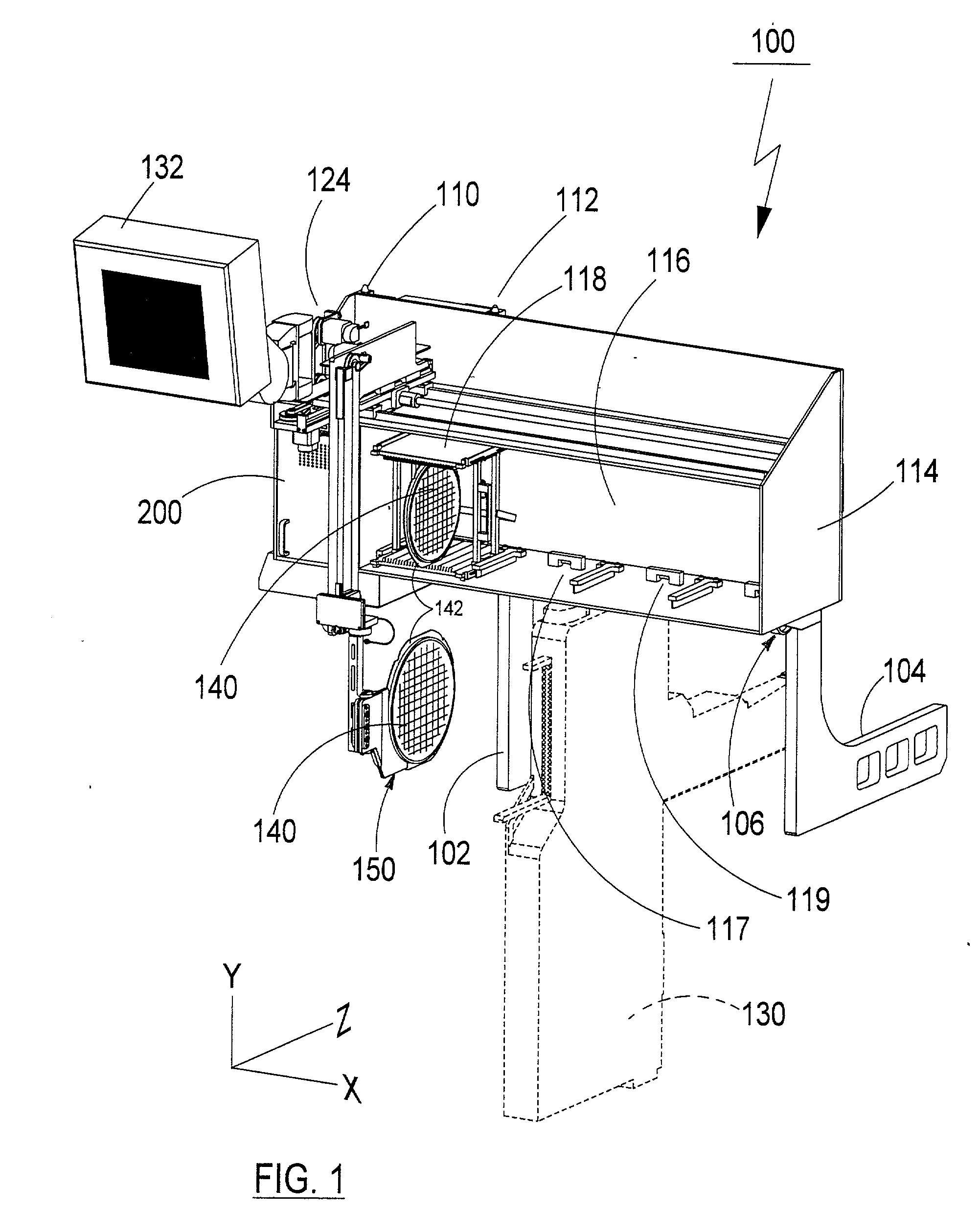
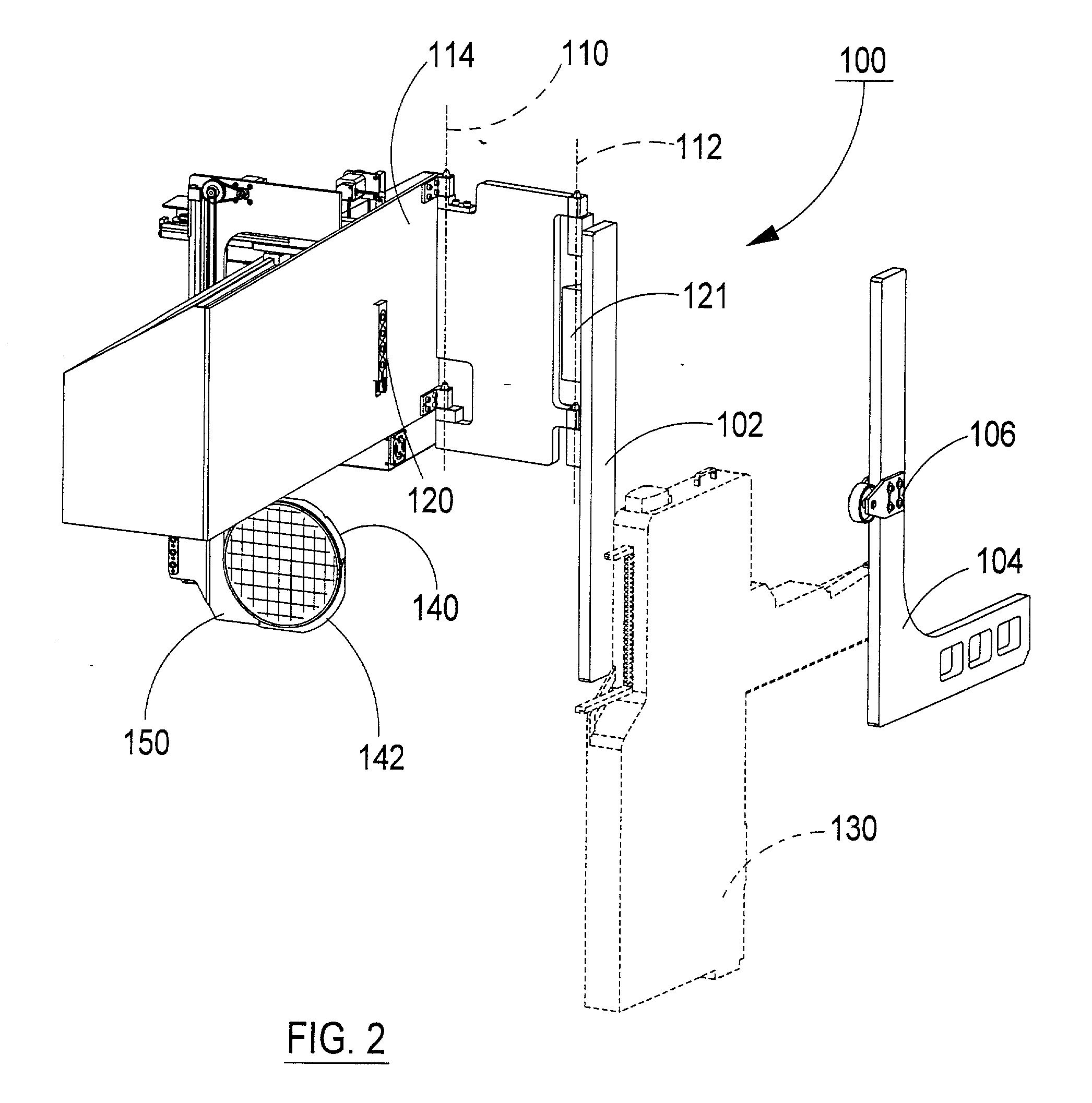
[0023] FIG. 1 depicts a perspective view of an embodiment of the component source interchange gantry 100 in an operating position as it may be configured for use as a supply of wafers for a direct die feeder. FIG. 2 depicts the same component source interchange gantry in an "open" position where it would allow access to an associated component feeder 130. Referring to FIGS. 1 and 2, frame support members 102 and 104 are intended to be integrally affixed to the frame or structure of a component pick-and-place assembly system (not shown). Frame member 102 preferably includes pivot axis 1 10 and 112 about which the storage bay and gantry frame 114 is hingedly affixed to the member 102. In one embodiment, the pivots provide a means for moving said gripper and gantry assembly away from the compon...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com