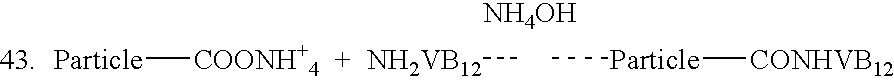Novel vitamin b12 - biodegradable micro particulate conjugate carrier systems for peroral delivery of drugs, therapeutic peptides/proteins and vaccines
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
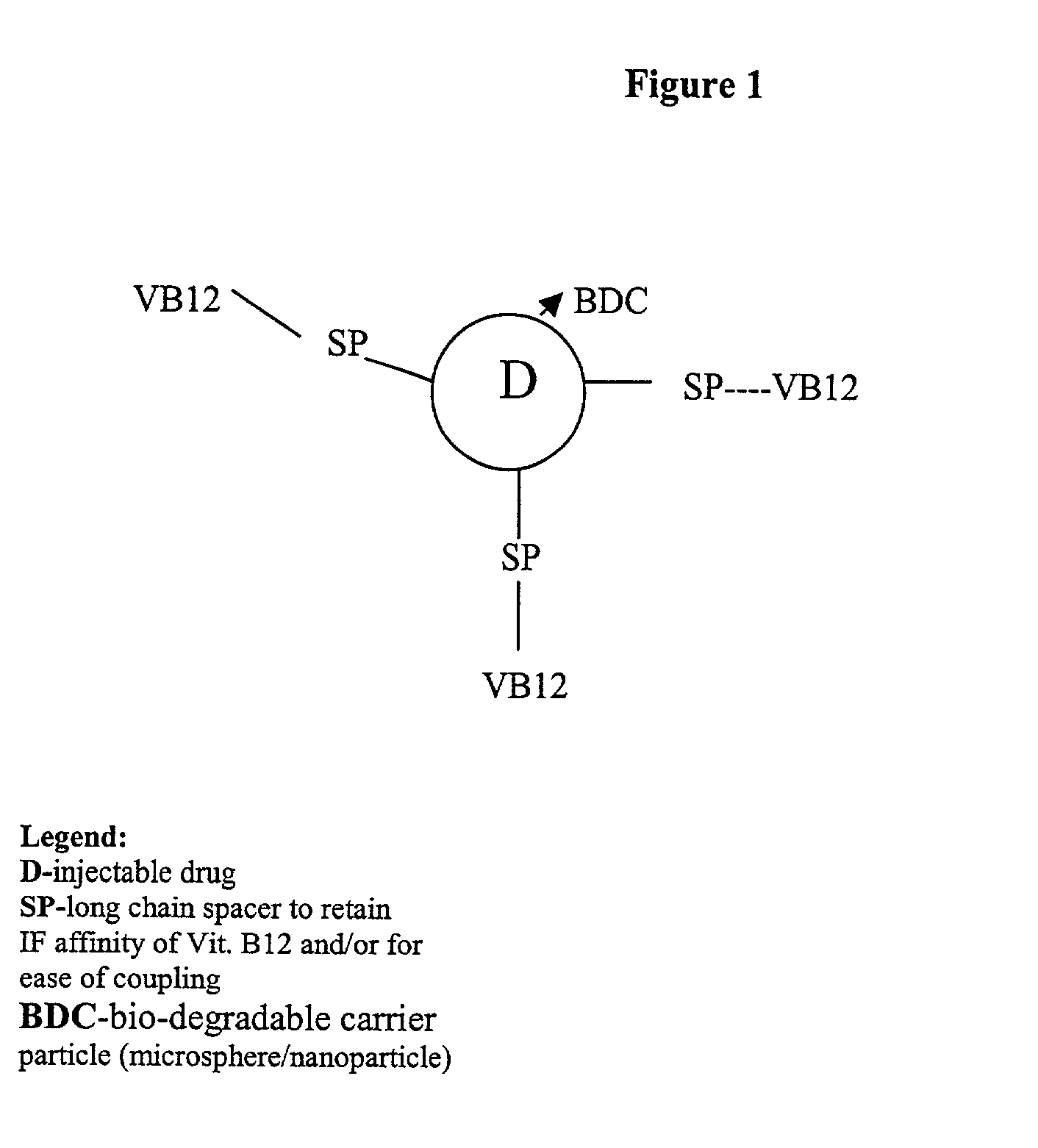
[0025] The conjugation of various peptides and proteins to the Vitamin B.sub.12 molecule has been shown to facilitate the in-vitro and in-vivo transport of these moieties across the epithelial cells of the intestine. However, pharmaceutically relevant oral delivery of many vitamin B12-pharmaceutical conjugates does not occur with many of these bioactives due to the limited uptake capacity of the VB.sub.12 transport system, loss of bioactivity of native protein during conjugation to VB.sub.12, loss of intrinsic factor (IF) affinity of the conjugates and finally due to the liability of the bioactives to GI degradation. In order to overcome these shortcomings we have endeavoured to develop vitamin B.sub.12-particulate (both microspheres and nanospheres) systems that could be taken up by the natural uptake mechanism for VB.sub.12. Different biodegradable particulate systems (microspheres and nanospheres) were prepared. These particles were surface modified with vitamin B.sub.12 and thes...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com