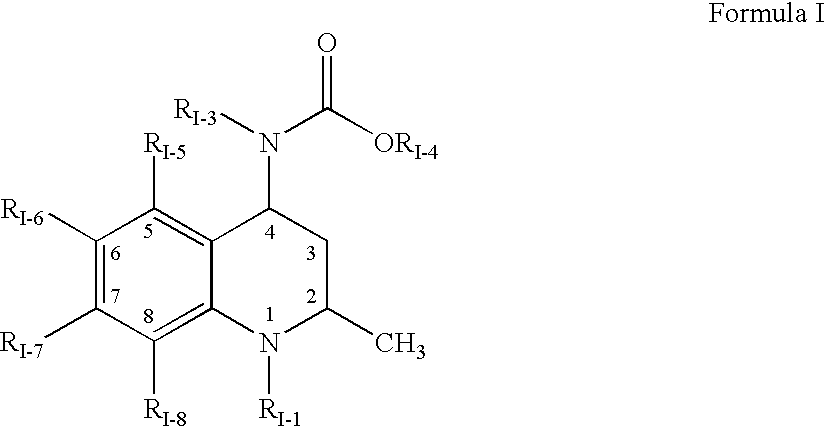
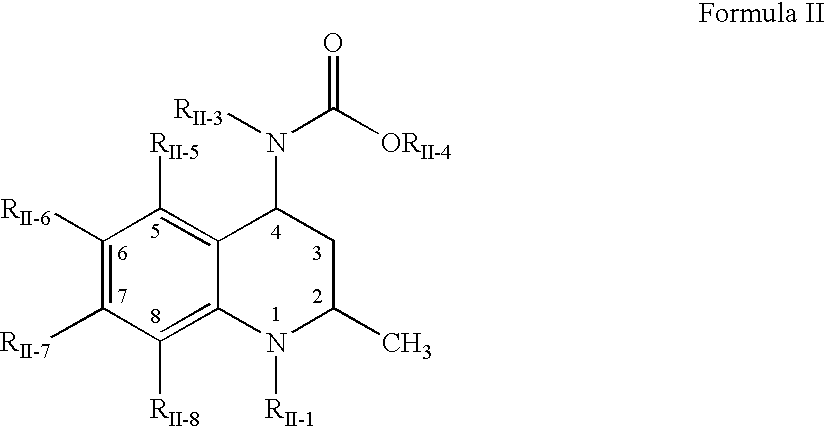
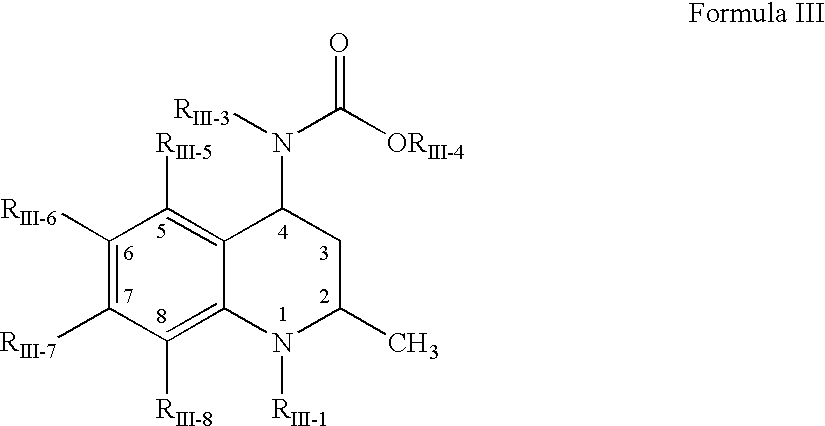
Pharmaceutical compositions of drugs and neutralized acidic polymers
a technology of neutralized acid and pharmaceutical compositions, applied in the field of pharmaceutical compositions of drugs and neutralized acidic polymers, can solve the problems of drug and/or dispersion not being physically stable, drug and/or dispersion may not be chemically stable within some dispersion polymers, and continue to present challenges in the distribution of low-solubility drugs in polymers, etc., to achieve superior concentration enhancement and improve the chemical stability of acid-sensitive drugs
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
examples 1-3
[1311] These examples disclose dispersions of a drug and a neutralized acidic polymer. For Examples 1-3, a dispersion of the acid-sensitive drug quinoxaline-2-carboxylic acid [4(R)-carbamoyl-1(S)-3-fluorobenzyl)-2(S), 7-dihydroxy-7-methyl-octyl] amide (Drug 1) and the neutralized acidic enteric polymer hydroxypropyl methyl cellulose acetate succinate (HPMCAS) was made by first preparing a solution containing drug, polymer and a base. For Example 1, the solution consisted of 1.25 wt % Drug 1, 0.513 wt % sodium acetate, and 3.75 wt % HPMCAS-HF (HF grade of HPMCAS from Shin Etsu, Tokyo, Japan) in methanol / water (9 / 1). For Example 2, the solution consisted of 1.25 wt % Drug 1, 0.32 wt % sodium bicarbonate, and 3.75 wt % HPMCAS-HF in methanol / water (9 / 1). For Example 3, the solution consisted of 1.25 wt % Drug 1, 1.42 wt % sodium borate, and 3.75 wt % HPMCAS-HF in methanol / water (9 / 1). For control Cl, the solution consisted of 1.25 wt % Drug 1 and 3.75 wt % HPMCAS-HF, with no added base....
example 4
[1313] Stability of the acid-sensitive drug in the dispersions of Examples 1-3 was determined by measuring the drug purity before and after storage for Examples 1-3 and control C1. Dispersions were stored under elevated temperature and humidity conditions to increase the rate of chemical and physical changes occurring in the materials in order to simulate a longer storage interval in a typical storage environment. Drug purity was determined using HPLC. A Kromasil C.sub.4 HPLC column was used with a mobile phase of 45 vol % of 0.2 vol % H.sub.3PO.sub.4, and 55 vol % acetonitrile. UV detection was measured at 245 nm. Drug 1 potency was the percent of the total HPLC peak area corresponding to the amount of drug originally present in the dispersion prior to storage. Results of potency analysis of dispersions of Drug 1 and neutralized HPMCAS after storage for five days at 40.degree. C. / 75% RH are shown in Table 2.
2TABLE 2 Aqueous- Drug 1 Potency Degree of Soluble Conc. In the Day 5 at De...
examples 5-6
[1315] These examples disclose dispersions of Drug 1 and an acidic polymer with different degrees of neutralization. Amorphous solid dispersions of Drug 1 and HPMCAS were made by first mixing Drug 1 in a solvent together with HPMCAS-MF and sodium hydroxide to form a solution. For Example 5, the solution comprised 0.29 wt % Drug 1, 0.89 wt % HPMCAS-MF, 0.038 wt % NaOH, and 98.782 wt % water / acetonitrile (9 / 1). (MF grade of HPMCAS available from Shin Etsu, Tokyo, Japan) The percentage of acidic groups on the polymer that were neutralized was approximately 99%. For Example 6, the solution comprised 0.31 wt % Drug 1, 0.94 wt % HPMCAS-MF, 0.019 wt % NaOH, and 98.731 wt % water / acetonitrile (9 / 1). The percent age of acidic groups on the polymer that were neutralized was approximately 50%. For Control C2, the solution comprised 0.33 wt % Drug 1 and 1.00 wt % HPMCAS-MF in 98.67 wt % water / acetonitrile (9 / 1). The solutions of Examples 5 and 6, and Control C2, were lyophilized to remove the s...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| glass transition temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| wt % | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| solubility | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com