Titanium alloy having high ductility, fatigue strength and rigidity and method of manufacturing same
a technology of titanium alloy and ductility, which is applied in the field of titanium alloys having high ductility, fatigue strength and rigidity and manufacturing methods, can solve the problems of not developing high hot workability and ductility, no improvement has been succeeded in achieving high ductility and ductility, and the effect of reducing fatigue strength and ductility
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0053] A titanium alloy having the composition shown in Table 1 was arc-melted in a vacuum melting furnace to form an ingot having a 140 mm diameter. The .beta. transus temperature of the titanium alloy used in the test was 1070.degree. C.
1TABLE 1 Composition of elements (mass %) Al V Mo B O H Ti 7.72 0.41 0.50 0.90 0.094 0.014 Bal.
[0054] By applying twice the hot forging and the solution treatment to the alloy ingot obtained under the following conditions, test pieces were produced:
[0055] 1. Rough-Forging
[0056] Size after forging: outside diameter 80 mm (working rate 68%, forging rate 3)
[0057] Heating temperature: 1170.degree. C. (the .beta. transus temperature+100.degree. C.)
[0058] 2. Finish Forging
[0059] Size after forging: outside diameter 25 mm (working rate 90%, forging rate 10)
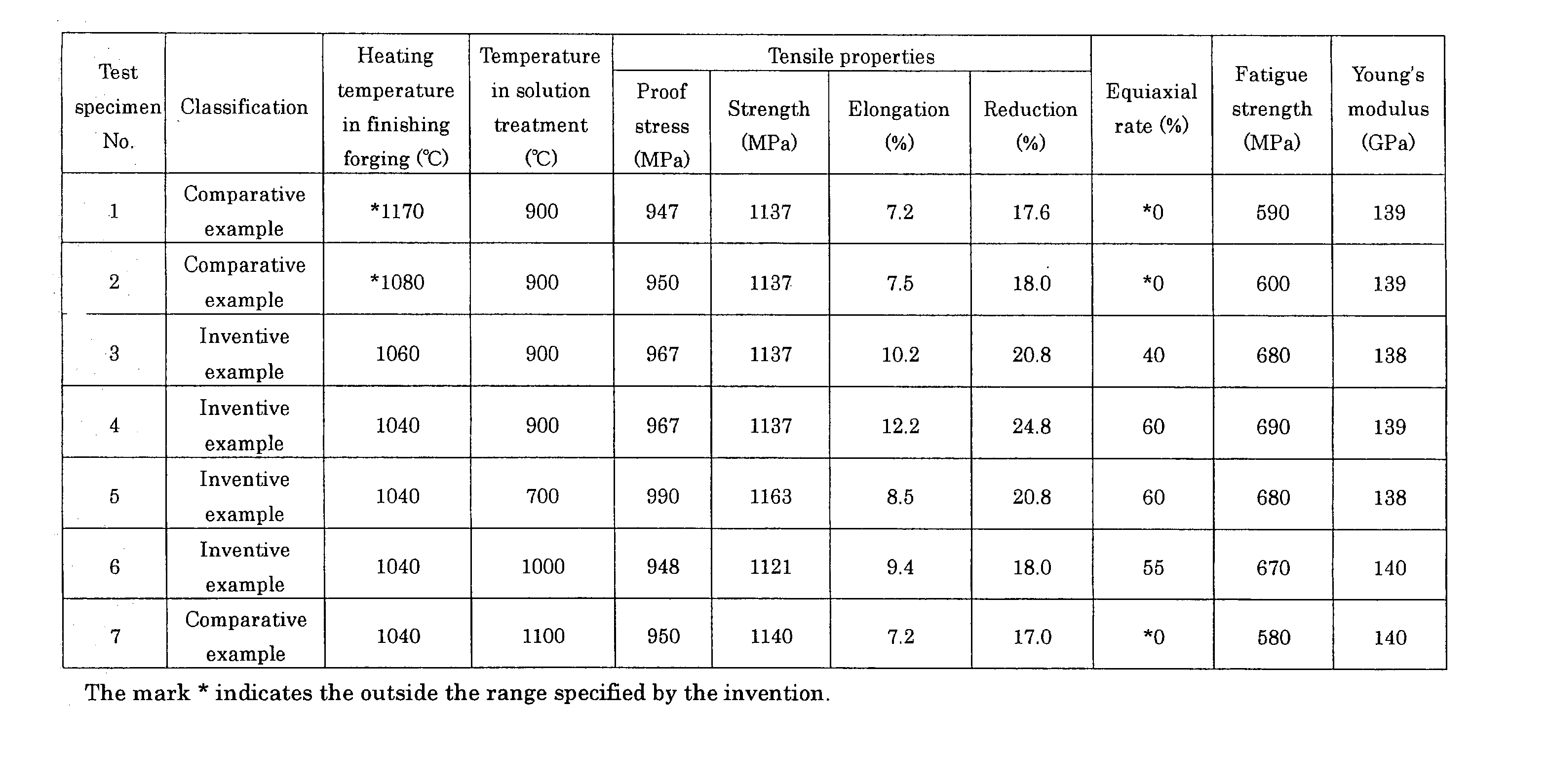
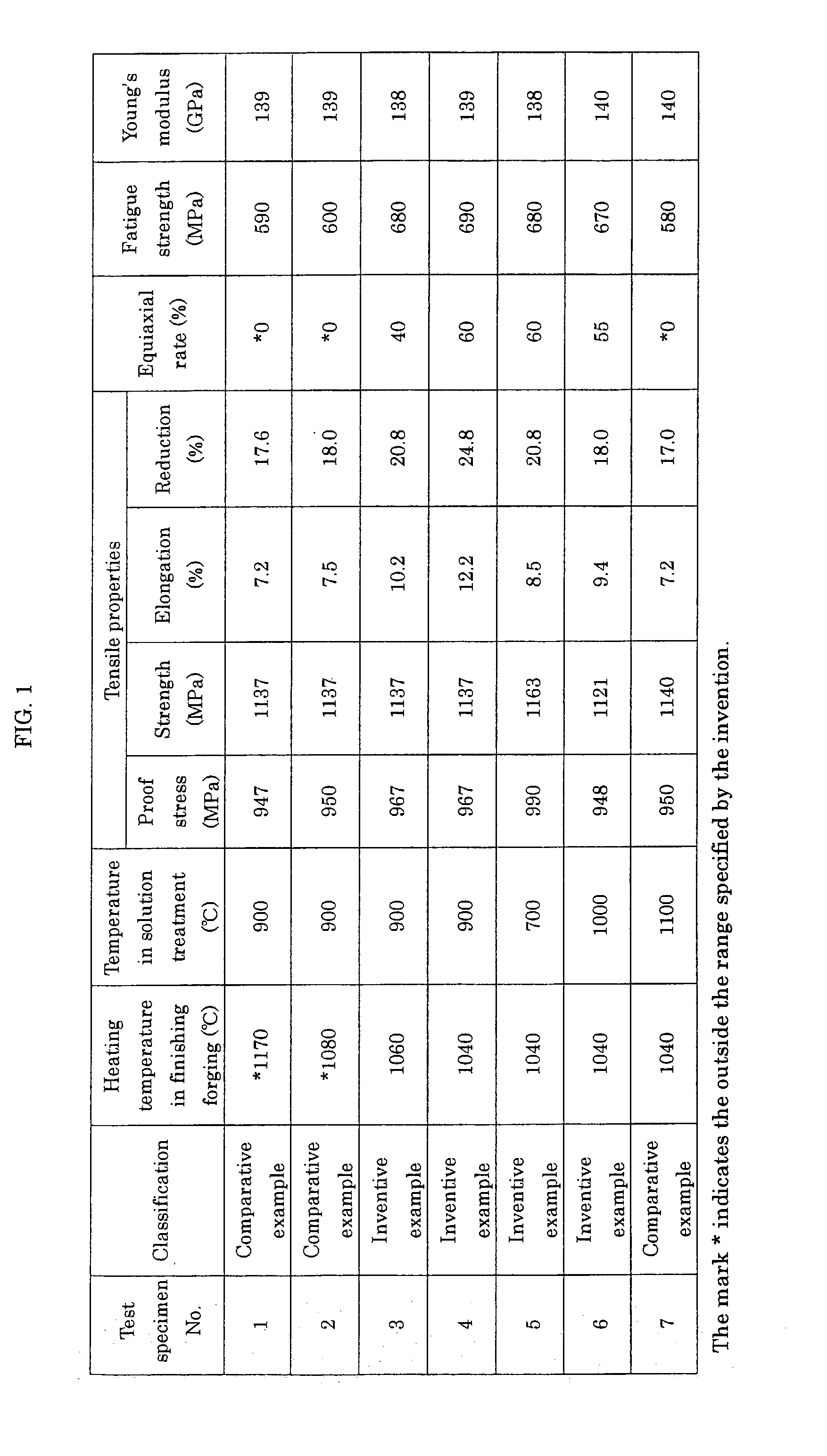
[0060] Heating temperature: 1040.degree. C. to 1170.degree. C. (the respective heating temperatures being indicated in FIG. 1)
[0061] 3. Solution Treatment
[0062] Heating temperature: 700.degree. C. to 11...
example 2
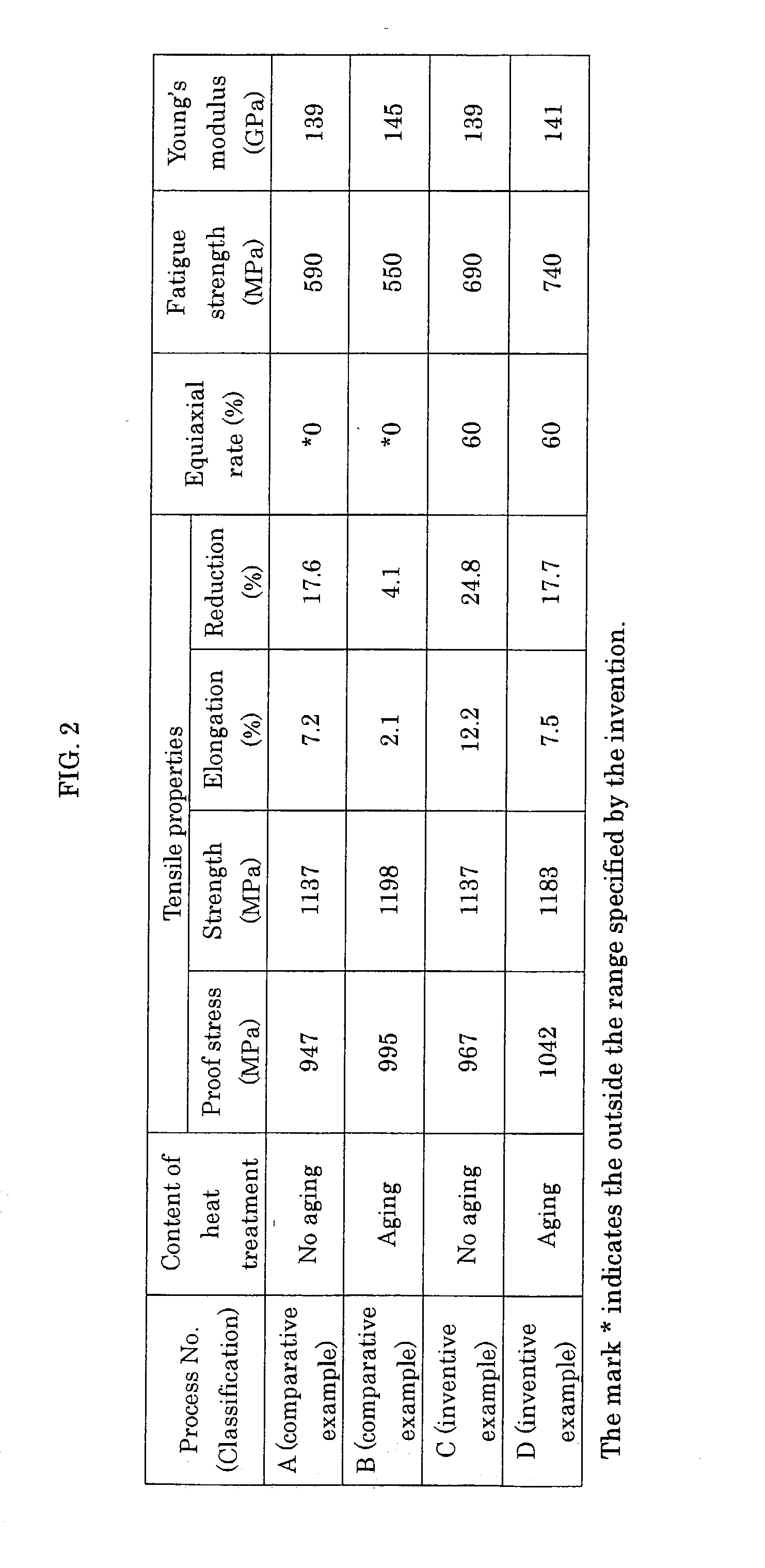
[0067] Utilizing the alloy ingot obtained in Example 1, the effect of the aging treatment after the solution treatment was studied by varying the conditions of hot forging. The titanium alloys used to test were treated according to the following processes A to D.
[0068] 1. Process A (Comparative Example)
[0069] 1-1. Finishing Forging
[0070] Size after forging: outside diameter 25 mm (working rate 97%, forging rate 30)
[0071] Heating temperature: 1170.degree. C. (the .beta. transus temperature+100.degree. C.)
[0072] 1-2. Solution Treatment
[0073] Condition of treatment: 900.degree. C..times.2 hours
[0074] 2. Process B (Comparative Example)
[0075] 2-1. Finishing Forging
[0076] Size after forging: outside diameter 25 mm (working rate 97%, forging rate 30)
[0077] Heating temperature: 1170.degree. C. (the .beta. transus temperature+100.degree. C.)
[0078] 2-2. Solution Treatment
[0079] Treatment condition: 900.degree. C..times.2 hours
[0080] 2-3. Aging Treatment
[0081] Treatment condition: 580.degree. ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com