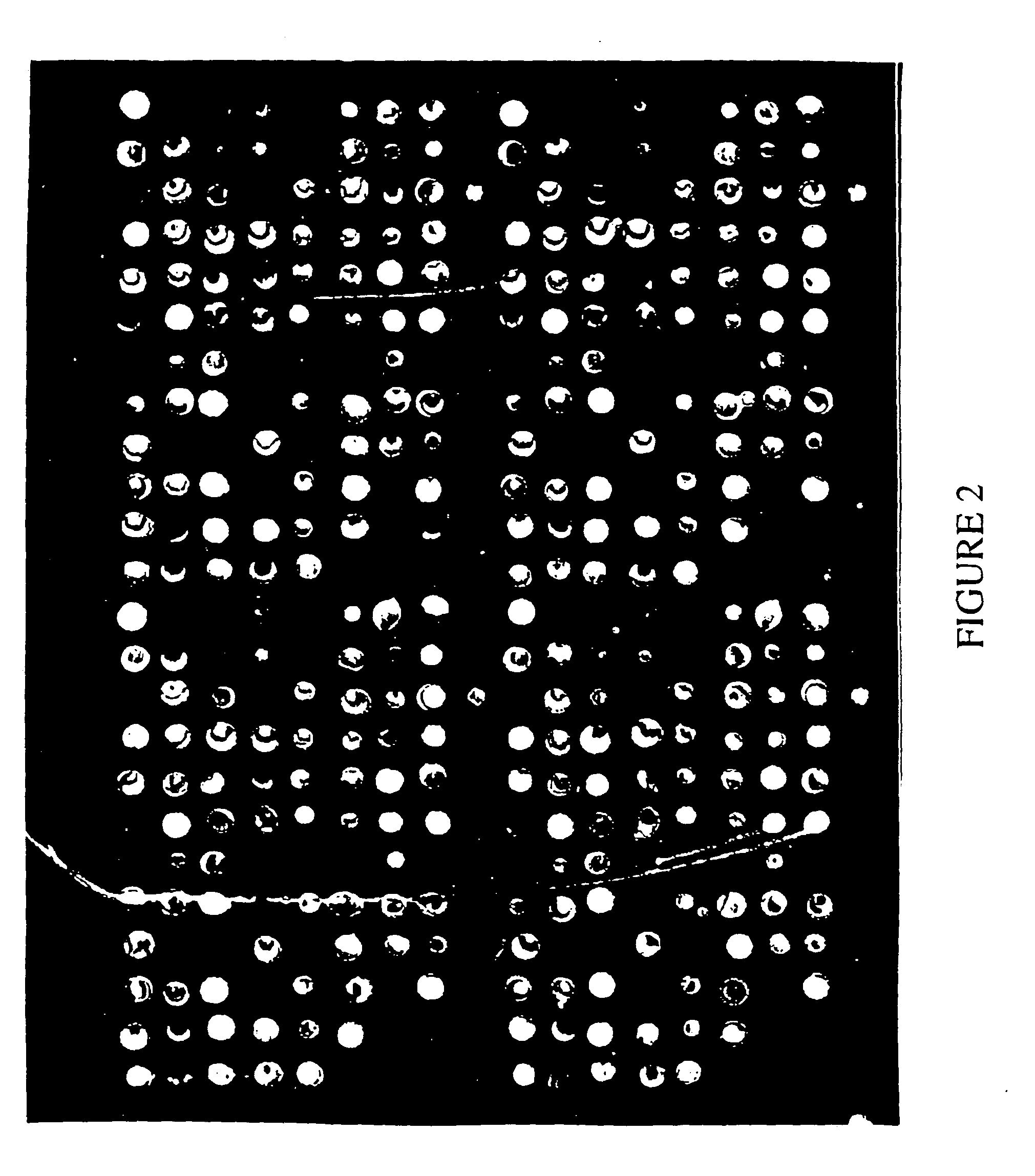
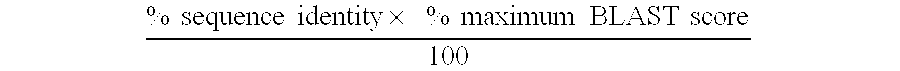Composition for the detection of blood cell and immunological response gene expression
a technology of immunological response and immunological response, applied in the field of composition for the detection of blood cell and immunological response gene expression, can solve the problems of a variety of limitations and 10% mismatch in the current cdna-based array, and achieve the effect of minimizing secondary structure and improving hybridization
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
second embodiment
[0057] In either case, a transcript profile is obtained showing the genes that are differentially expressed in biological samples consisting of hematopoietic cells or tissues associated with an immunological response rather than with noninflamed and nonhematopoietic biological samples. In one embodiment, the top 100 most abundant transcripts, more preferably the top 40 most abundant transcripts, are selected to generate first polynucleotide probes. In a second embodiment all upregulated transcripts are selected. By upregulated is meant that the genes are not detectable in the subtraction transcript profile but are preferably at levels of at least about 2 copies per cell, more preferably at least about 3 copies per cell, in the target transcript profile.
[0058] A second selection protocol (II) can provide for second polynucleotide probes derived from genes abundantly expressed in an immunological response. A number of target cDNA libraries are prepared from second biological samples. ...
examples
[0108] I cDNA Library Construction
[0109] For purposes of example, the preparation and sequencing of the LNODNOT03 cDNA library, from which Incyte Clones 1573272, 1573553, 1574415, 1574617, 1574637, and 1576661 were isolated, is described in detail. Preparation and sequencing of cDNA libraries in the LifeSeq.RTM. database have varied over time, and the gradual changes involved use of kits, plasmids, and machinery available at the particular time the library was made and analyzed.
[0110] The LNODNOT03 cDNA library was constructed from microscopically normal lymph node tissue excised from a 67-year-old Caucasian male. This tissue was associated with tumorous lung tissue. The patient history included squamous cell carcinoma of the lower lobe, benign hypertension, arteriosclerotic vascular disease, and tobacco abuse. The patient was taking Doxycycline, a tetracycline, to treat an infection.
[0111] The frozen tissue was homogenized and lysed using a Brinkmann Homogenizer Polytron PT-3000 (B...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Time | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com