Method of timing calibration using slower data rate pattern
a data rate pattern and timing calibration technology, applied in the direction of digital transmission, instruments, generating/distributing signals, etc., can solve the problems of increasing reducing the timing margin for data capture, and correspondingly reducing the timing budget allocated, so as to reduce the overhead of die size and reduce the cost and complexity of system devices. , the effect of simplifying logi
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0034] The invention will now be described with respect to the aspect of the invention wherein any pattern of bits may be used as a calibration pattern. In the following, a novel method and associated apparatus is described for transmitting and receiving a calibration bit pattern at a rate slower than a normal operating rate of a receiving logic circuit to ensure correct capture of the calibration bit pattern. However, other methods of ensuring the correct transmission and capture of a calibration pattern at a logic device in a digital circuit are possible, and the invention is not to be limited to any particular method of transmission or capture of digital bits.
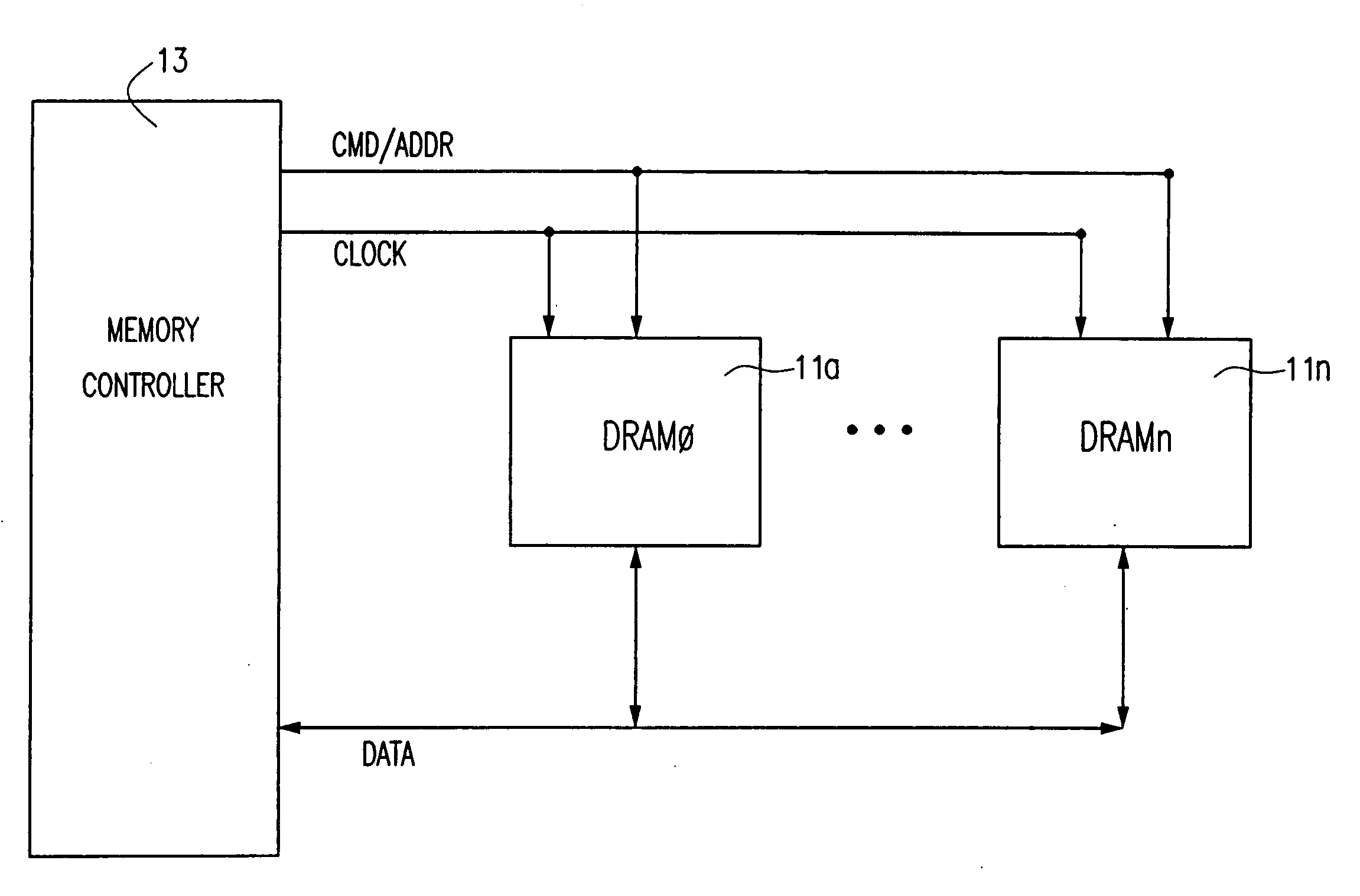
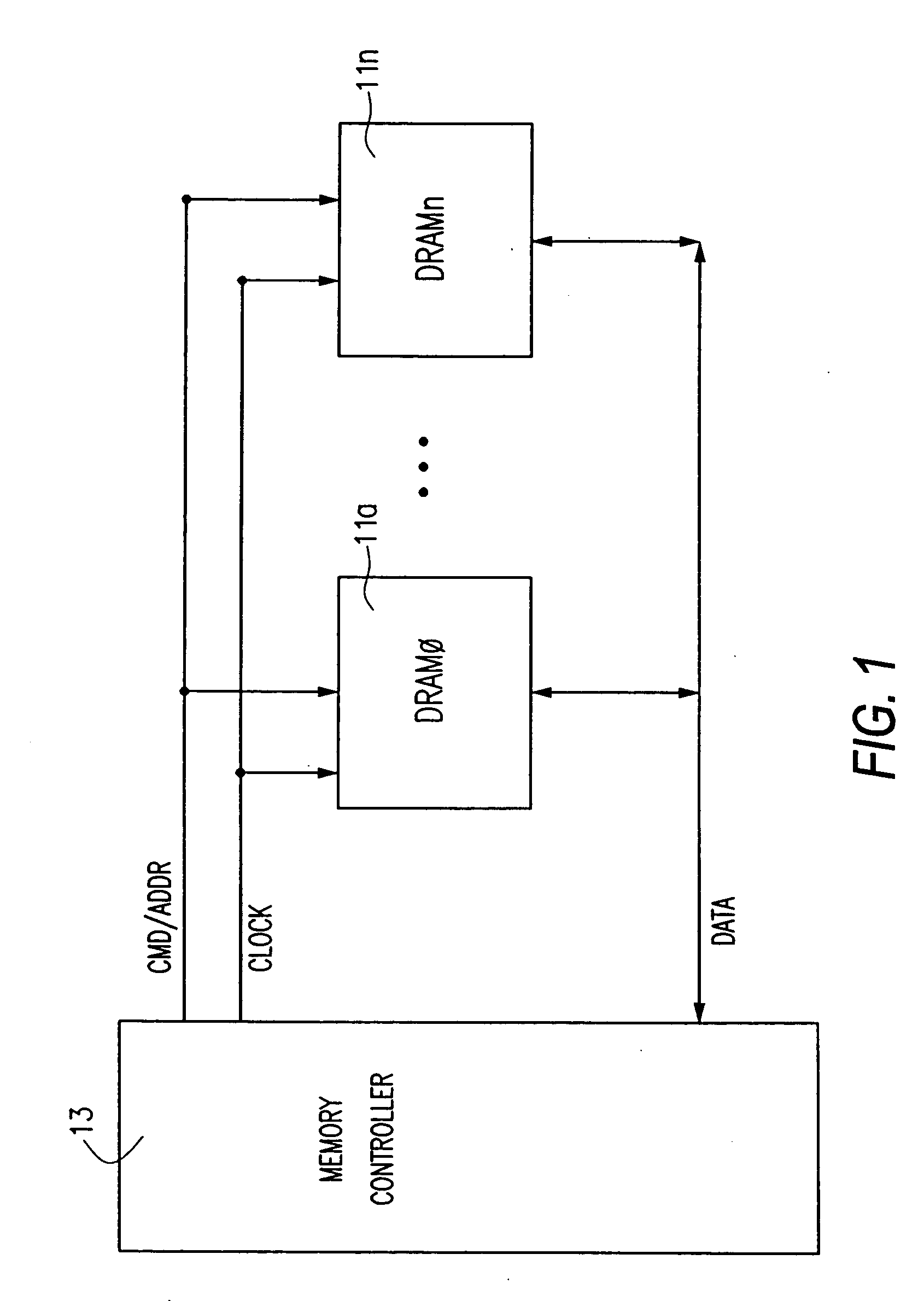
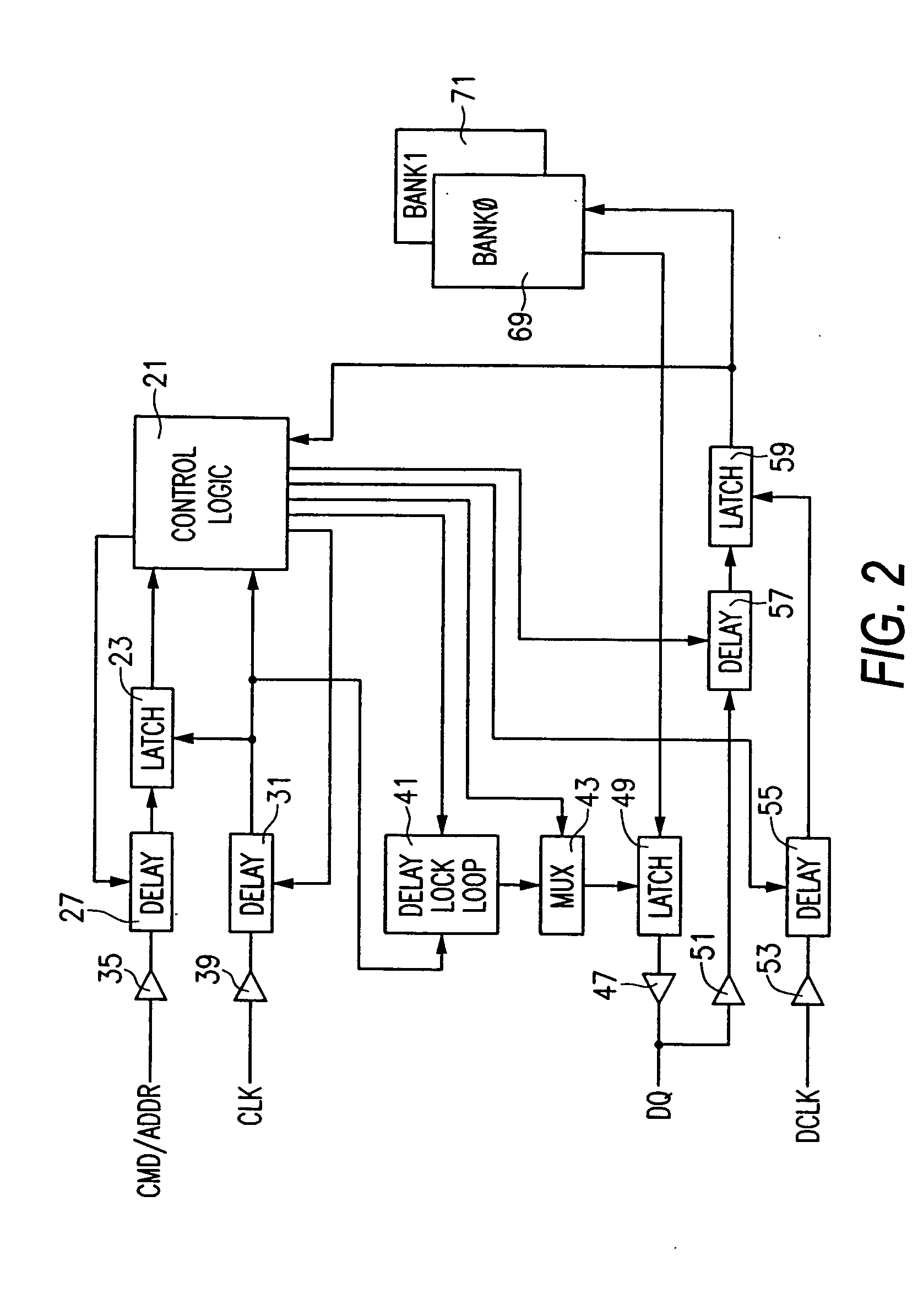
[0035] FIGS. 9(A) and 9(B) show an embodiment of the invention used in an exemplary digital circuit, such as a memory circuit. Referring to FIG. 9(A), a digital circuit topology is shown including two logic devices 101, 103 connected by a bus 107. Each of the logic devices 101, 103 includes a control logic circuit 21, such ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com