Method for verifying geographical location of wide area network users
user technology, applied in the field of communication using a wide area network, can solve the problems of unable to use public access codes by another users, etc., and achieve the effect of reducing the likelihood of success in guessed access codes, reducing the possibility of misuse, and reducing the likelihood of access codes being successfully guessed
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
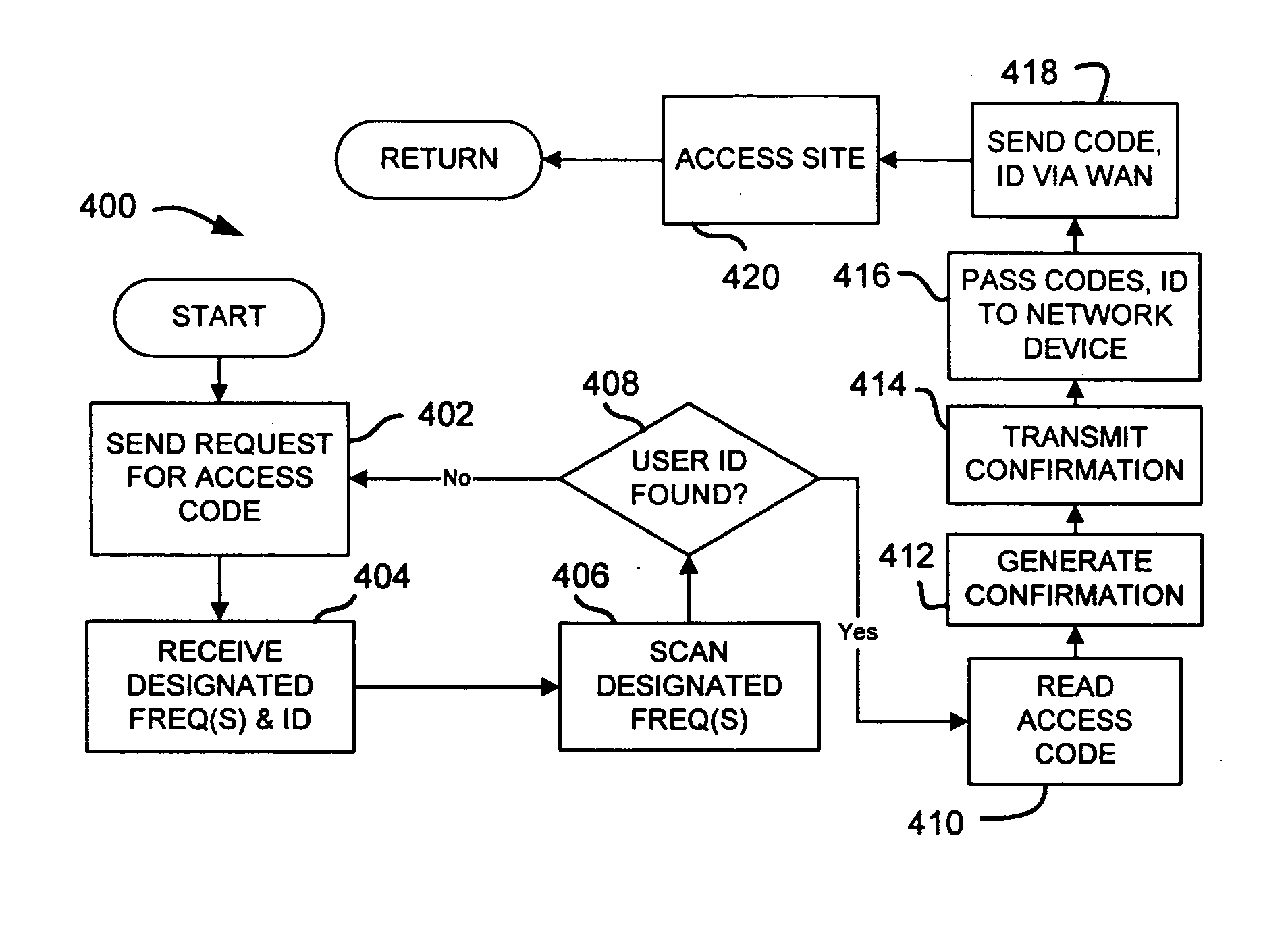
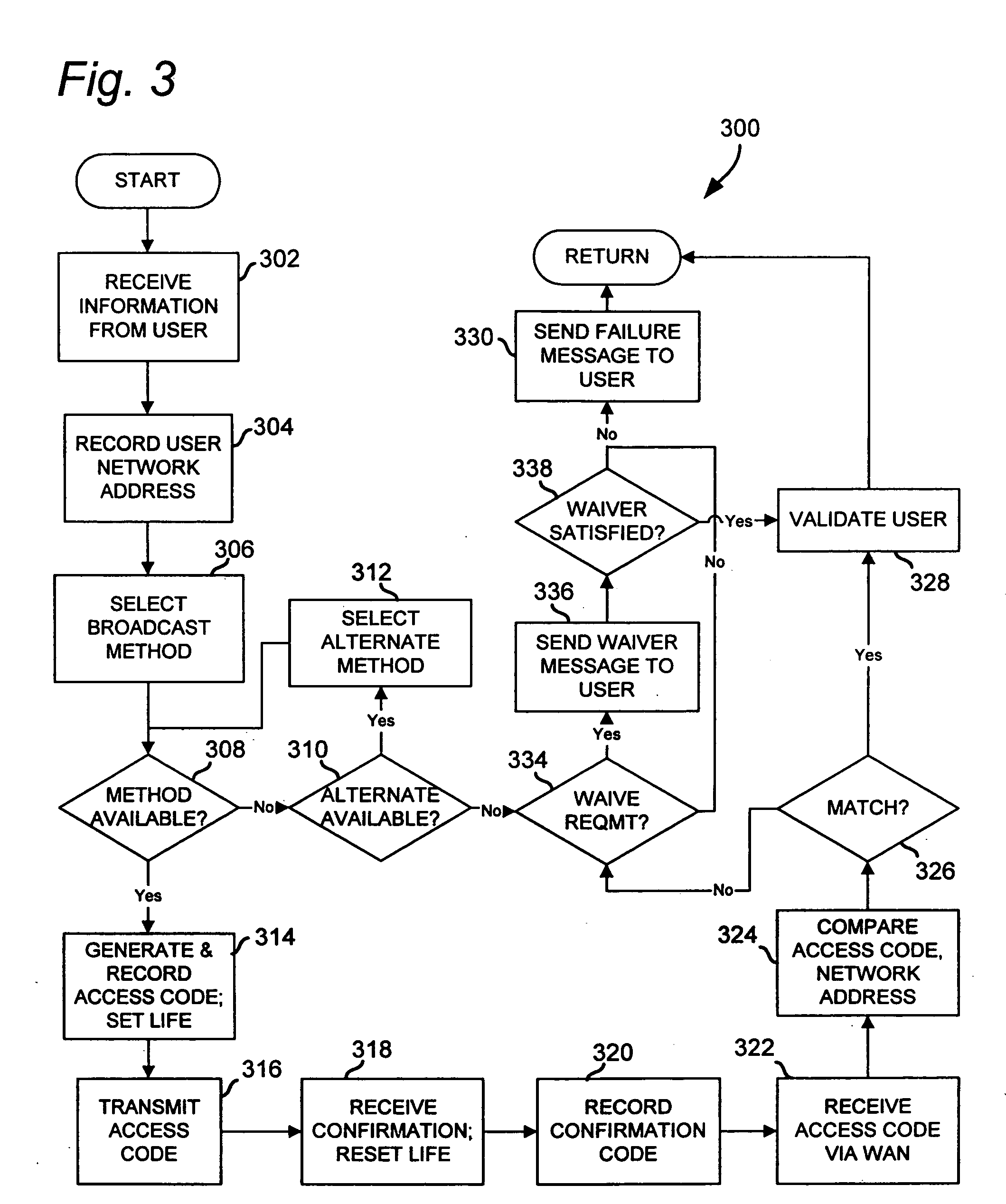
[0020] The present invention provides a method and system for verifying a geographical location of a user of a wide area network. The method can be quickly and cost-effectively implemented using presently available equipment, and can be implemented without requiring dedicated equipment at the client side.
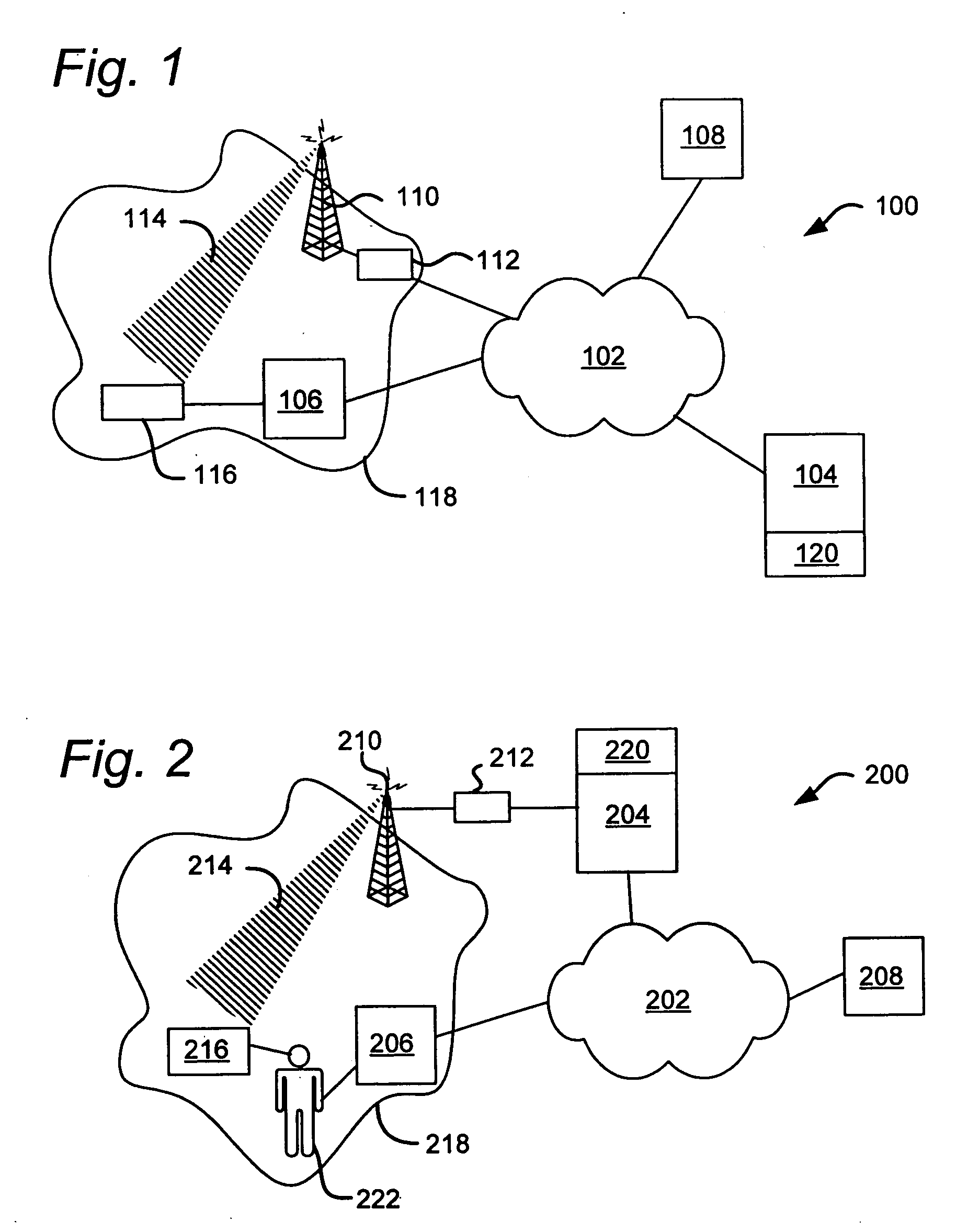
[0021]FIG. 1 shows an exemplary system 100 for implementing a method according to the invention. System 100 comprises a wide area network (WAN) 102, such as the Internet, connected by communication links as known in the art to user devices 106 and 108 and to a host computer 104, which is in turn connected to a computer memory 120. Each of user devices 106, 108 may comprise any suitable client device as known in the art for connecting to the wide area network, including but not limited to a personal computer. In an embodiment of the invention, wide area network 102 is the Internet, but the invention is not limited thereto. It should be apparent that a large plurality of user devices...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com