Conductive polymer composite structure
a composite structure and polymer technology, applied in the direction of electrolytic capacitors, transportation and packaging, synthetic resin layered products, etc., can solve the problems of difficult formation of conductive polymers on the conductive substrate, and achieve good deformation properties
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0136] Electrolytic solution was prepared by dissolving pyrrole which is a monomer and a dopant ion salt as shown in Table 1 into medium stated in Table 1 by a publicly known stirring method. This electrolytic solution has monomer concentration of 0.25 mol / l and the dopant salt in Table 1 is 0.5 mol / l. Conductive polymer composite structures of Example 1 having the shapes shown in Table 1 were obtained by using this electrolytic solution and by conducting electrochemical polymerization with constant current methods with the current density of 0.2 mA / cm2 by setting working electrodes and counter electrodes. As said working electrodes, conductive substrates shown in Table 1 (metal mesh, trade name “Au Ami 0.1 mmφ, 100 mesh”, manufactured by Tokuriki Honten Co., Ltd) were used. As said counter electrodes, commercially available Pt electrodes were used. In addition, in the tables, “-” shows that there were no appropriate matters,
example 2
[0137] Conductive polymer composite structures of Example 2 were obtained in the same way as in Example 1, except that conductive substrates of Table 1 (metal mesh, Ni mesh (0.05 mmφ, 200 mesh) manufactured by Rare Metallic Co., Ltd.) were used.
examples 3 to 8
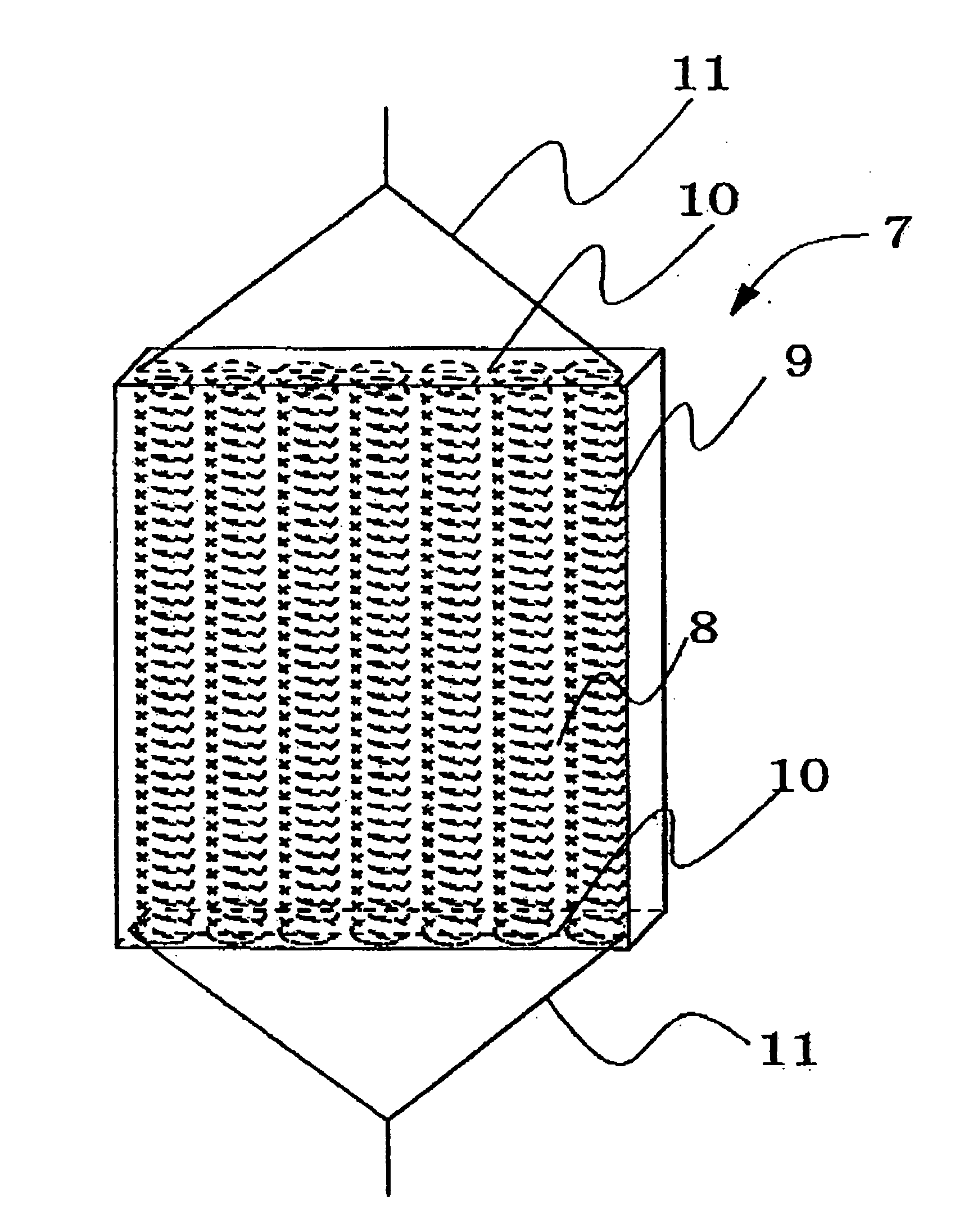
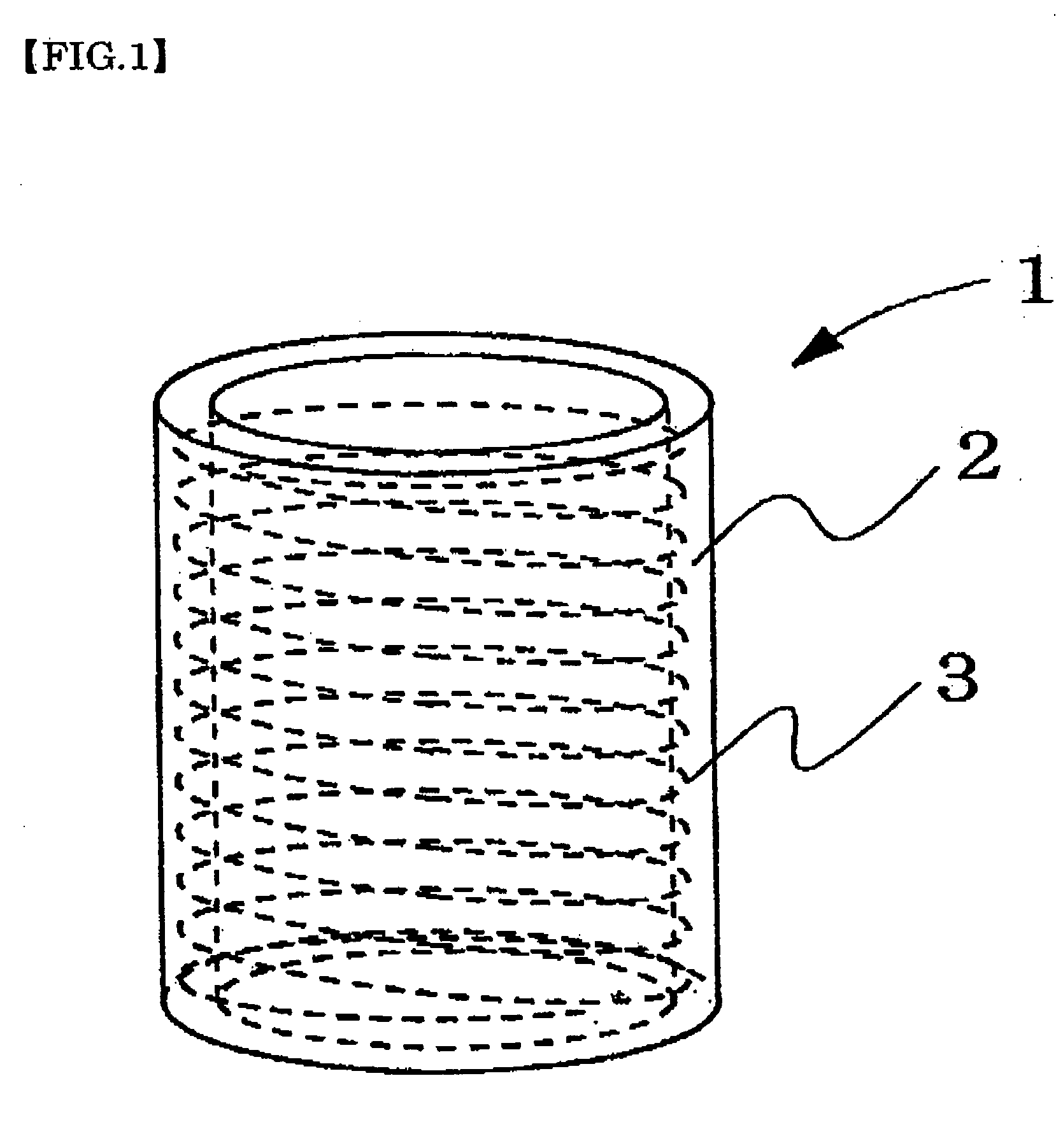
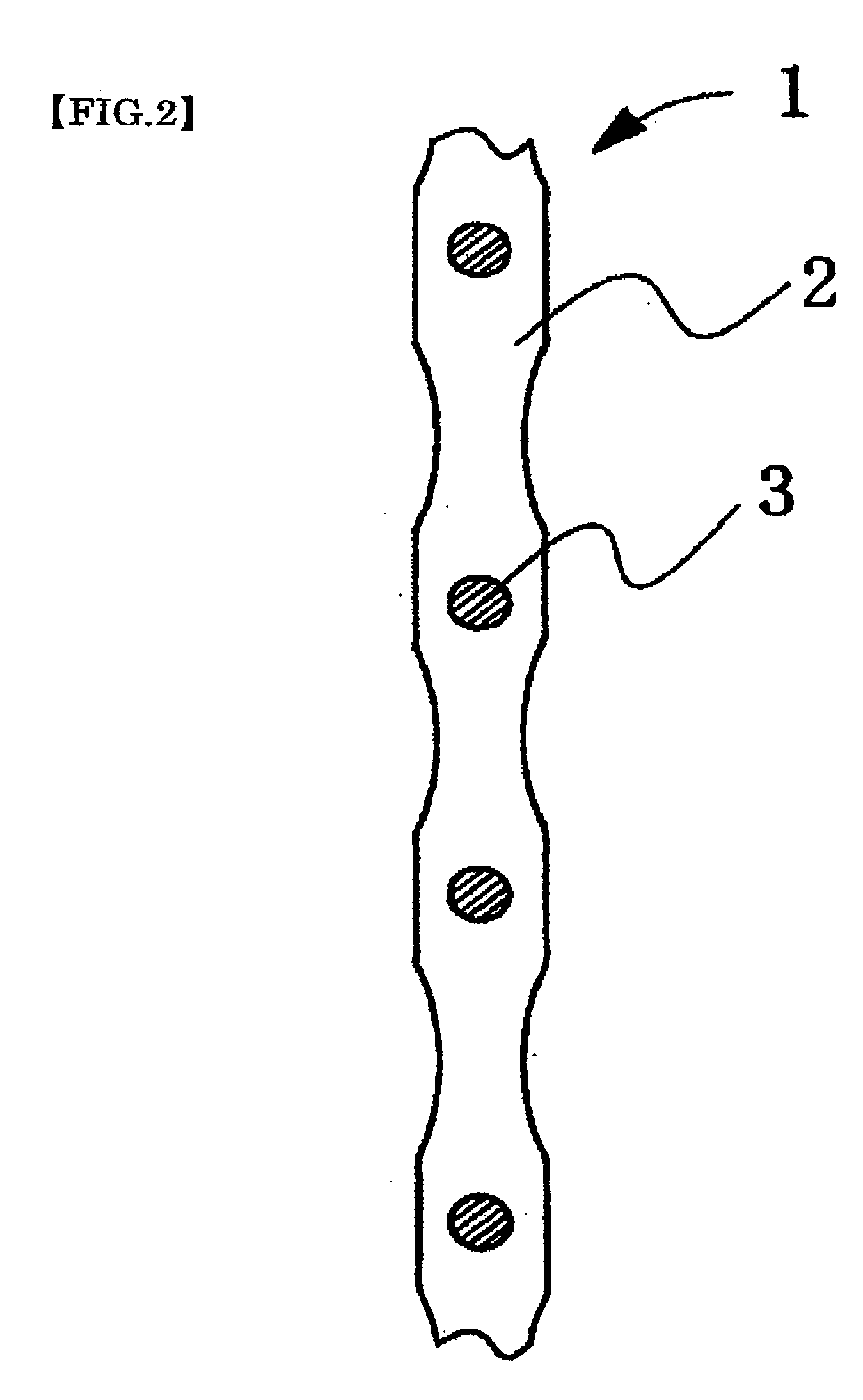
[0138] Conductive polymer composite structures of Examples 3 to 8 were obtained in the same way as in Example 1, except that conductive substrates which were coiled spring members of Tables 1 and 2 were used and that the solvent and dopant salt of Table 1 or 2 were used. In addition, as coiled spring members used in Example 3, spring members formed as a characteristic of Table 1 were used by using “Ni wire, wire diameter 0.10 mmφ” (manufactured by Rare Metallic Co., Ltd.) and as coiled spring members used in Example 4, trade name “SUS / Ni plated coil, outer diameter 0.5 mmφ, wire diameter 40 mmφ, pitch 110 μm” (manufactured by Nippon cable system Inc.) were used. As coiled spring members used in Example 5, “Pt / w coil, outer diameter 0.5 mmφ, wire diameter 40 μmφ, pitch 110 μm” (manufactured by Nippon cable system Inc.) were used. And in Examples 6 and 8, “W coil, outer diameter 0.25 mmφ, wire diameter 0.03 mm, pitch 60 μm” (manufactured by Nippon cable system Inc.) were used. In Exam...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| conductivity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| width | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| conductivity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com