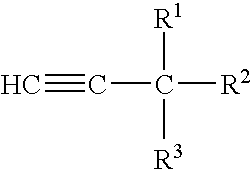
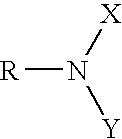Corrosion inhibitor
a corrosion inhibitor and corrosion technology, applied in the direction of other chemical processes, chemistry apparatus and processes, wellbore/well accessories, etc., can solve the problems of steel surface corroding, acidic corrosion of production or workover conduits used in wells in such applications, and particularly aggravated corrosion problems, so as to improve corrosion inhibition
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 5
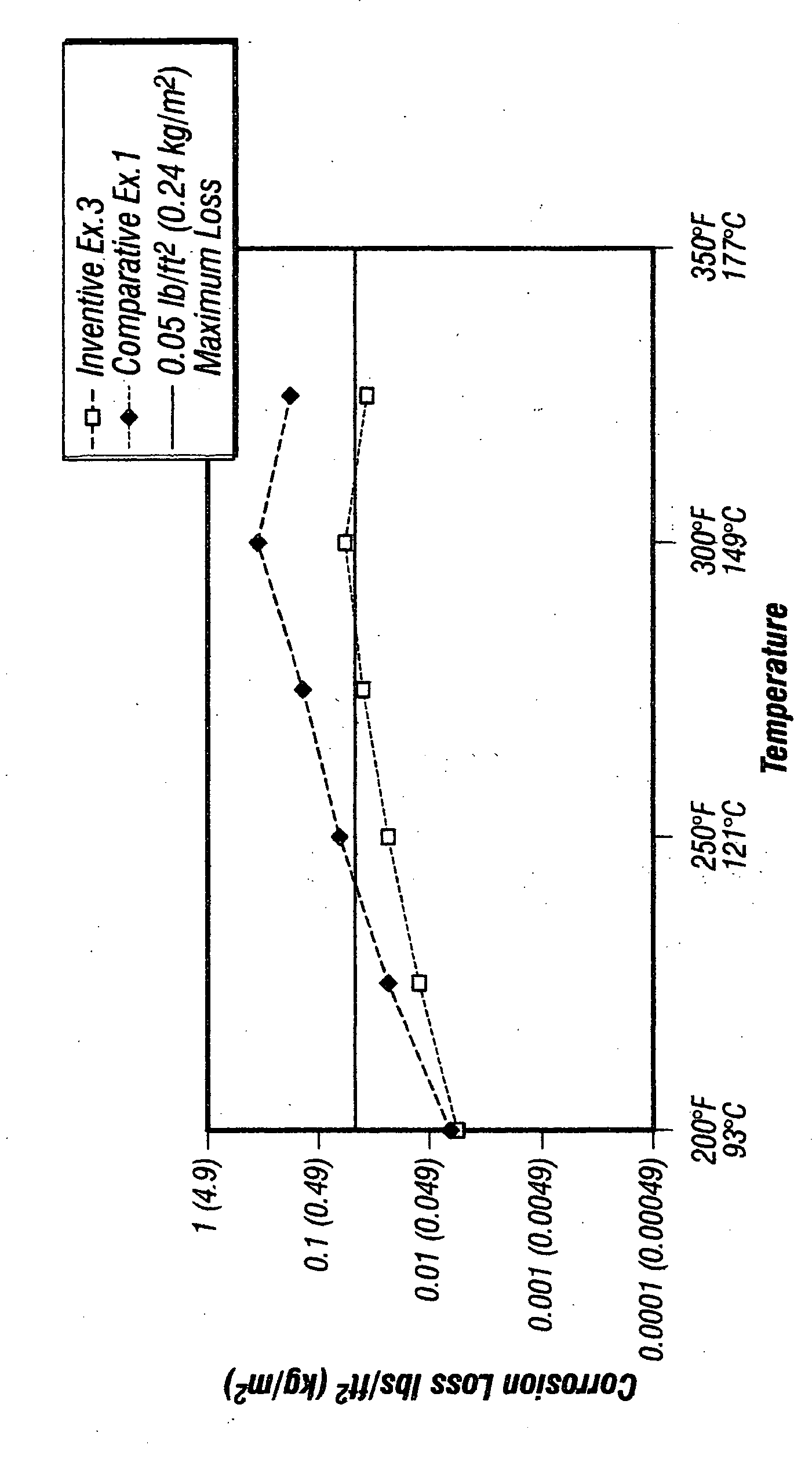
[0045] The corrosion loss of corrosion inhibitors of Inventive Example 3 and Comparative Example 1 are compared in the Figure chart as a function of temperature. It should be remembered that the corrosion loss scale of the y-axis is a logarithmic scale. This data, presented below in Table ll, was collected using N-80 tubing steel in 15% HCl. It may be seen that the corrosion inhibitor of Inventive Example 3 far outperforms that of Comparative Example 1.
TABLE IIComparison of Corrosion Inhibitors of InventiveExample 3 with Comparative Example 1 on N-80 in 15% HClInventive Example 3Comparative Example 1TemperatureCorrosion LossCorrosion Loss° F. (° C.)lbs / ft2kg / m2lbs / ft2kg / m2200 (93) 0.0060.0290.0070.034225 (107)0.0130.0630.0230.112250 (121)0.0230.1120.0650.317275 (135)0.0390.1900.1400.683300 (149)0.0610.2980.3731.820325 (163)0.0370.1810.1870.913
examples 6-9
[0046] Blends D and E were used in Examples 6-9, the results of which are presented in Table III. Blend D is a blend of active corrosive inhibiting materials and dispersing agents in a non active solvent (methanol)—a closest comparative blend to an inventive embodiment. Blend E is the same blend of active corrosive inhibiting materials and dispersing agents of Blend D where formic acid replaced the methanol—and represents one embodiment of the corrosion inhibitor composition herein.
[0047] Blends D and E contain the same dispersing agents (surfactants) as those used in Formulae A and B of Examples 1 and 3 of Table l above, which surfactants fall within the surfactant definition herein.
[0048] The Mannich reaction product corrosion inhibitor base used in Blends D and E herein was the same as that in Formulae A, B, and C of Examples 2, 3, and 4, respectively, of Table l noted above, and as described in U.S. Pat. No. 3,077,454 discussed previously. The Mannich reaction product, formic ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| volume % | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| vol. % | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com