Prevention and treatment of amyloid-associated disorders
a technology of amyloid plaques and amyloid-associated disorders, which is applied in the field of neurological diseases involving amyloid plaque formation, can solve the problems that cerebrovascular arnyloid deposits may interfere with cognitive functions, and achieve narrowly tailored therapeutic agents and fewer general side effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Preparation and Characterization of Primary Glia Cell Cultures
[0088] As co-culture with astrocytes is known to promote the resting state for cultured microglia, mixed primary glial cultures are a particularly suitable system in which to examine PGE2:Aβ synergy. Briefly, cortices from P3 wild type mice were dissected in Ca2+ and Mg2+ free HBSS (Gibco). Meninges were carefully dissected away, and the tissue transferred to a dish containing HBSS supplemented with 0.53 mM EDTA and 0.05% trypsin. The tissue was incubated for 18 minutes at. room temperature with occasional gentle agitation. Trypsin was removed and the tissue washed with HBSS twice prior to titration in growth medium consisting of high glucose DMEM supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS), 110 mg / L sodium pyruvate, and 5 units / ml penicillin / streptomycin. The cell suspension was plated at 9 cortices in growth medium into one T75 and one T25 flask. The next day, nonadherent cells were removed. The culture was refed wi...
example 2
Aβ:PGE2 Synergy Experiments in Primary Mixed Glial Cells
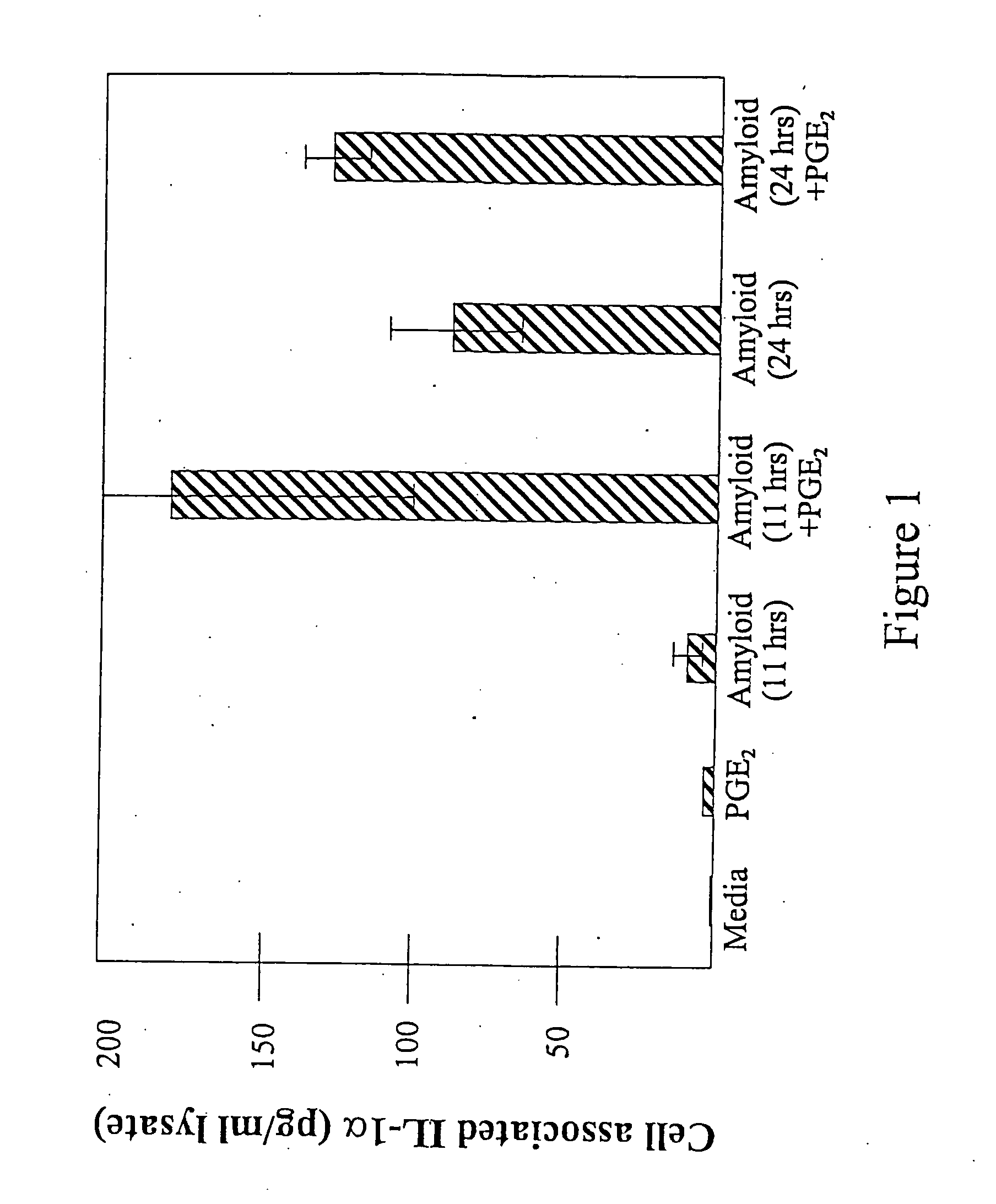
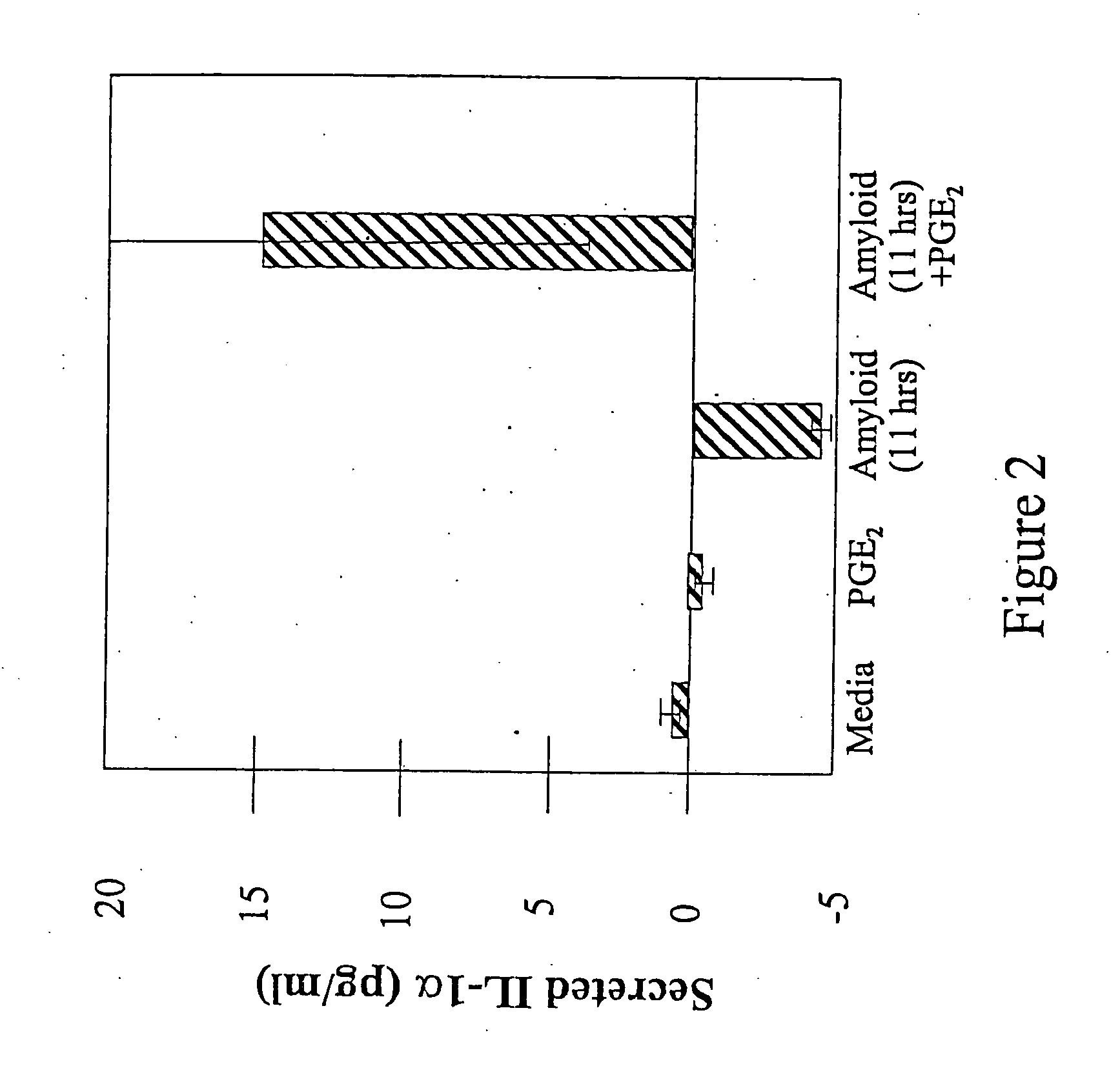
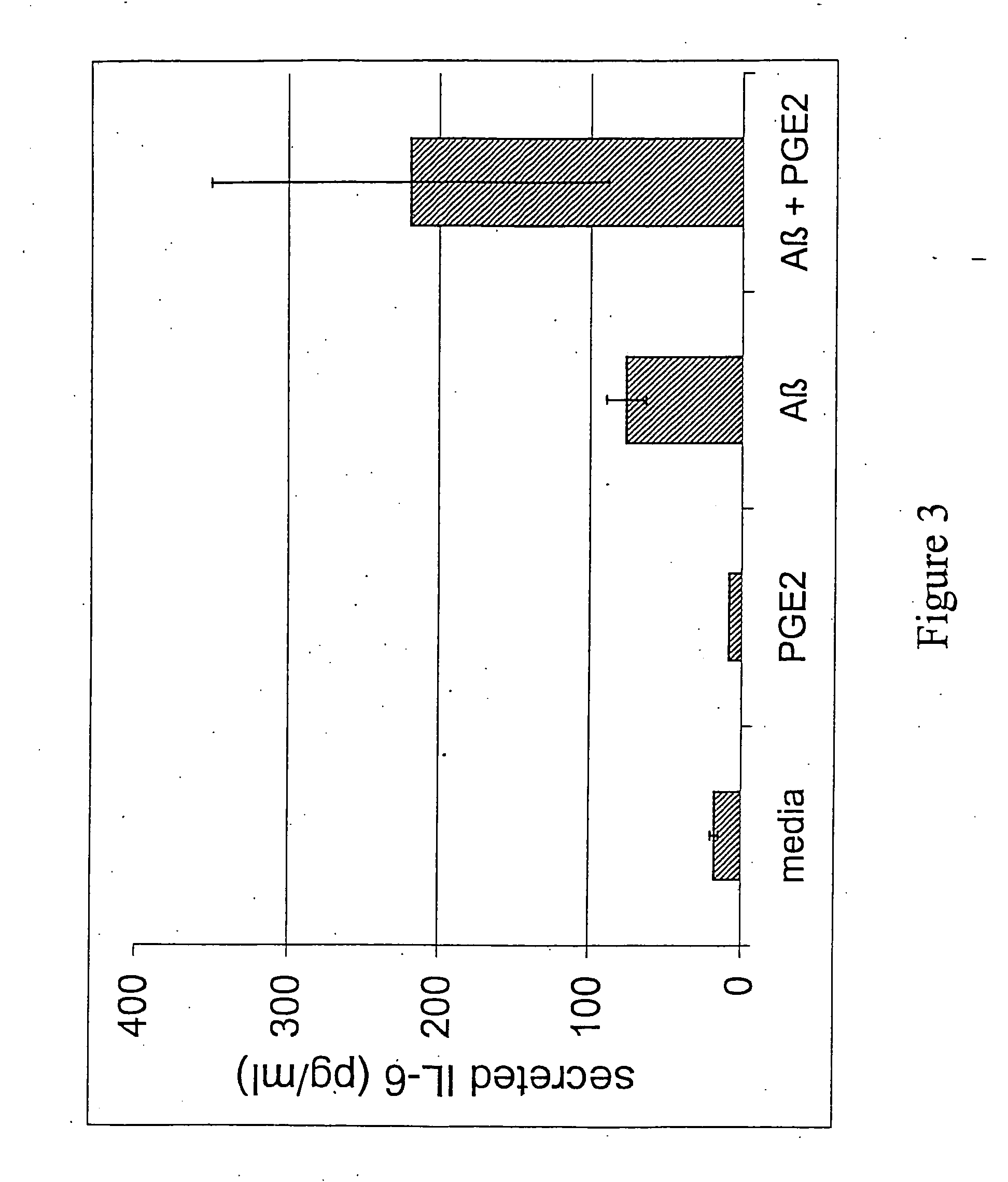
[0093] Endogenous PGE2 levels and the ability of indomethacin to suppress PGE2 were investigated by assaying medium conditioned by mature (confluent) primary mixed murine glial cultures in 48 well plates for 48 hours. Under basal conditions, PGE2 was observed at just under 200 pg / ml conditioned media, in keeping with literature reports for primary cultures. Exposure to 100 ng / ml LPS dramatically increased this level to a concentration that saturated the assay at medium dilutions used, demonstrating the ability of the cultures to respond robustly to stimulus. Treatment of the cultures during the conditioning.period with 14 μM indomethacin suppressed PGE2 secretion to about 30 pg / ml in 48 hours. This is within the range in which would allow PGE2:Aβ synergy to be observed.
[0094] The effect of Aβ in the presence and absence of exogenous PGE2 was investigated in these primary cortical mixed glial cultures. An Aβ peptide was resusp...
example 3
Aβ:PGE2 Synergy Experiments in MMGT-16 Mouse Microglial Cell Culture
[0097] The protocol described above in Example 2 was then used to examine the synergy between PGE2 and Aβ in the mouse microglial cell line MMGT-16.
[0098] Synergy in MMGT-16 cells was examined by measuring secretion of both TNF-α (FIG. 4) and IL-1β (FIG. 5). The secretion of IL-1β was unaffected by the addition of either PGE2 or Aβ alone, while addition of both resulted in a dramatic increase in the secretion of IL-1β. PGE2 had no discernable effect on TNF-α secretion as well, while Aβ alone had a modest affect on TNF-α secretion. The addition of both Aβ and TNF-α together, however, resulted in a synergistic increase in the secretion of TNF-α
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| time | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com