Oriented thermoplastic elastomer film and process for producing the same
a technology of thermoplastic elastomer and oriented thermoplastic, which is applied in the direction of thin material handling, transportation and packaging, etc., can solve the problem that thermoplastic elastomer films do not have the suitable stretching dynamics, and achieve the effect of reducing gas permeability and improving fatigue resistan
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
examples 1-8
[0047] BIMS was pre-compounded with curatives in a Banbury internal mixer and pelletized with the anti-block agent prior to its mixing with Nylon. Mixing and dynamic vulcanization of Nylon and BIMS were done in a twin-screw extruder at about 230° C. These mixes were then cast or blown into films. 2″ diameter disks were punched out from these films and conditioned in a vacuum oven at 60° C. overnight prior to the permeability measurements. Oxygen permeation values of these films at 60° C. were measured using a Mocon OX-TRAN 2 / 61 permeability tester. Principal refractive indices along the three principal directions of these films were determined using a Metricon prism-coupling device. The operation wavelength was 632.8 nm generated by a low-power He-Ne laser. Using the three principal refractive indices, the average refractive index could be calculated as:
n>=(n1+n2+n3) / 3
wherein, is the average refractive index. 1, 2, and 3 refer to machine, transverse, and normal (normal to the fil...
examples 9-13
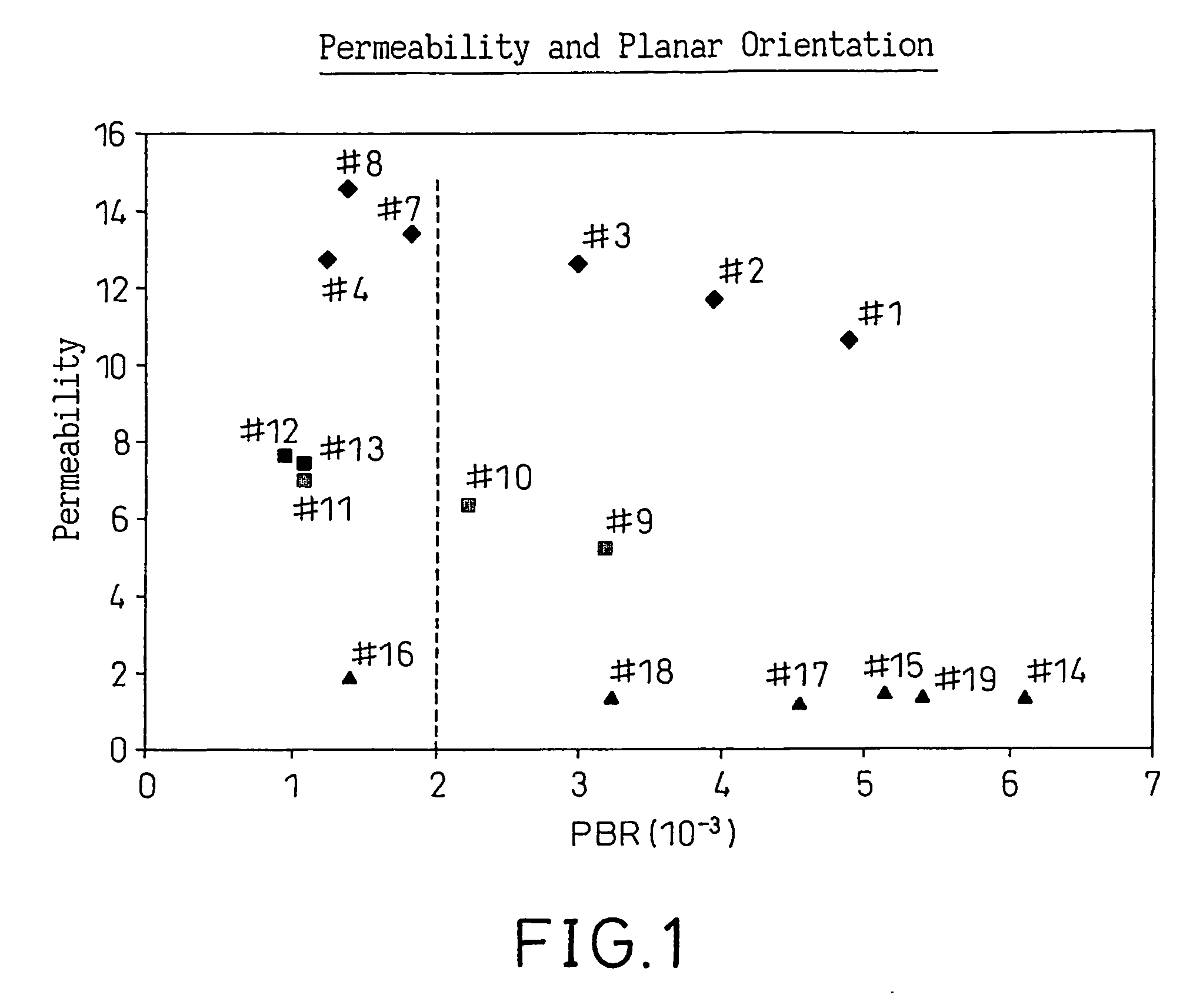
[0049] In Examples 9 to 13, Nylon 1 matrix was used but without the plasticizer and compatibilizer. 6PPD could be a curative at the mixing temperature of 230° C. by crosslinking BIMS through benzylic bromines and, hence, removing them from reactive compatibilization. DM16D is a viscosity enhancer for BIMS that also react with benzylic bromine of BIMS. This modification of the interfacial bonding with the usage of DM16D and 6PPD could significantly lower the planar orientation and raise the film permeability as shown in Table 2. The results are shown in FIG. 1. Regardless, a good correlation could be found between PBR and permeability. The higher refractive index value in comparison with that in Table 1 reflects the fact that the Nylon matrix has no plasticizer. Hence, higher density or higher refractive index is expected.
TABLE 2Example No.91011*112*113*1Formulation(parts byweight)BIMS100100100100100DM16D001.02.03.06PPD00.6000ZnO0.150.150.150.150.15St-acid0.600.600.600.600.60ZnSt0....
examples 14-19
[0050] In Examples 14-19, Nylon 2 matrix, without N11 and without plasticizer, was used. In blending with Nylon 2, viscosity modifier, such as DM16D and 6PPD, is required to provide good viscosity matching and fine BIMS rubber dispersions. The concentration used for the anti-blocking agents listed in Table 3 is 0.5 to 1 phr. As indicated in Table 3, using ZnO as the anti-blocking agent could significantly affect the orientation. This anti-blocking agent may act as curative and, hence, remove benzylic bromines from BIMS for its reactive compatibilization with Nylon. A large removal of benzylic bromines from BIMS could lower the interfacial bonding between the Nylon and BIMS dispersions and reduce the ability of the film manufacturing process to orient Nylon. However, overall correlation between PBR and permeability holds. The even higher refractive index value as compared with that in Table 2 is the result of the N6 / 66 matrix used. The results are also shown in
TABLE 3Example No.141...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| softening point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| wavelength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com