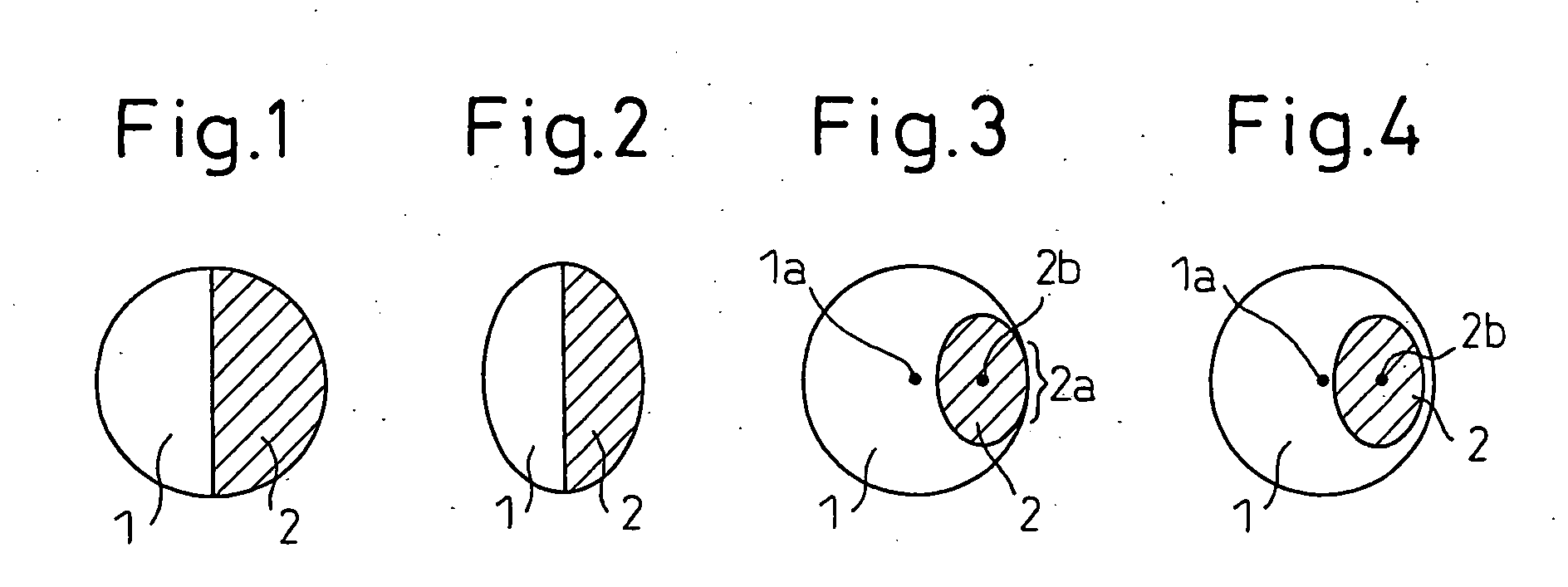
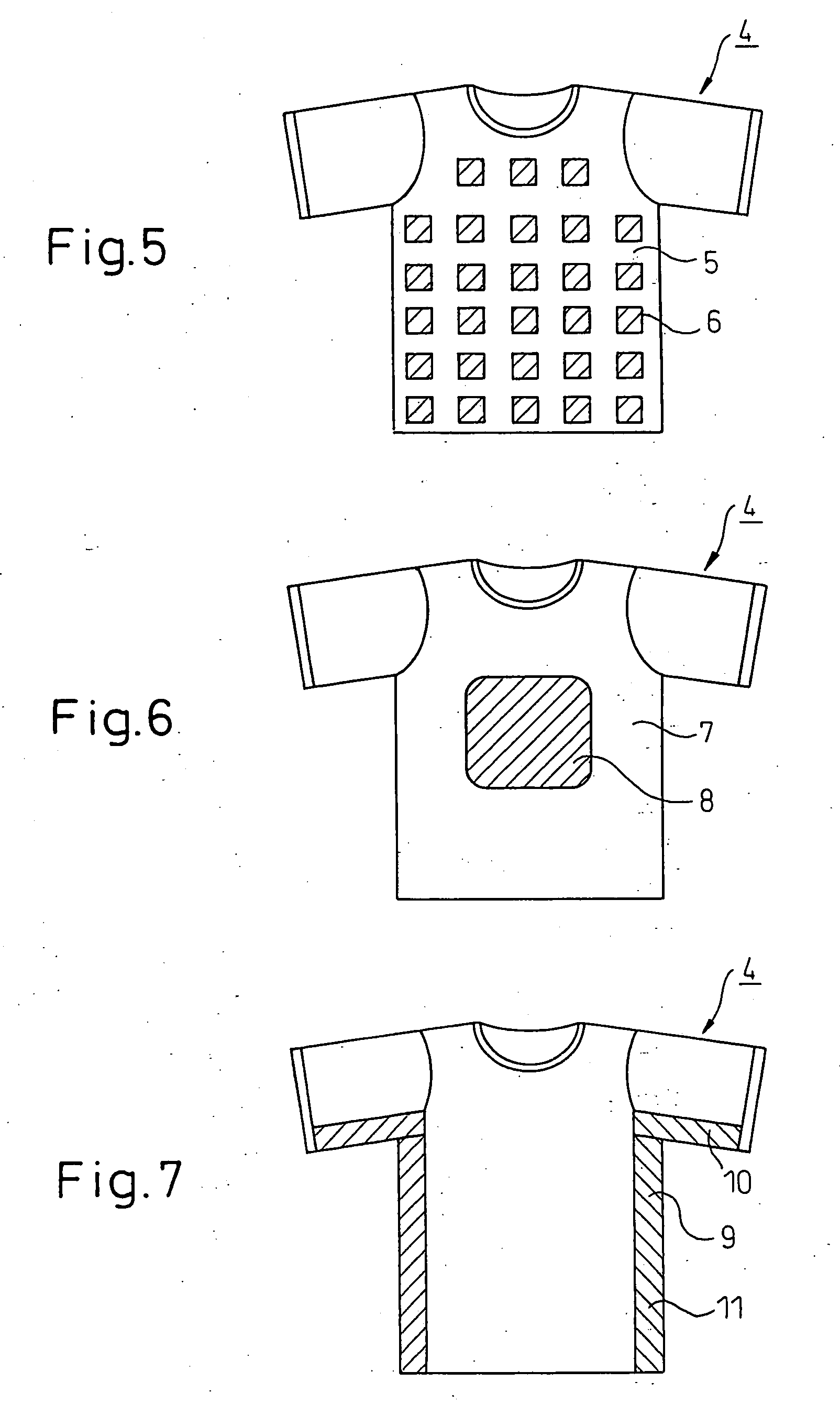
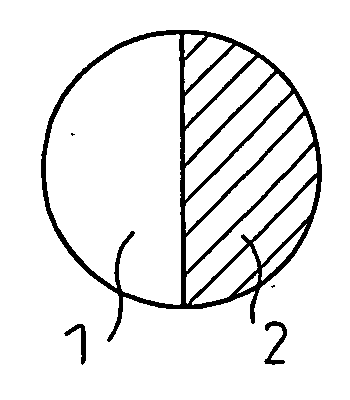Woven or Knitted Fabric and Clothes Containing Crimped Composite Filaments and Having an Air Permeability Which Increases When the Fabric is Wetted With Water
a composite filament and air permeability technology, which is applied in the direction of knitting, weaving, warp knitting, etc., can solve the problems of insufficient change in air permeability, slow drying speed, wearer discomfort, etc., and achieve the effect of increasing air permeability, decreasing air permeability, and increasing air permeability of clothes
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0141]A nylon 6 having an intrinsic viscosity [η] of 1.3 was melted at 270° C., and a modified poly(ethylene terephthalate) in which 2.6 mol % of 5-sodium sulfoisophthalic acid was copolymerized and that had an intrinsic viscosity [η] of 0.39 was melted at 290° C. Both molten polymers were extruded through a spinneret for side-by-side type composite filaments in an extrusion rate of 12.7 g / min for each polymer. The spinneret was one described in Japanese Unexamined Patent Publication (Kokai) No. 2000-144518. The spinning nozzle was formed from two arc-shaped slits A and B arranged substantially on one the same circumference at a spacing d. The area SA of the arc-shaped slit A, the slit width A1, the area SB of the arc-shaped slit B, the slit width B1 and the area SC surrounded by the inner peripheral faces of the arc-shaped slits A and B simultaneously satisfy the following requirements (1) to (4):
[0142](1) B11
[0143](2) 1.1≦SA / SB≦1.8
[0144](3) 0.4≦(SA+SB) / SC≦10.0
[0145](4) d / A1≦3.0
The...
example 2
[0150]The same composite filaments yarn as used in Example 1 and a conventional poly(ethylene terephthalate) multifilaments yarn (84 dtex / 30 f) were used. Using 28-gauge double tubular knitting machine in the same manner as in Example 1, the composite filaments yarns and the poly(ethylene terephthalate) multifilaments yarns were alternately fed to the machine with every one yarn to form a tubular knitted fabric having an interlock stitch with a knitting density of 54 courses / 2.54 cm and 34 wales / 2.54 cm. The tubular knitted fabric was subjected to dyeing, water absorbent treatment and dry heat final set in the same manner as in Example 1.
[0151]The knitted fabric thus obtained had a basis weight of 206 g / m2, and exhibited a stretch percentage of 50% in the warp direction, a stretch percentage of 100% in the weft direction, an air permeability upon drying of 150 ml / cm2 / sec, an air permeability upon being wetted with water of 280 ml / cm2 / sec and a change in air permeability of 87%. The ...
example 3
[0155]The same side-by-side type composite filaments yarns as in Example 1 were produced. The composite filaments yarns were supplied to a conventional 28-gauge tricot knitting machine. The composite filaments yarns were fed to a back guide bar of the knitting machine at a full set. On the other hand, a conventional false twisted, crimped poly(ethylene terephthalate) multifilament yarns (33 dtex / 36 fil.) having a percentage of crimp of 20% were simultaneously fed to a front guide bar of the tubular knitting machine at a full set to give a knitted fabric having a half tricot stitch (back: 10-12, front: 23-10) with an on-machine density of 80 courses / 2.54 cm.
[0156]The knitted fabric was dyed at 130° C. for a peak temperature-keeping time of 15 minutes so that the latent crimpability of the composite filaments was manifested. The knitted fabric was then subjected to padding treatment with a fluororesin water repellent treatment liquid. The treated knitted fabric was then dried at a tem...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| pressure | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| RH | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com