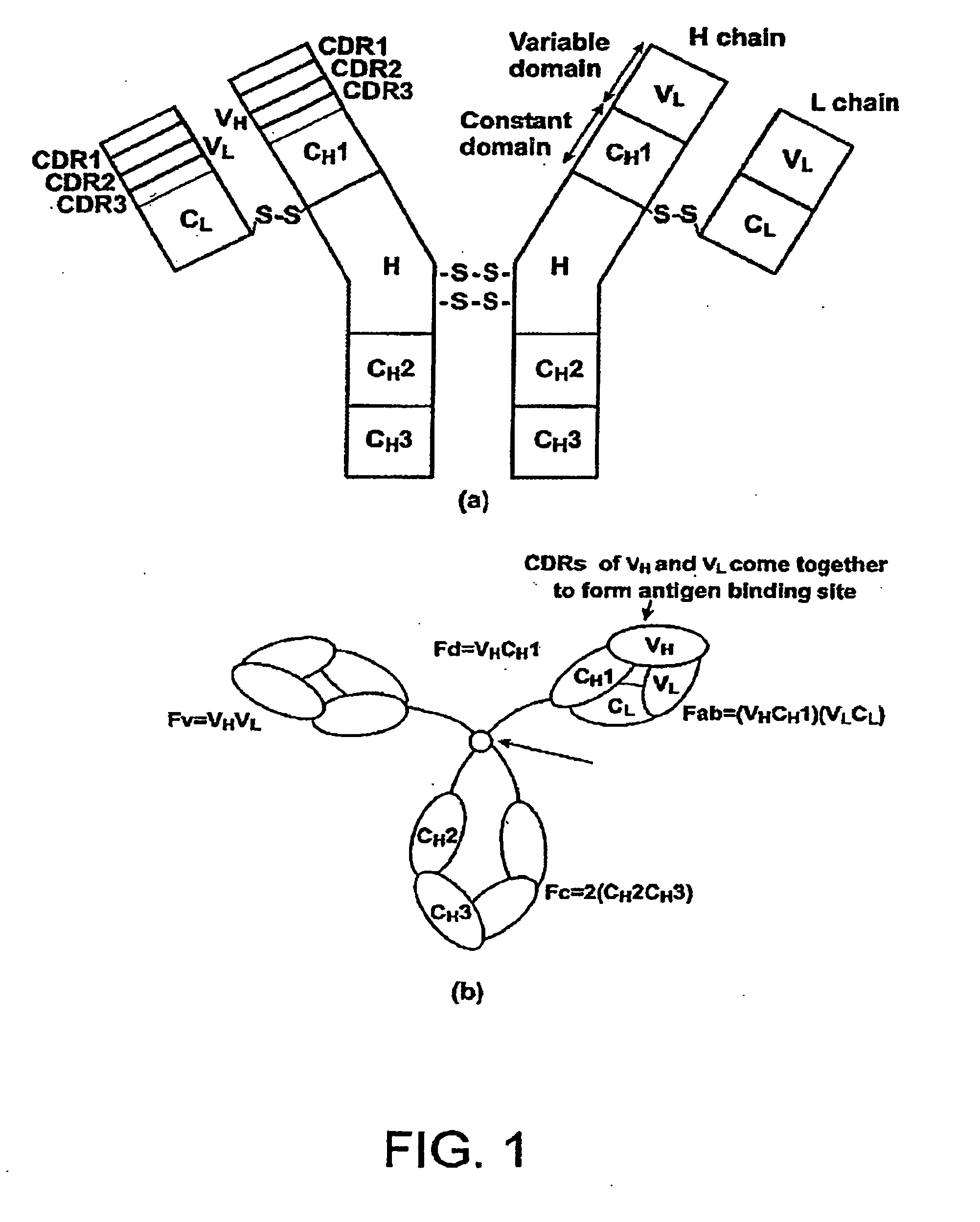
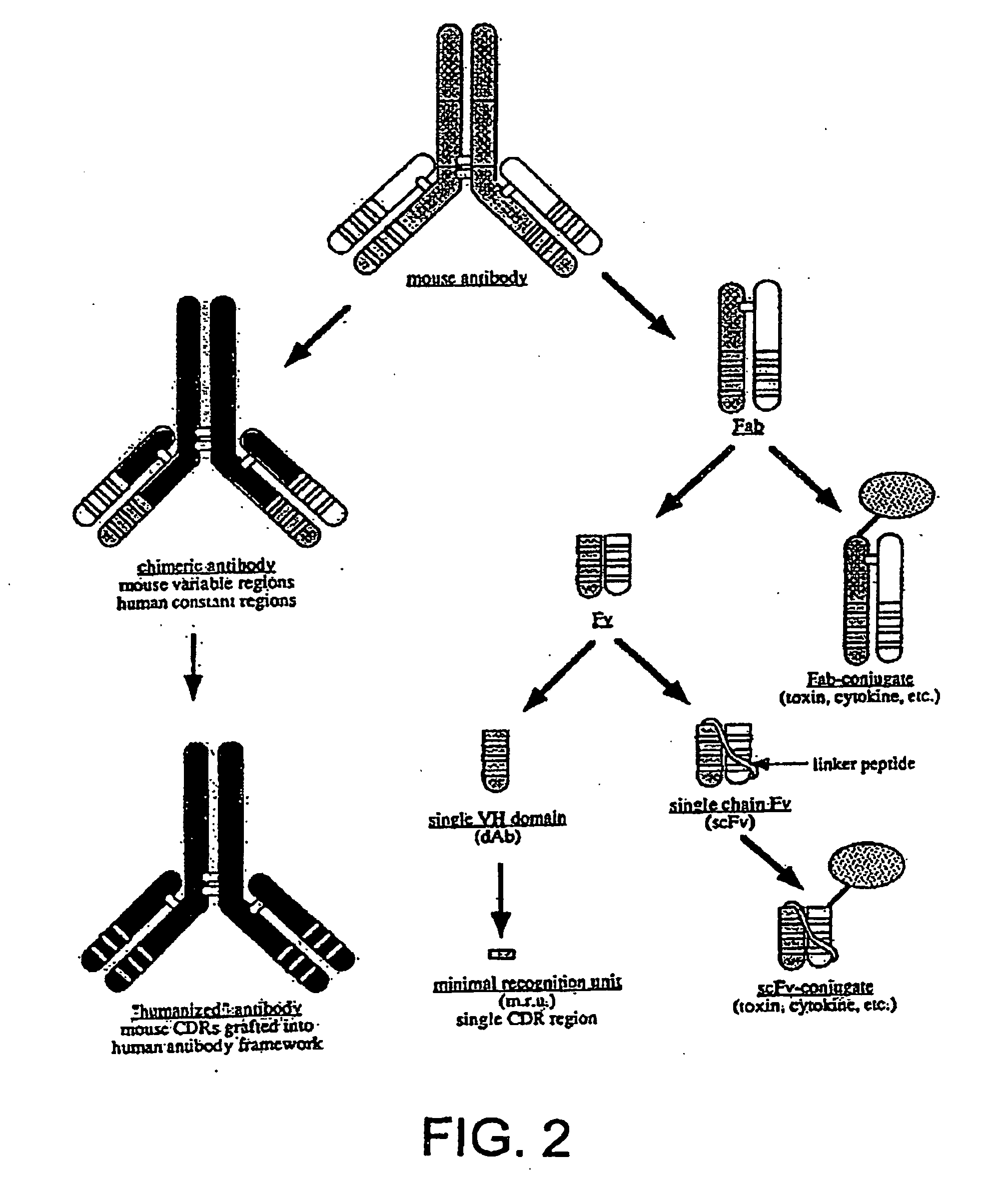
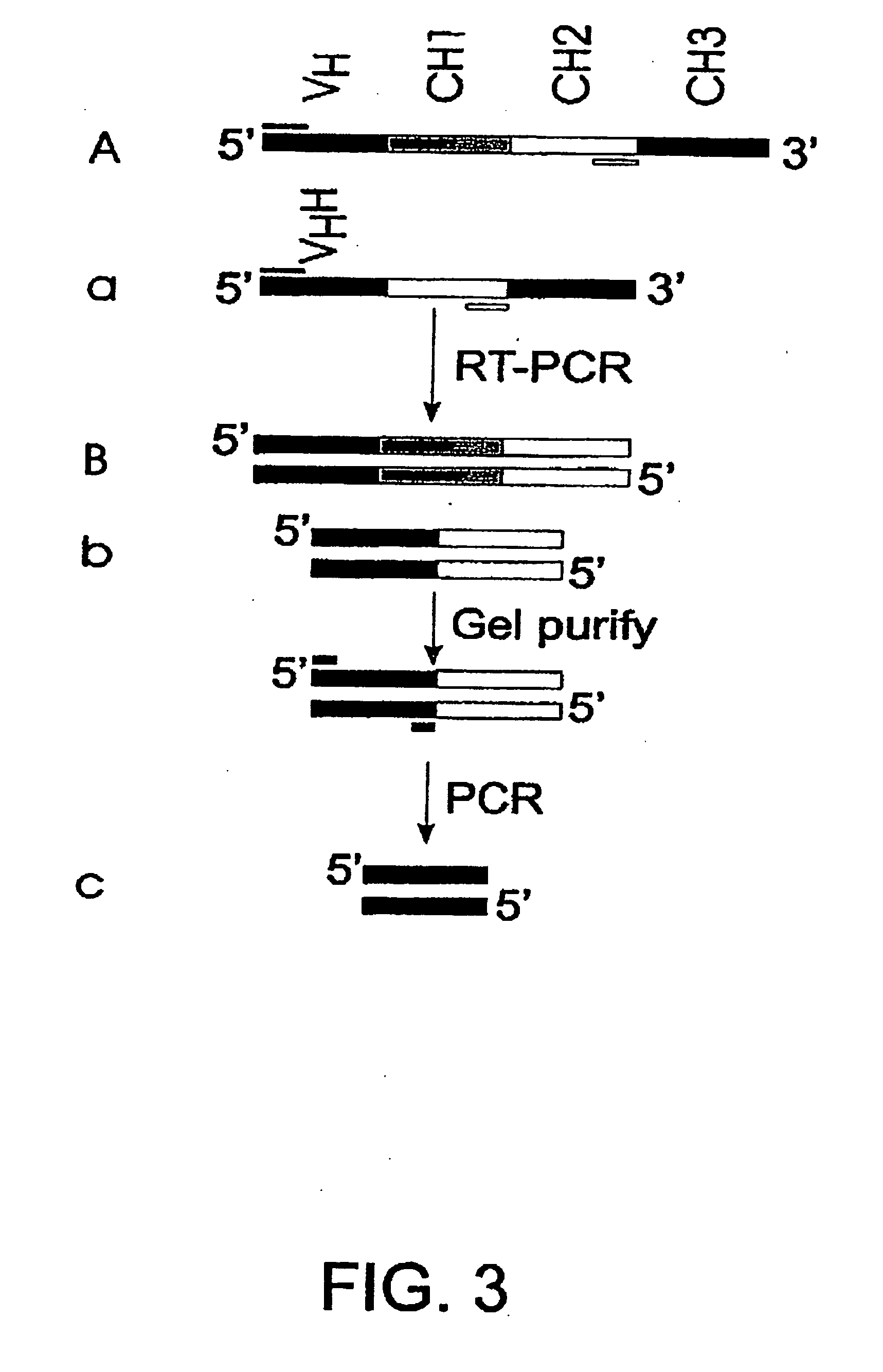
Single-domain antigen-binding antibody fragments derived from llama antibodies
a single-domain, antigen-binding technology, applied in the field of antigen-binding proteins, can solve problems such as endangering their lives, and achieve the effect of increasing the probability of isolating
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0029] In the following, positions of amino acid residues in antibodies and antibody fragments are indicated according to the Kabat numbering.
[0030] The present invention provides a large size (in the order of 109) phage display library of single-domain fragments of variable heavy domains (VH and VHH) of llama antibodies. The library, which has been generated using lymphocytes of a non-immunized animal (naive library), can be used for in vitro selection against any antigen of interest as a target. The size of the library makes it highly probable that an antibody specific to the target will be identified among the library's sdAb fragments. This utility of the library has been demonstrated by isolating therefrom sdAbs binding specifically to various preselected antigens as targets.
[0031] The choice of a naive library as the source of llama antibodies was based in part on the fact that the immune system of camelids has evolved over time in harsh environments and that its unique physi...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| total volume | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| pH | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| volume | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com