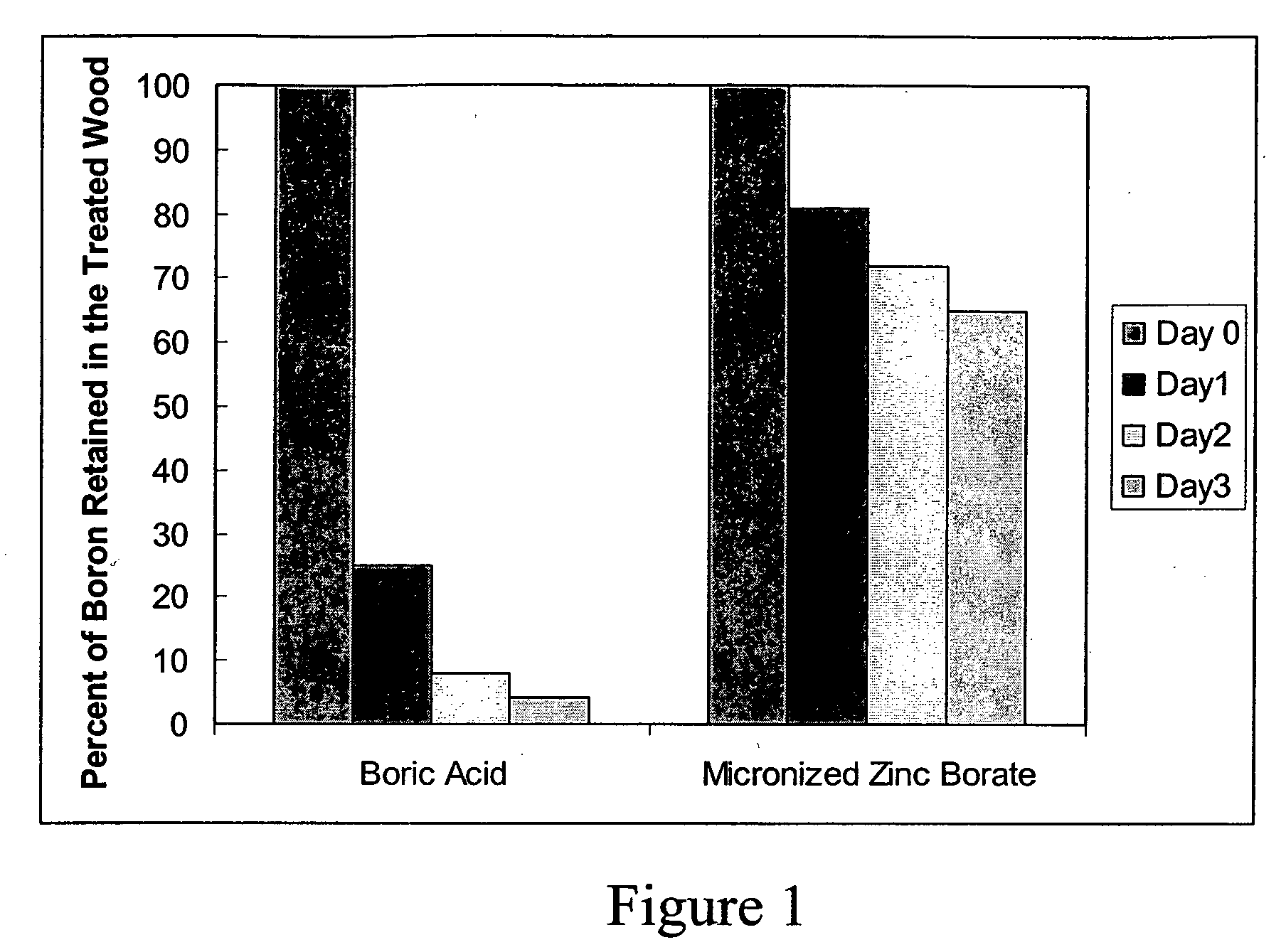
Micronized wood preservative formulations comprising boron compounds
a technology of micronized wood and preservatives, which is applied in the direction of biocides, manufacturing tools, paints, etc., can solve the problems of wood being subject to destruction or degradation, wood being prone to decay, and being prone to fire, so as to improve the decay-, insect- and fire-resistant properties of wood
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0074] 500 g of zinc borate were added to a container containing 650 grams of water and 100.0 grams of commercially available dispersants / wetting agents. The mixture was mechanically stirred for 5 minutes and then placed in a laboratory grinding mill. The sample was ground for about 45 minutes, and a stable dispersion containing about 40% zinc borate was obtained. The particle size of the zinc borate dispersion was analyzed by Horiba LA-910 Particle Size Distribution Analyzer (PSDA). The average particle size was 0.21 micrometers (um) with a distribution range of 0.04 um to 2.0 um.
example 2
[0075] 1000 grams of Ulexite was mixed with 1047 grams of water and 175.0 grams of commercially available wetting agents / dispersants. The mixture was mechanically stirred for 10 minutes. The mixture was then placed in a grinding mill and ground for about 60 minutes. A stable dispersion was obtained with an average particle size of 0.199 micrometers.
example 3
[0076] 1000 grams of Colemanite was mixed with 1300 grams of water and 200 grams of wetting agents / dispersants. The mixture was mechanically stirred for about 10 minutes. The mixture was then placed in a grinding mill and ground for about 45 minutes. A stable dispersion containing 40% Colemanite was obtained with an average particle size of 0.200 micrometers.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com