Conditioning system for cooling and heating surfaces, particularly automobile seats
a technology for heating surfaces and cooling and heating surfaces, applied in the field of automobile seats, can solve the problems of dark leather seats, adversely affecting the feel of seats, and serious burns of skin, and achieve the effects of low porosity, low fluid loss over the service life, and low porosity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
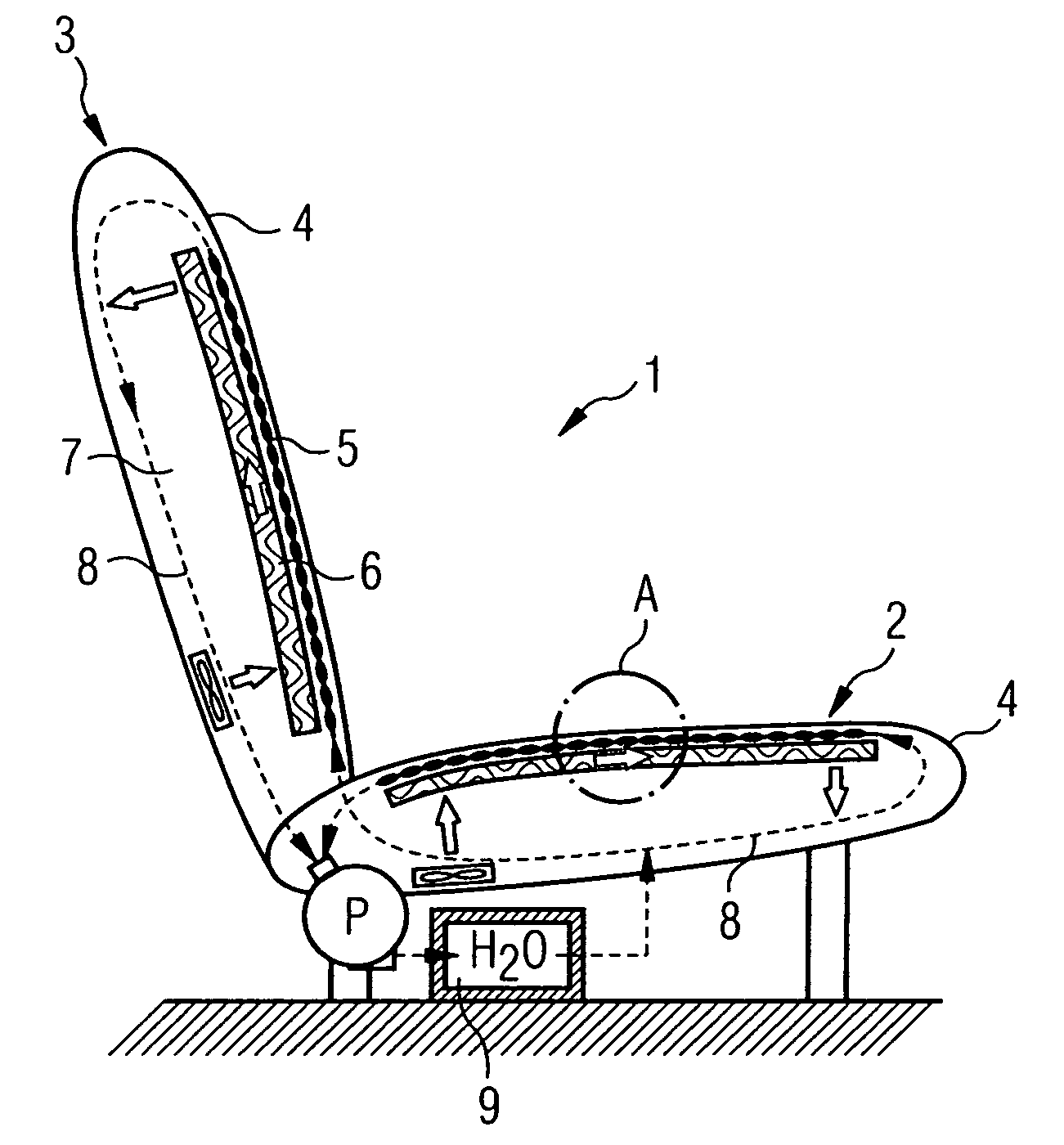
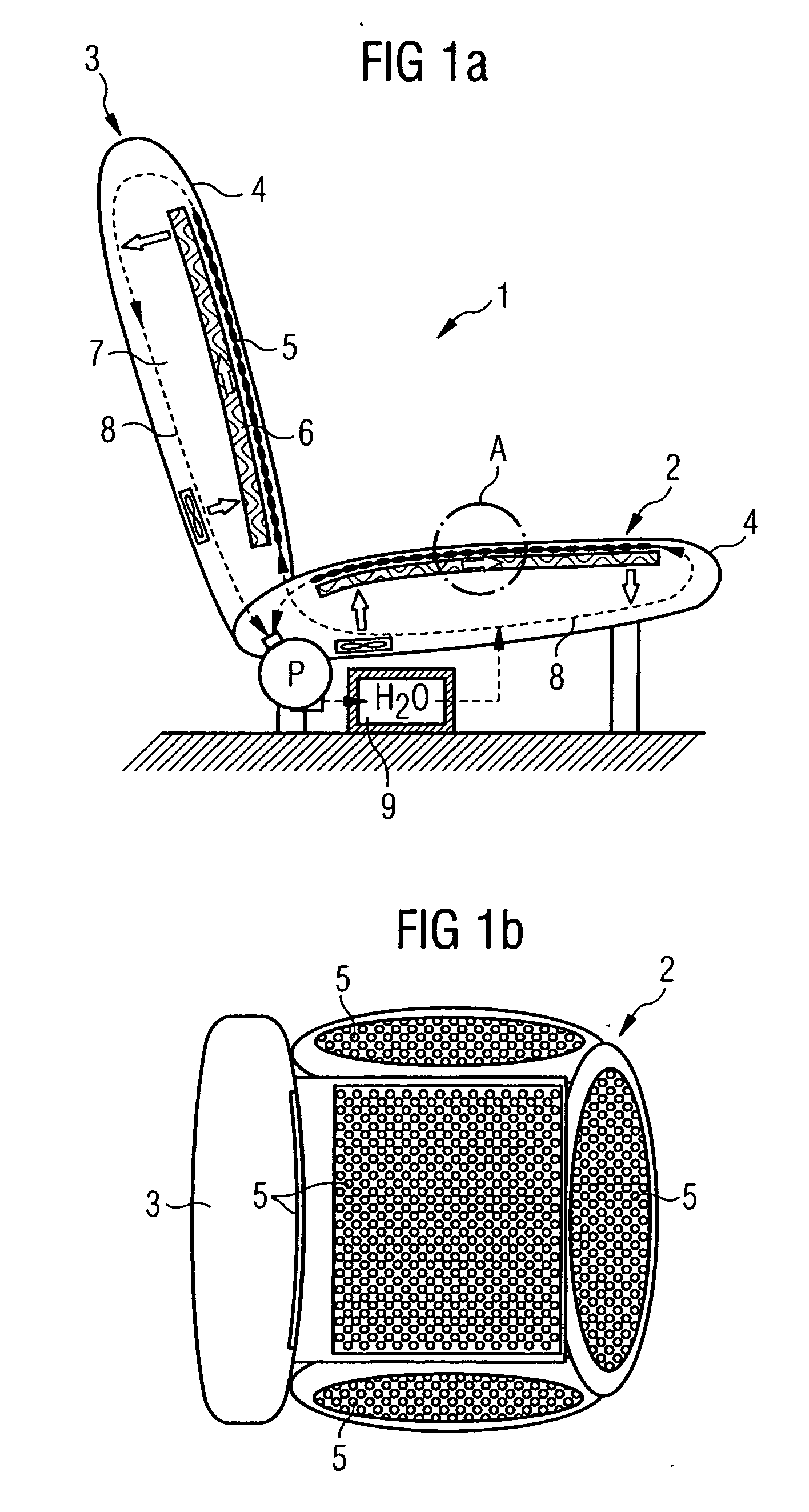
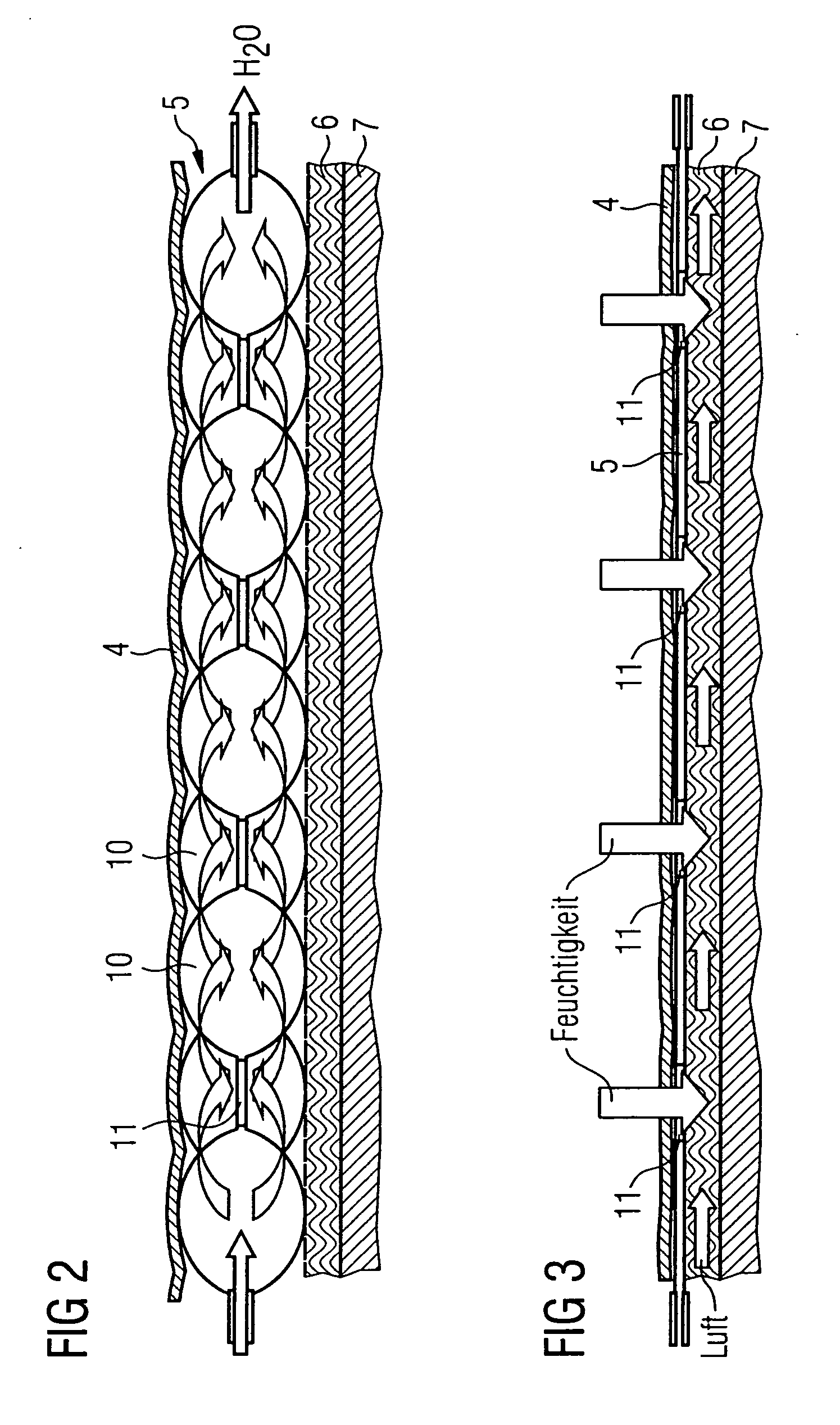
[0048]FIG. 1a shows a car seat 1 comprising a seat element 2 and a backrest element 3. Located under the seat coverings 4 both of the seat element 2 and of the backrest element 3 there is in each case a temperature control mat 5, which is kept at a distance from the cushion core 7 by a spacer structure 6. Water (H2O) is pumped as a temperature control fluid by means of a pump P from a storage tank 9 through the temperature control mat 5 through a system of fluid lines 8, which is represented as dashed lines with thin, black arrows, in order to control the temperature of (temperature control phase), in particular to cool (cooling phase), the seat covering 4 from the rear side. After completion of the temperature control phase, air is made to flow through the spacer structure 6 by means of a fan (white arrows), in order to assist the dissipation of perspiration moisture passing through the seat covering 4.
[0049]FIG. 1b shows the arrangement of the temperature control mat 5 in the car...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com