Plasma ethching apparatus and plasma etching process
a plasma etching and apparatus technology, applied in the direction of electric discharge tubes, solid-state devices, semiconductor devices, etc., can solve the problems of significant waste of insulating materials, difficult to etch the reaction product enough, etc., to prevent the forming of the chamber of insulating materials with reliability, reduce the effect of forming the chamber and reducing the number of defects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
first embodiment
[0042] Hereinafter, an explanation is given to a plasma etching apparatus and a plasma etching process according to a first embodiment of the present invention with reference to the drawings.
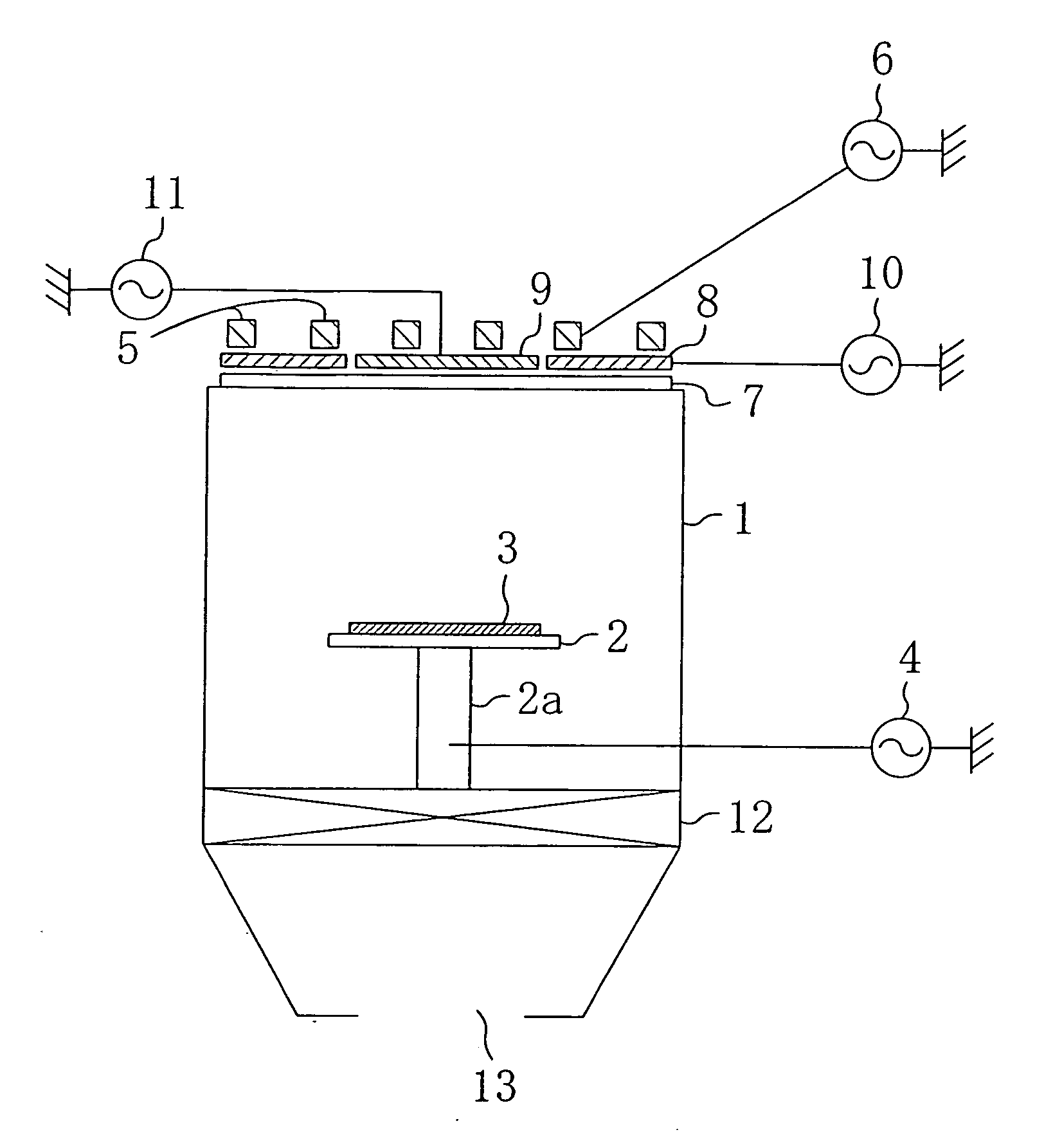
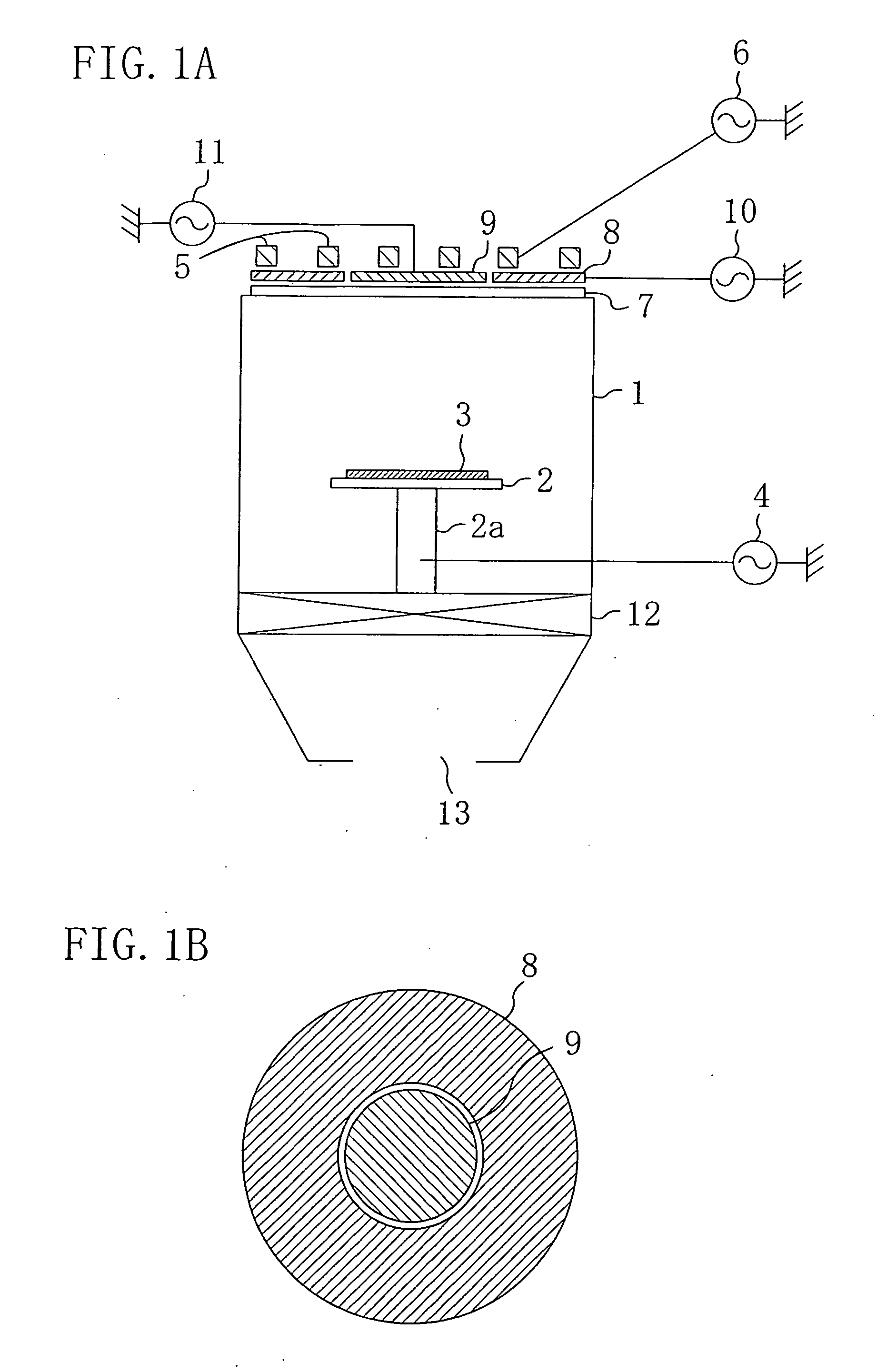
[0043]FIG. 1A is a view illustrating a schematic configuration of the plasma etching apparatus according to the first embodiment of the present invention. The plasma etching apparatus of the present embodiment allows generation of plasma which couples inductively with an ICP coil and plasma which couples capacitively with an FS electrode. As to be described later, a major feature of the apparatus is that the FS electrode is separated in two or more.
[0044] More specifically, as shown in FIG. 1A, the apparatus of the present embodiment includes an electrode 2 serving also as a wafer support arranged in a chamber 1 for performing plasma treatment such as dry etching, i.e., a chamber 1 capable of reducing pressure. The electrode 2 is installed on the bottom of the chamber 1 via a support member 2a...
second embodiment
[0065] Hereinafter, an explanation is given to a plasma etching apparatus and a plasma etching process according to a second embodiment of the present invention with reference to the drawings.
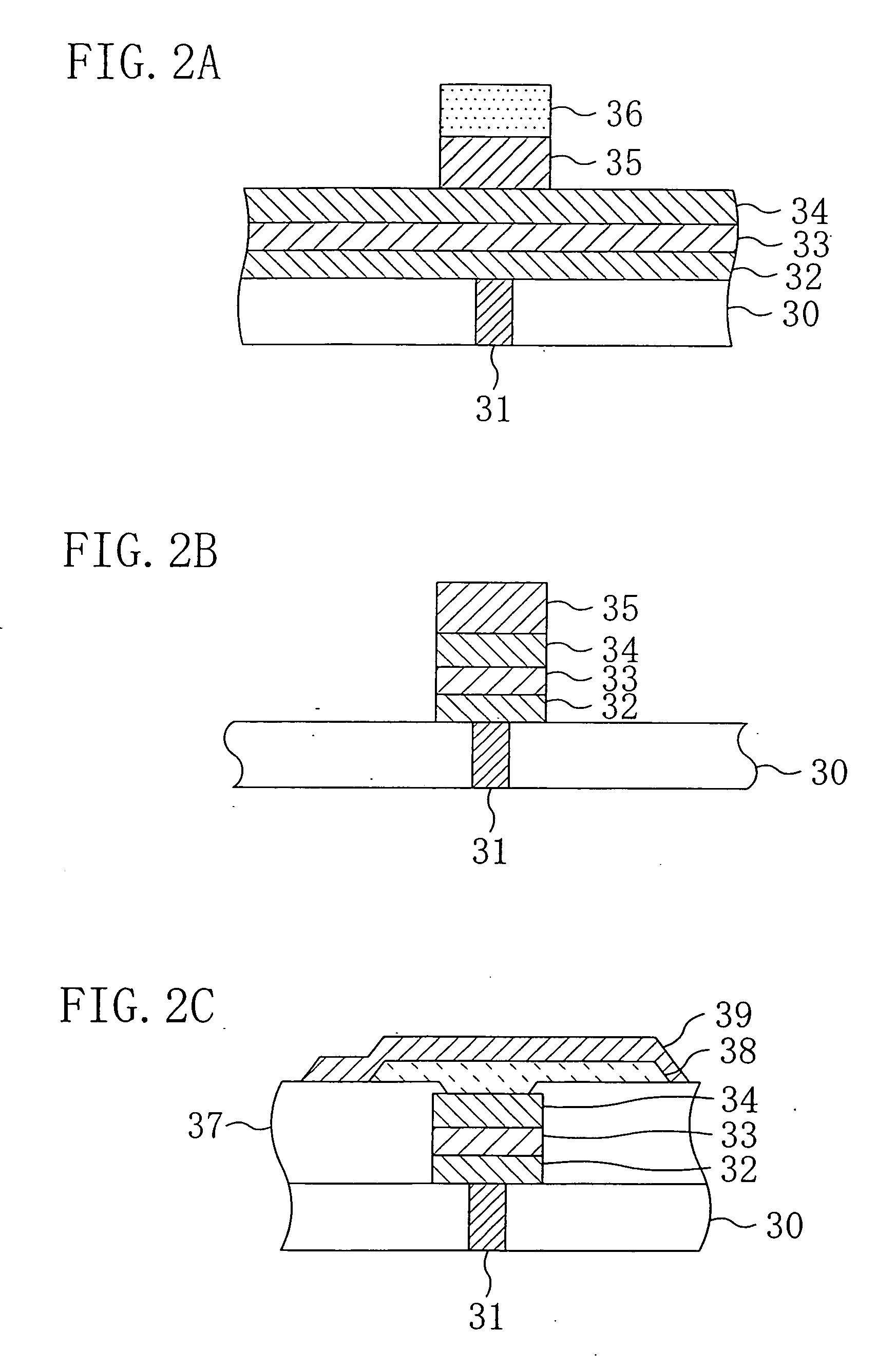
[0066]FIG. 4A is a view illustrating a schematic configuration of a plasma etching apparatus according to the second embodiment of the present invention. The plasma etching apparatus of the present embodiment allows generation of plasma which couples inductively with an ICP coil and plasma which couples capacitively with an FS electrode. Major features thereof are that the FS electrode moves in a creeping manner along a top plate at the top of a chamber 1 and that a device for monitoring in-situ a deposit adhered to the top plate (etching reaction product) is provided. That is, according to the etching process of the present invention, the etching is carried out while the step is repeated of specifying a position on the top plate where the reaction product is adhered by the in-situ monitoring ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| boiling point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| frequency | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com