Method of extracting sucrose esters from oriental tobacco
a technology of sucrose esters and oriental tobacco, which is applied in the field of extracting sucrose esters from oriental tobacco, can solve the problems of undesirable, overpowering the characteristics of the smoke of those tobaccos, and increasing the amount, and achieves the effects of enhancing the solvating power of the fluid, enhancing the selectivity of the extraction of sucrose esters, and high fluid pressur
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Extraction Procedures
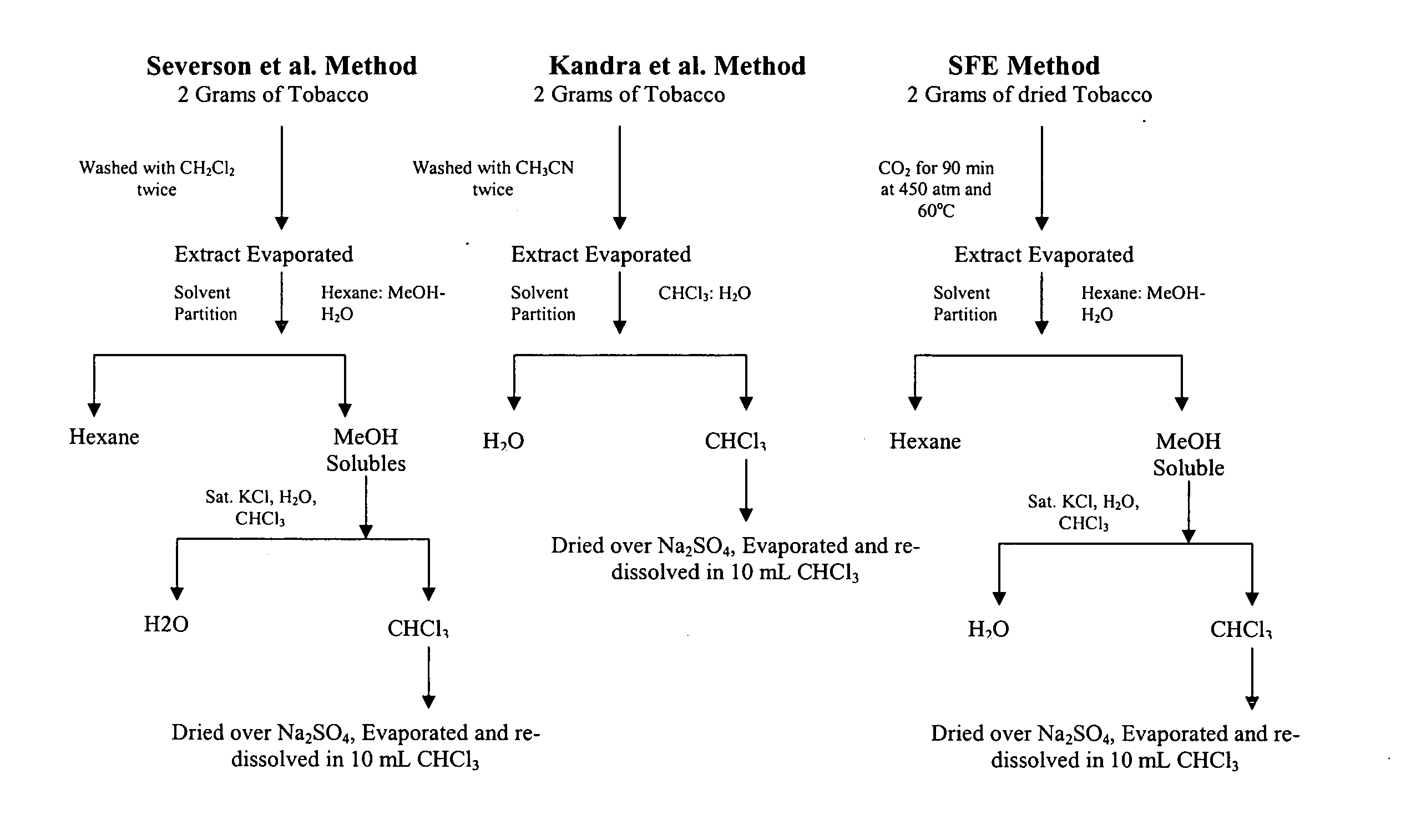
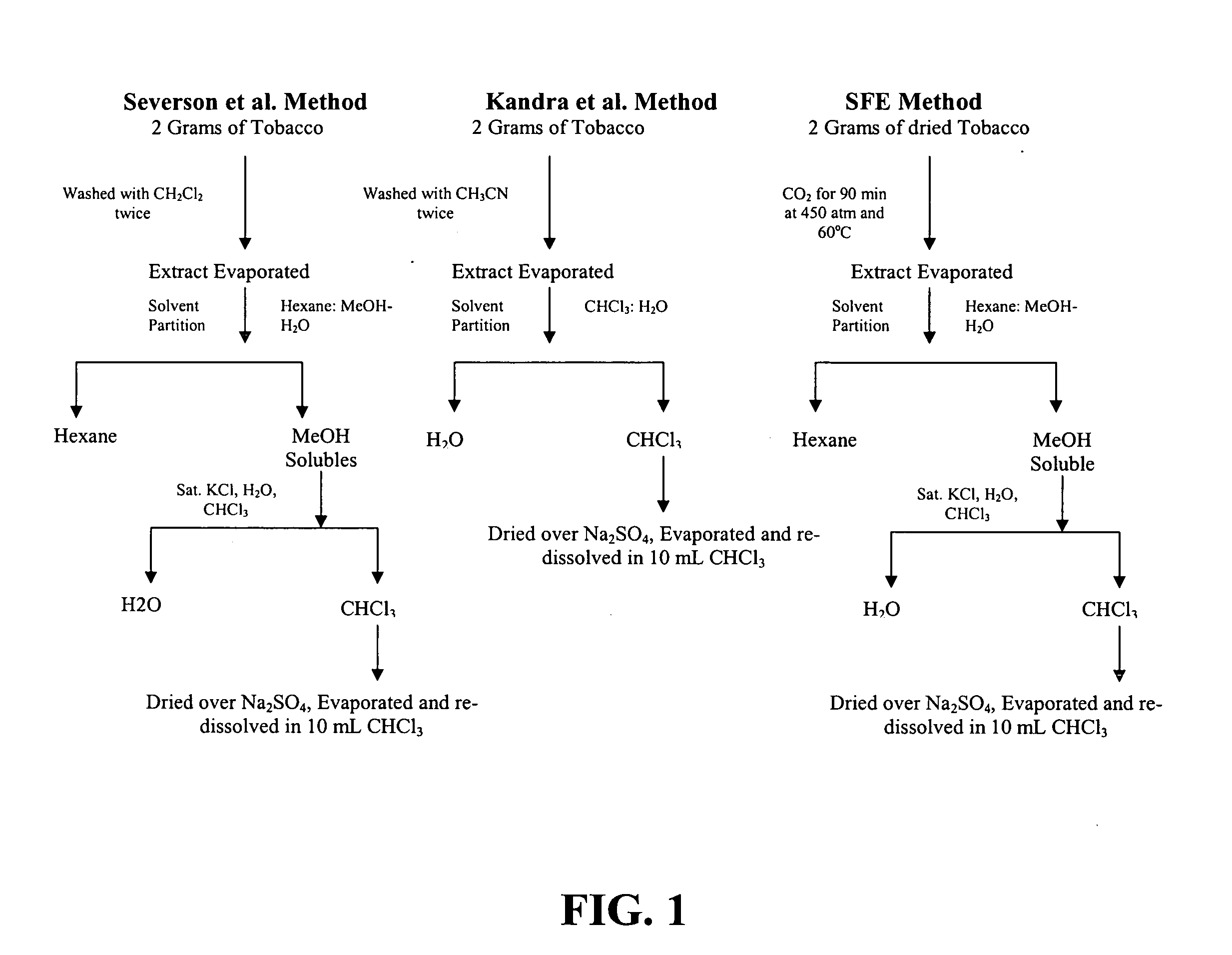
[0045] Three different extraction procedures are used to extract and isolate SE from tobacco, each of which is set forth in FIG. 1. Two of the extraction methods substantially replicate prior art methods of extracting SE from Oriental tobacco. In the first extraction method, listed as the Severson method in FIG. 1, 2 grams of tobacco are transferred into a 100-mL bottle fitted with a Teflon coated cap. Then, 20 mL of CH2Cl2 is added to the bottle and the sample was manually shaken for 3-5 minutes. The solution is filtered using a type 1 filter paper (Whatman Co., Maidstone, UK). Next, the residual tobacco and filter paper are transferred into the bottle where tobacco was re-extracted using an additional 20 mL of fresh CH2Cl2. Next, the combined CH2Cl2 extracts are evaporated to dryness using a nitrogen stream. The residue is then partitioned between 20 mL each of hexane and 80 / 20% MeOH—H2O. The MeOH—H2O solution is re-extracted a second time using an additiona...
example 2
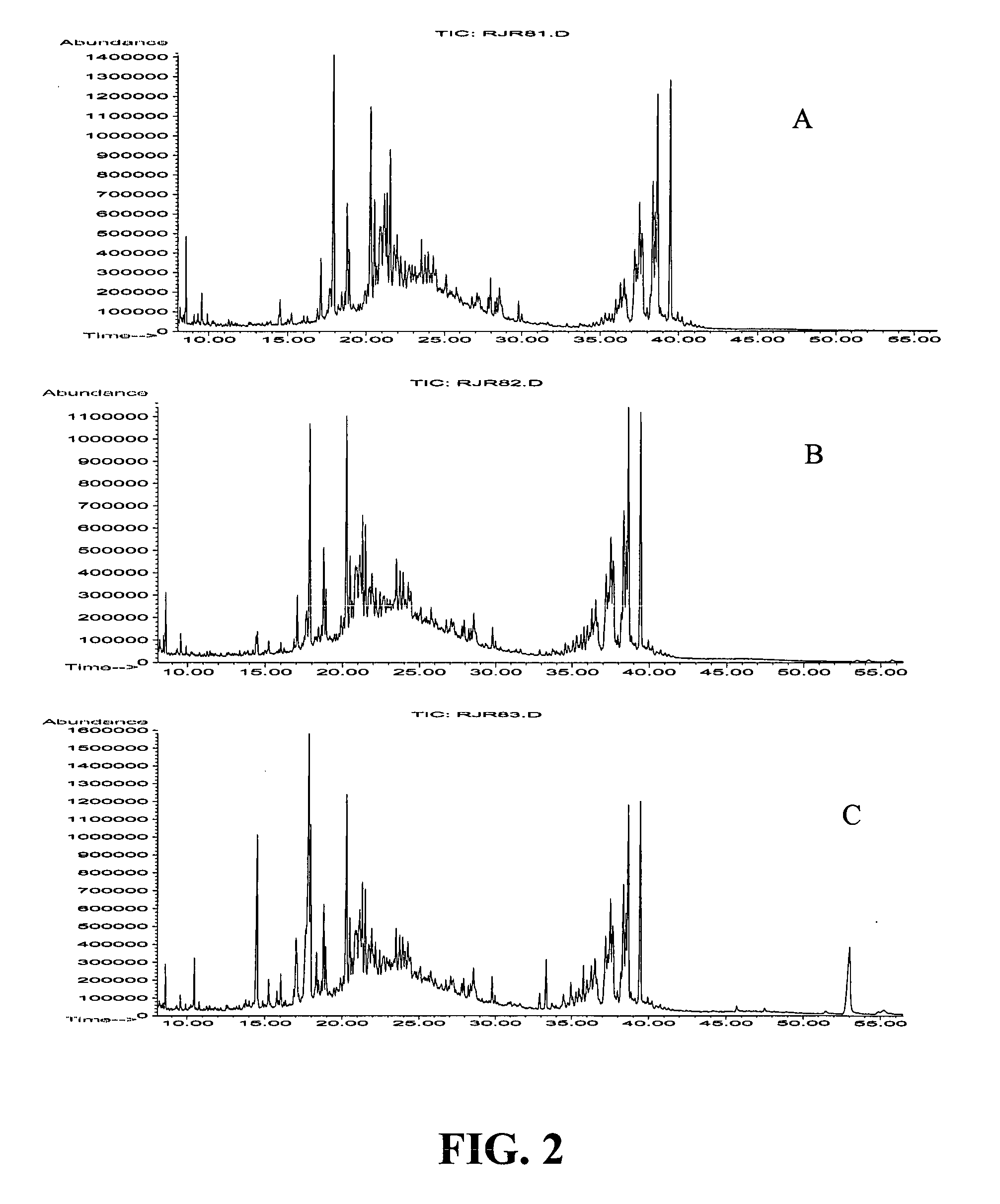
[0054] In this example, SE from a Turkish tobacco is isolated via selective fractionation with no semi-preparative HPLC step. In order to show the feasibility of this process, 2 grams of tobacco is extracted at different pressures and temperatures. In this part of the study, extraction time for each fraction is 75 minutes using 2 mL / min of liquid CO2. First, the tobacco sample is extracted at four pressures (150, 200, 350 and 450 atm) and two temperatures. No modifier is used since all SE are extractable with pure C02. FIG. 5 shows the GC / MS traces of the various derivatized fractions at 60° C. As can be observed, at 150 atm (FIG. 5A), no SE is extracted. When the CO2 pressure is systematically increased, however, from 150 to 200 and 350 atm (FIG. 5B and 5C), a mixture of SE's begins to appear in the extract at retention time ˜35-40 minutes. At 450 atm, after continuous extraction of the same sample at the three lower pressures, a relatively small amount of SE is observed in this ex...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com