Fluid transportation device
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
first embodiment
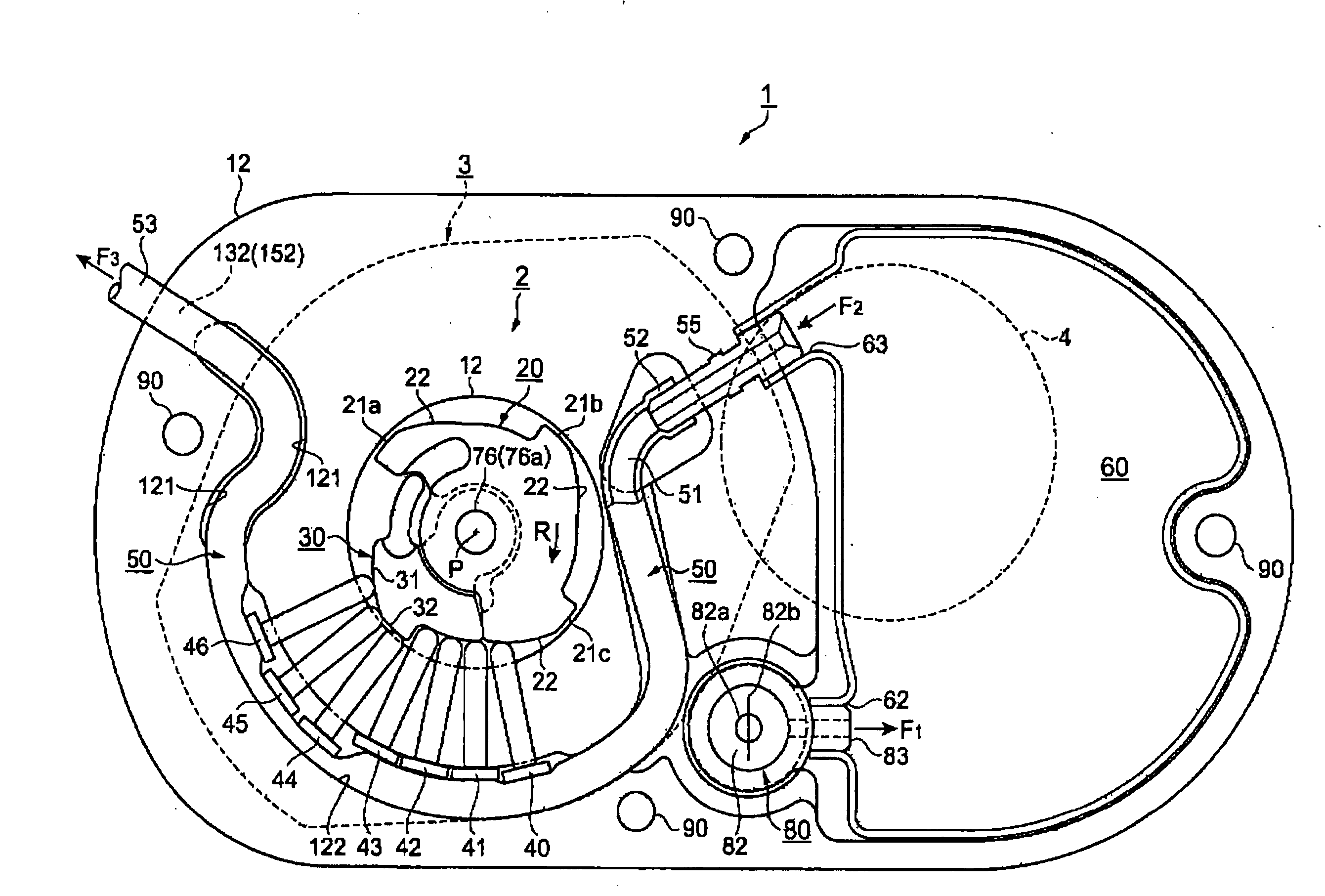
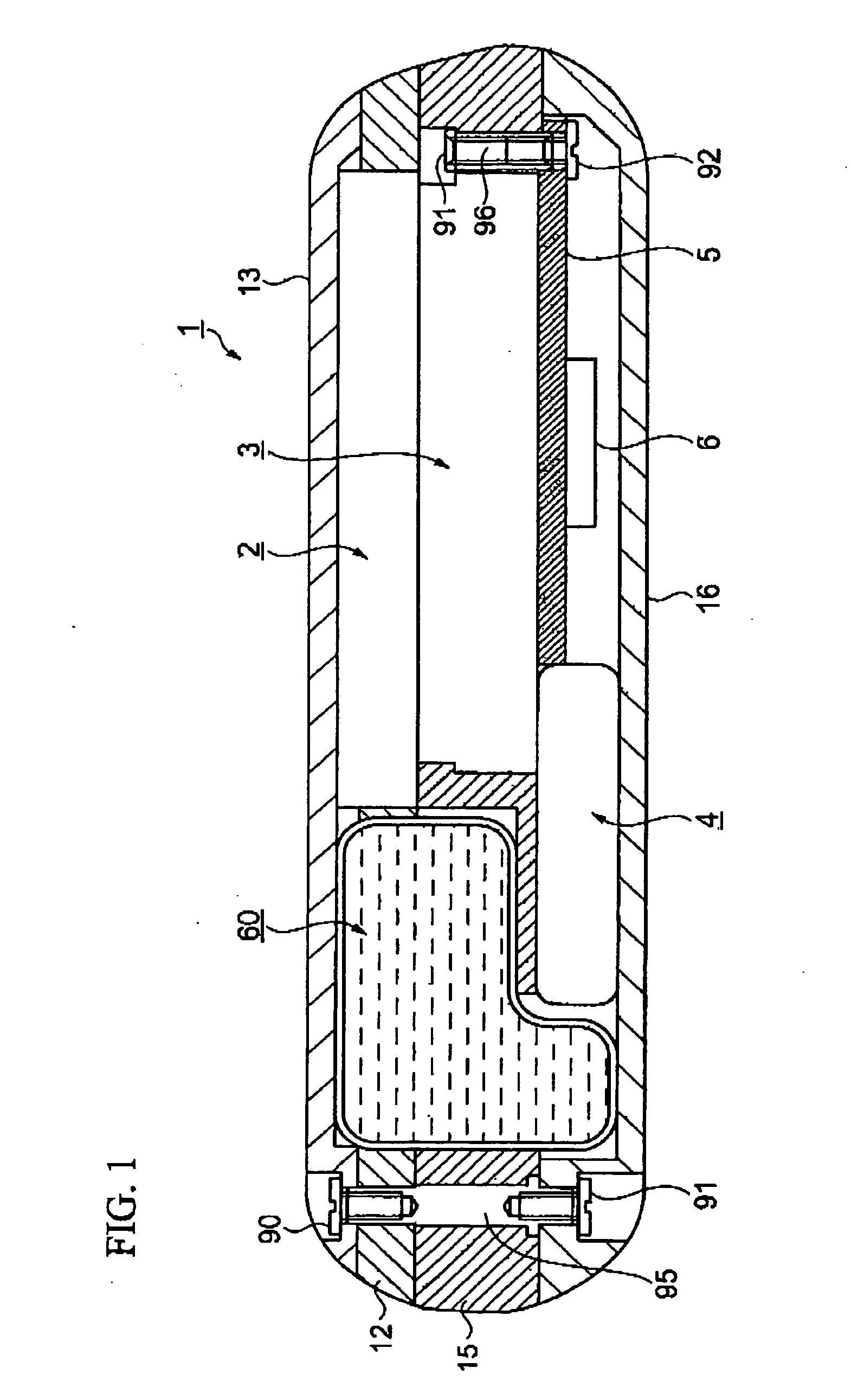
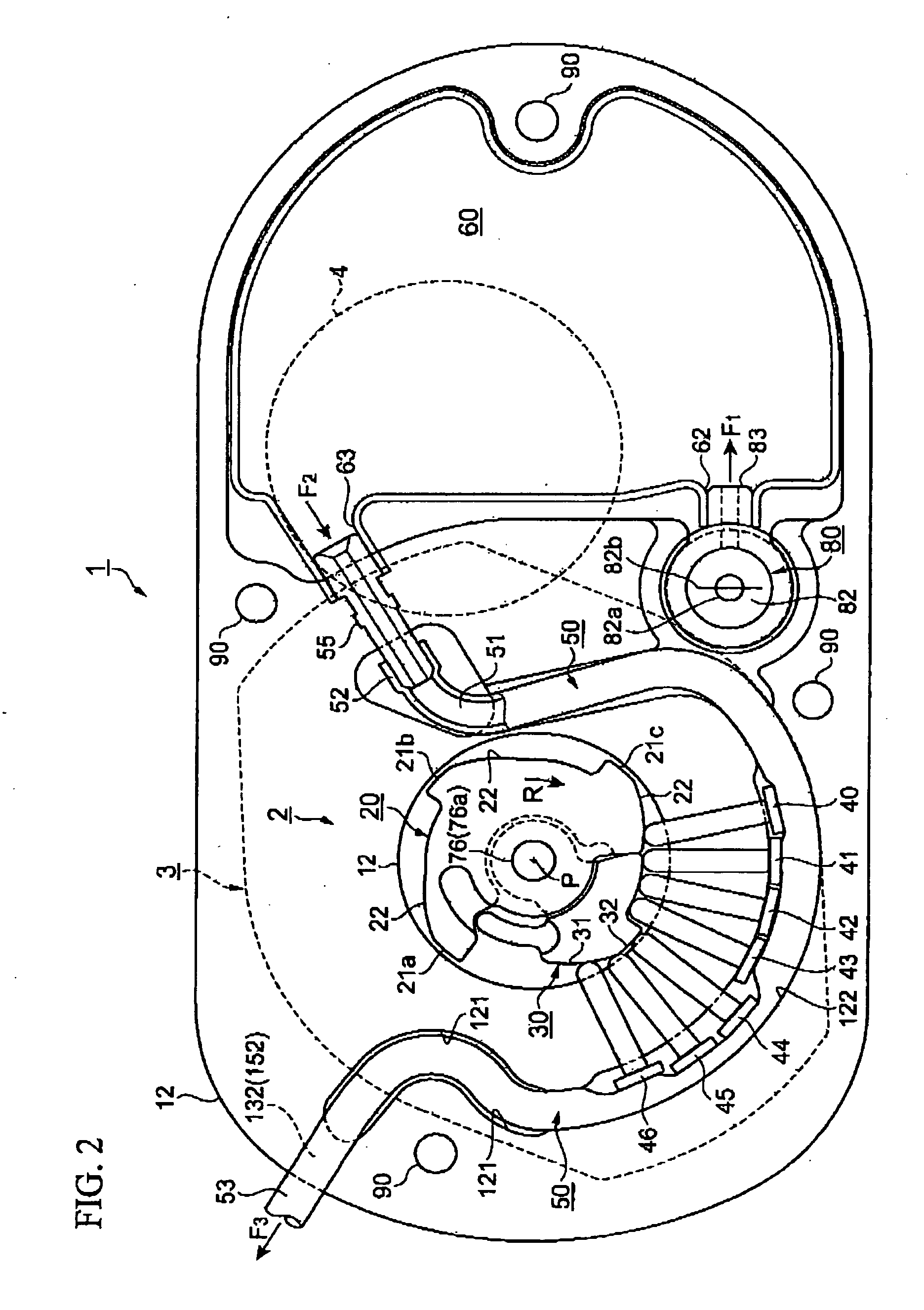
[0237] FIGS. 1 to 6 show a fluid transportation device according to a first embodiment of this invention.
[0238]FIG. 1 shows an arrangement in a thickness direction, FIG. 2 shows the arrangement in a plan view direction, FIG. 3 is a plan view of a watch movement that is employed as a driving force transmission mechanism, FIG. 4 is a cross-sectional view of portions of the driving force transmission mechanism and a fluid transport mechanism, FIG. 5 is a cross-sectional view of a structure related to injection and outflow of a fluid, and FIG. 6 is a plan view of the fluid transport mechanism.
[0239] With the present embodiment, a fluid transportation device that is implanted in a living body of a human being, animal, etc., and uses a drug solution as a fluid shall be described as an example.
[0240] Gel-like fluids and gases are included in the definition of “fluid.”
[0241]FIGS. 1 and 2 are respectively a cross-sectional view and a plan view of the basic arrangement of a fluid transport...
second embodiment
[0389] FIGS. 7 to 9 show a fluid transportation device according to a second embodiment of this invention.
[0390]FIG. 7 shows an arrangement in a planar direction.
[0391]FIGS. 8A and 8B are diagrams of arrangements in a thickness direction, with FIG. 8A being a diagram as viewed from a narrow width side and FIG. 8B being a diagram as viewed from a wide width side.
[0392]FIGS. 9A to 9C are diagrams of a reservoir frame, with FIG. 9A being a plan view, FIG. 9B being a front view, and FIG. 9C being a side view.
[0393] The present embodiment is the same as the first embodiment in that a fluid transportation device, which is implanted in a living body of a human being, animal, etc., and uses a drug solution as a fluid, is described as an example, although gel-like fluids as well as gases are also included in the meaning of “fluid.”
[0394] The main points of difference of a fluid transportation device 160 according to the second embodiment shown in FIGS. 7 and 8 with respect to the fluid t...
third embodiment
[0454] As the third embodiment of this invention, a drug solution feeder (fluid transportation device) for implantation under the skin of an experimental animal shall be described.
[0455] Here, a drug solution is used as the fluid, and the implantation subject is an experimental animal.
[0456]“Experimental animal” refers to a small animal, such as a mouse, rat, guinea pig, etc., on which an animal experiment concerning the drug solution can be performed.
[0457]“Drug solution” refers, for example, to a medical liquid or nutrient liquid or to any liquid for performing an animal experiment for development of such liquids or performing a medical treatment on an animal.
[0458]FIGS. 10A to 10D are external views of the drug solution feeder for implantation under the skin of an experimental animal.
[0459]FIG. 10A is a lower side view as viewed from a lower side of the drug solution feeder and is a side view as viewed from the nearer side of the paper surface of FIG. 12, FIG. 10B is an uppe...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com