Powered sterile solution device
a sterile solution and water purification device technology, applied in the direction of disinfection, chemical/physical/physical-chemical processes, energy-based chemical/physical/physical-chemical processes, etc., can solve the problems of limited production capacity of existing water purification devices that produce pharmaceutical grade water in remote locations, complicated medicament preparation in the field or under sub-optimal conditions,
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
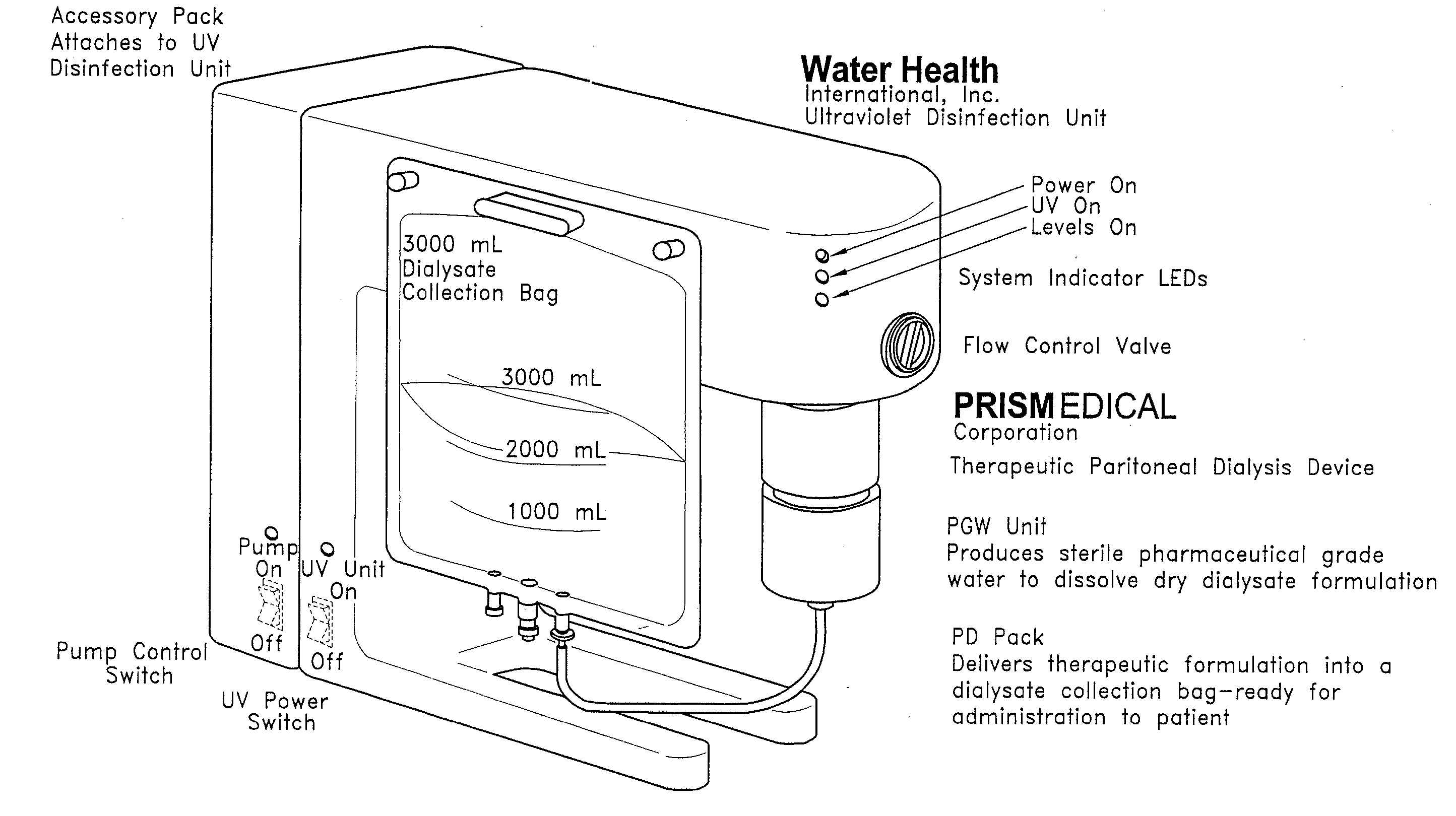
[0021] While the illustrated embodiments are described in the context of particular formulations and relative proportions of reagents, the skilled artisan will find application for the described methods and devices in a variety of different formulations and proportions of reagents. Examples of these uses and solutions include, but would not be limited to, sterile water for injection or irrigation, sterile solution diluent for intravenous solutions, vaccines, oral re-hydration solutions, medical grade drinking water and intravenous drug delivery.
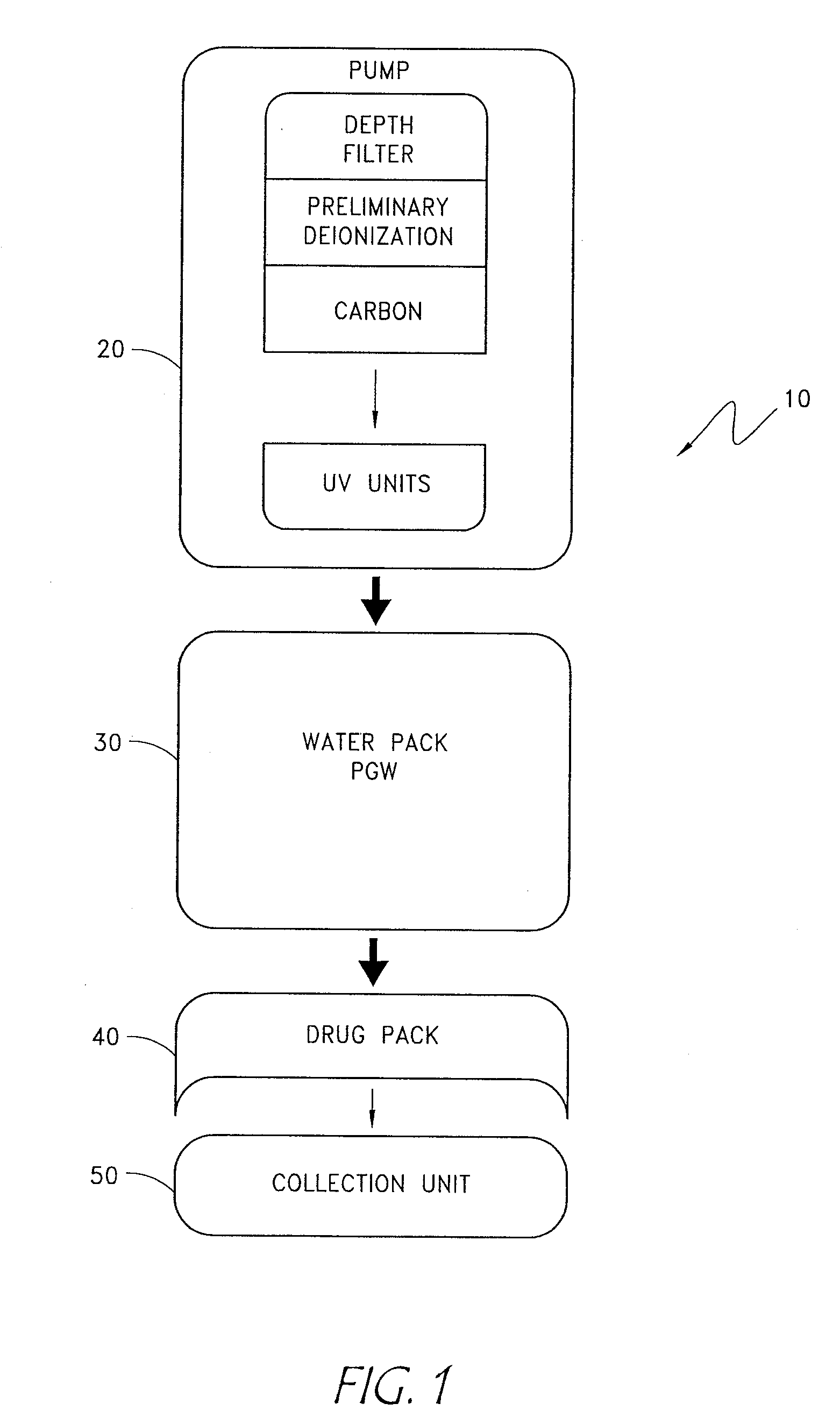
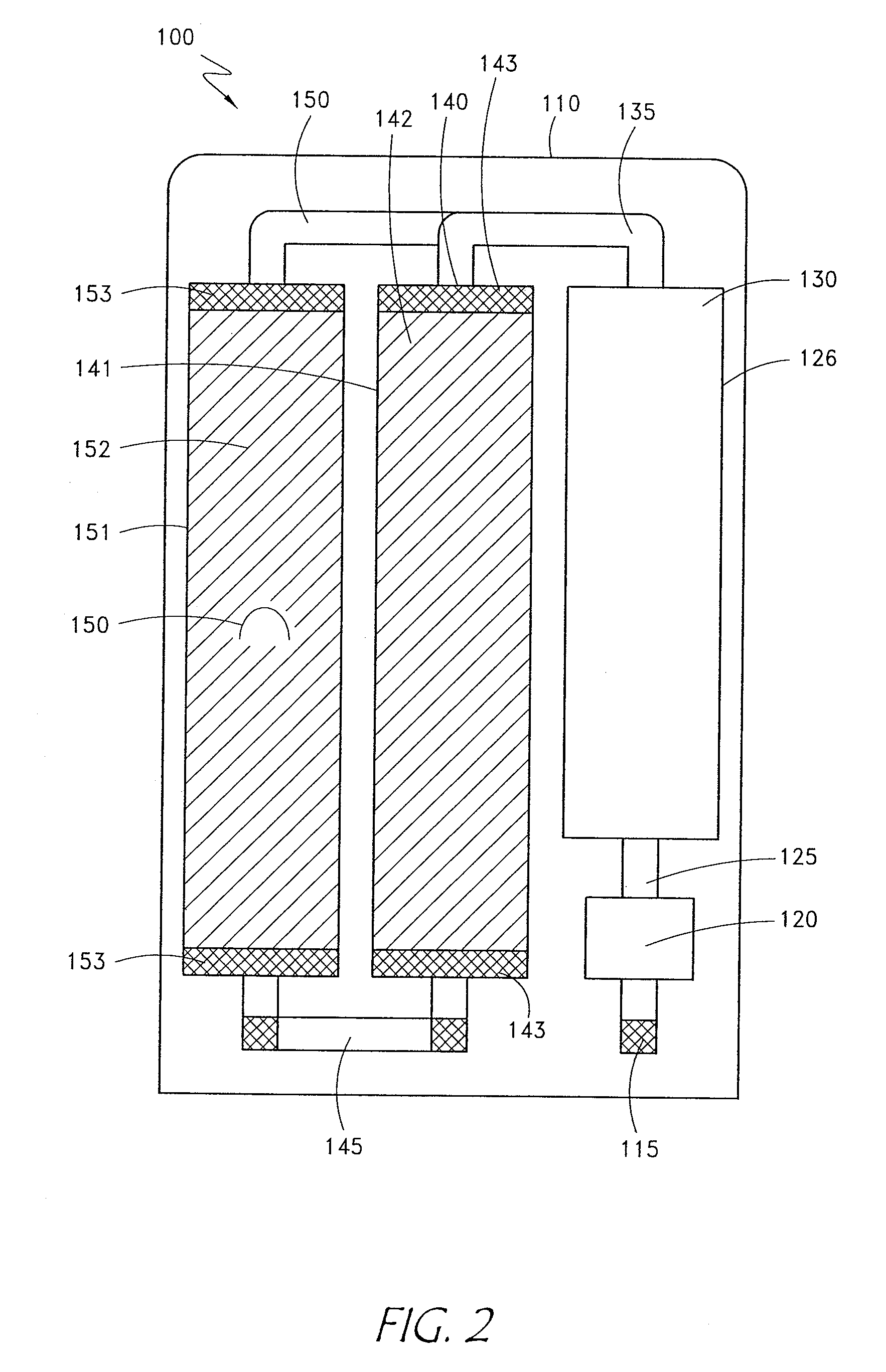
[0022] The apparatus and methods disclosed below provide the means by which to purify otherwise unpurified water available from the vast majority of water sources to a level of quality sufficiently high (pharmaceutical grade) for use in production of medical therapeutic solutions, then utilizes reagent delivery components to produce therapeutic solutions. A preferred embodiment consists of a preliminary filtration component, a purification c...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| wavelength range | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com