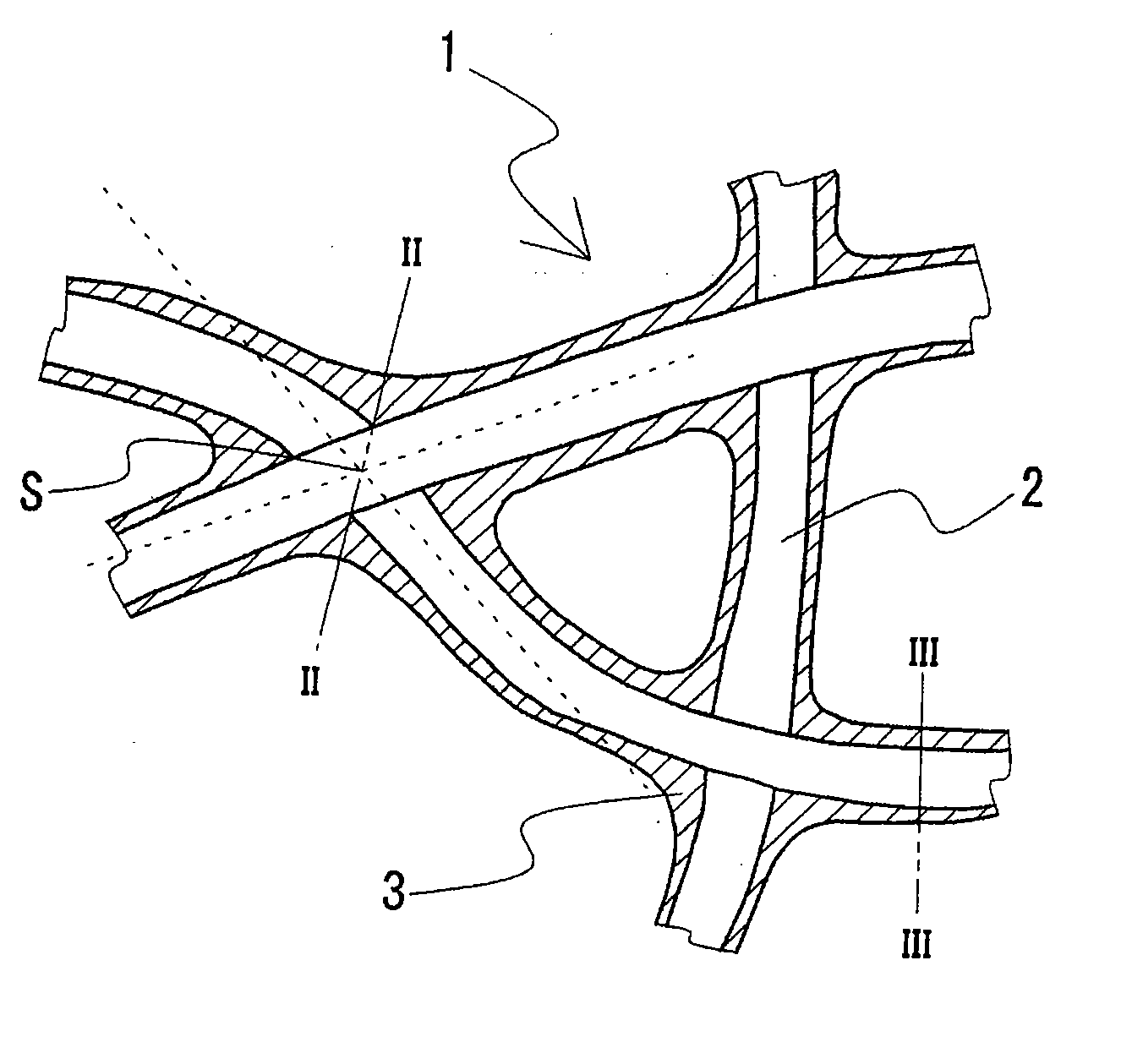
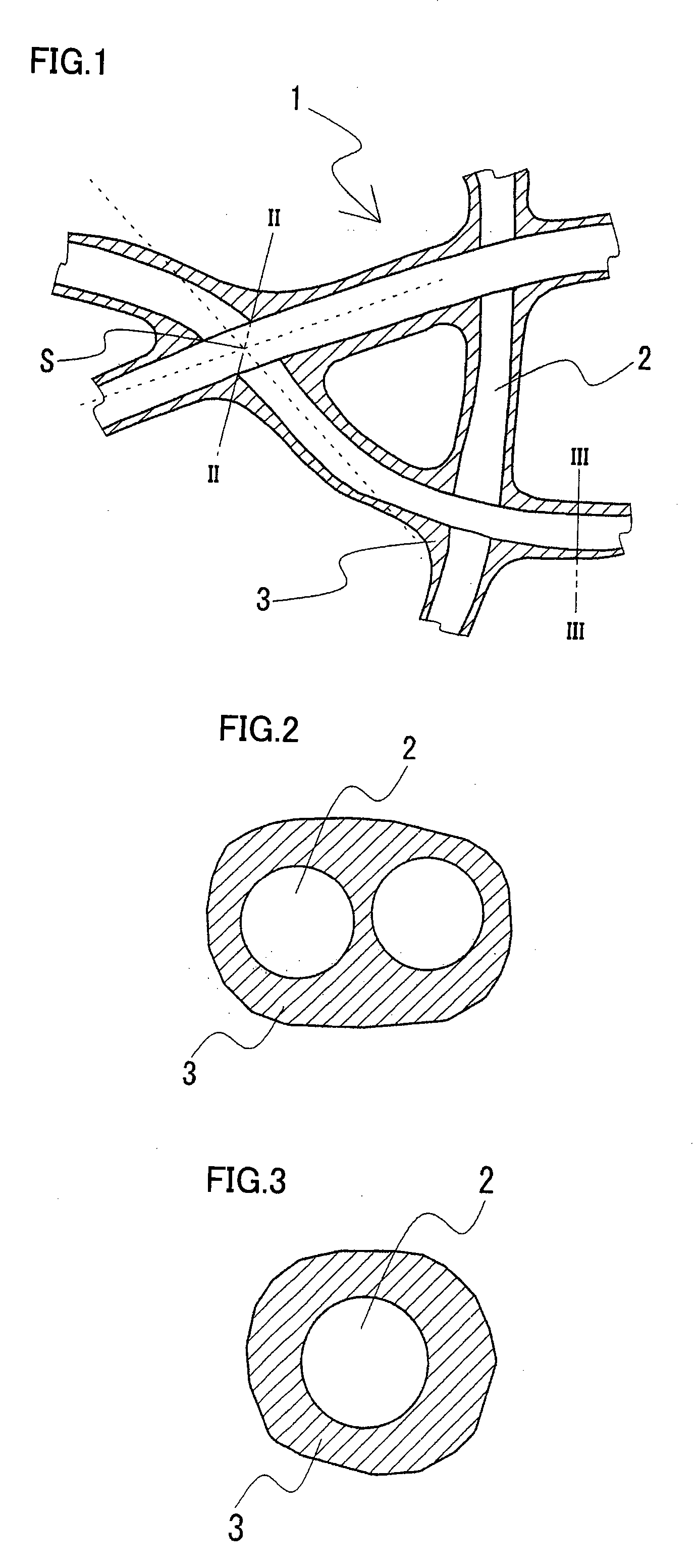
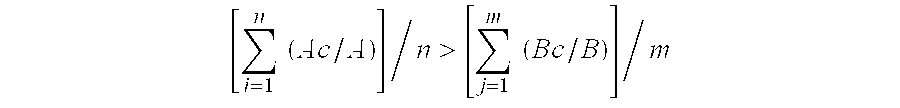Battery electrode substrate, and electrode employing the same
a battery electrode and electrode technology, applied in the direction of basic electric elements, non-aqueous electrolyte accumulator electrodes, cell components, etc., can solve the problems of nickel foam that has not yet reached the stage of practical use, nickel foam that has the problem of easy damage, cracks in nickel foam, etc., and achieves less likely to reduce the effect of capacity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0072] Example 1 corresponds to an electrode substrate having a nonwoven base coated with nickel. A plurality of electrodes were produced with different thickness of the electrode substrate and different compression ratio on the electrode substrate. The active material introduced into the electrode substrate was an active cathode material for a nickel-hydrogen battery. The produced electrode was an electrode destined for a nickel-hydrogen battery.
[0073] In the production of a nickel-hydrogen battery, first five nonwoven fabrics were prepared, having the average pore size of 10, 20, 35, 50 and 65 μm. This nonwoven fabric was formed of fibers in a sheath-core structure with the outer circumference of a polypropylene (PP) fiber coated with polyethylene (PE). For the nonwoven fabric, the mass ratio of polypropylene to polyethylene (PP / PE ratio) was 3 / 7, and the thickness was 0.9 mm. Additionally, two nonwoven fabrics (base) having the average pore size of 20 and 50 μm were prepared. Fo...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| pore size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| porosity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| porosity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com