Stabilized Laser Source with Very High Relative Feedback and Narrow Bandwidth
a laser source and relative feedback technology, applied in the direction of lasers, laser details, electrical equipment, etc., can solve the problems of reducing low-frequency power fluctuations, contributing significantly to the complexity and cost of laser sources, and none of the above prior art addresses the solution of high-power (i.e. >100 mw) laser sources, which are capable of stable, and achieve low-noise amplification, avoid complicated signal conversion, and improve speed and reliability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
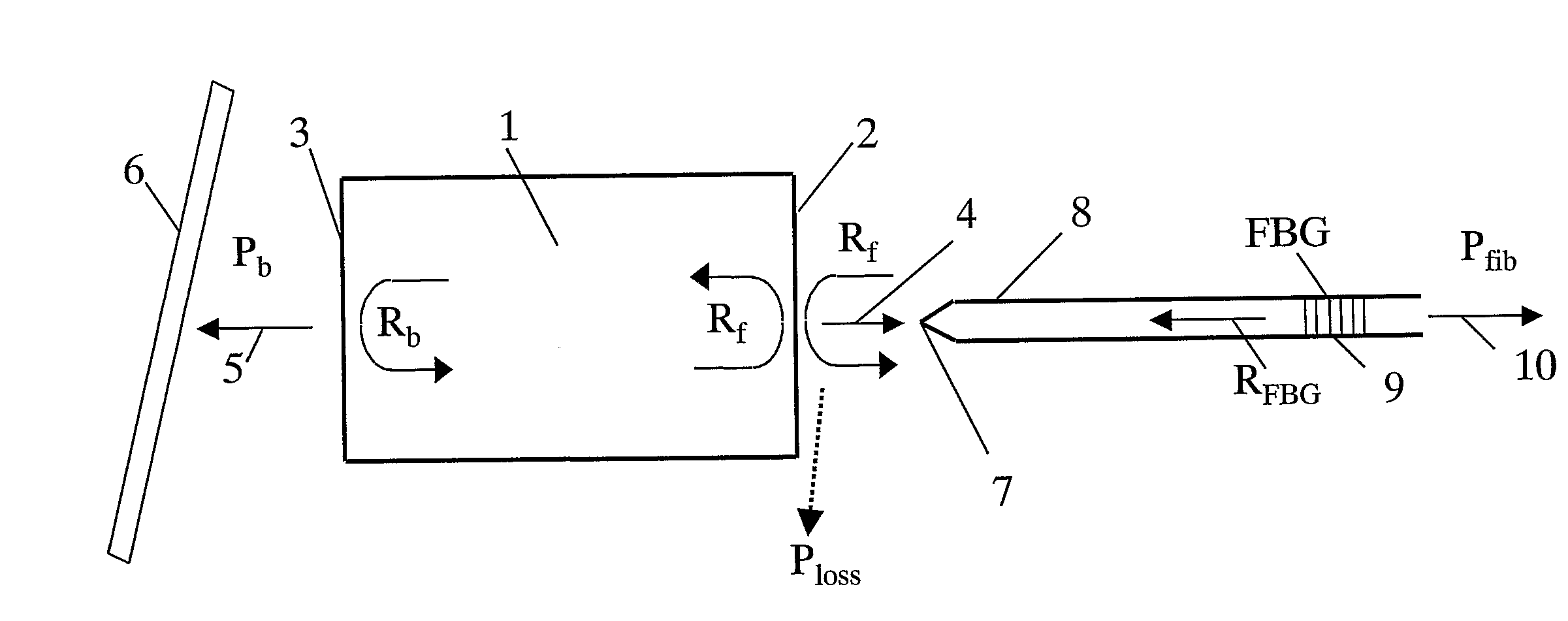
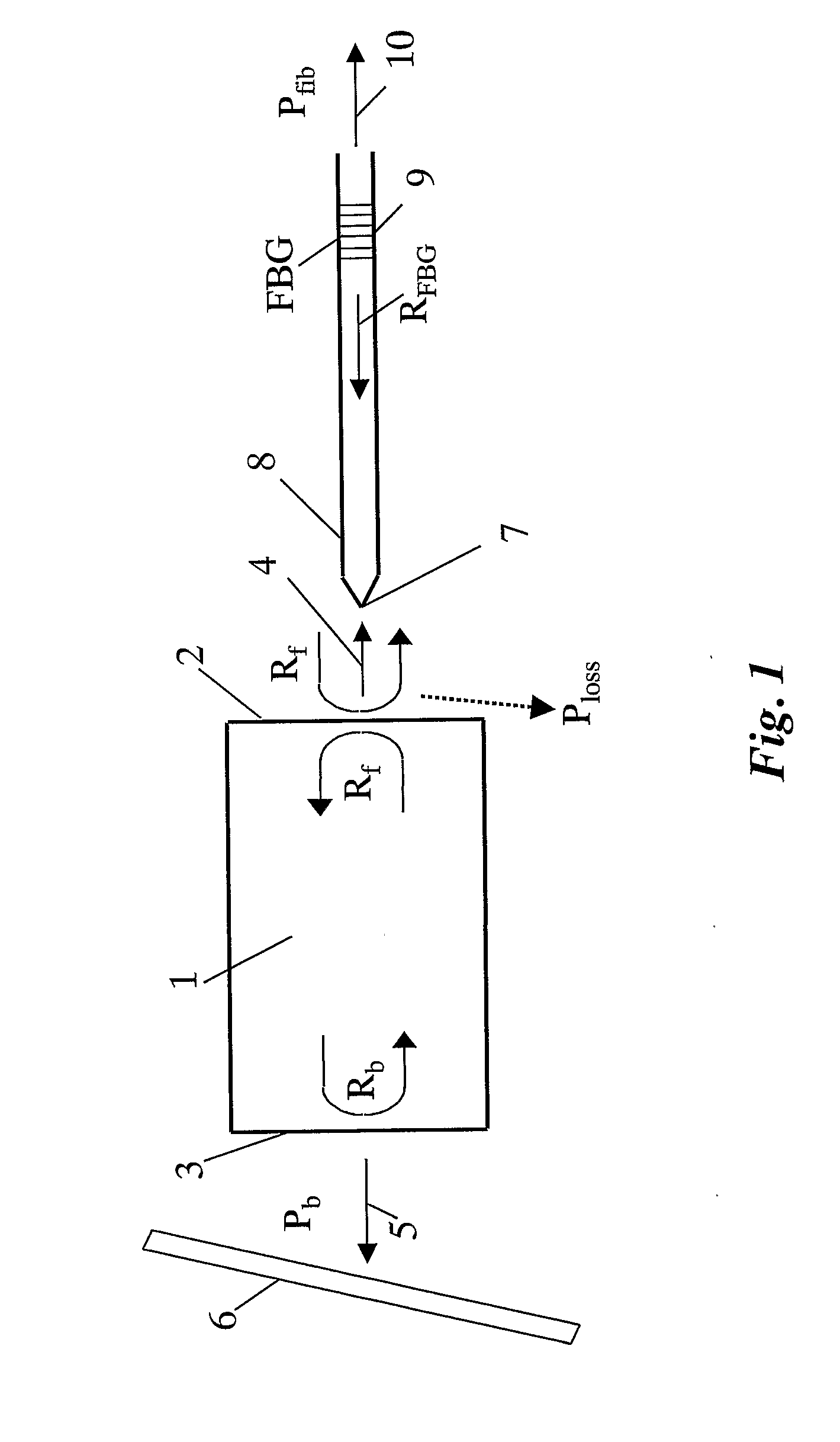
[0037]FIG. 1 shows the basic layout of a first and preferred embodiment according to the invention. A semiconductor laser diode 1, e.g. a high-power laser diode operating at a wavelength of approximately 980 nm, generates a laser beam 4 that is emitted predominantly from the front facet 2. At the back facet 3 with a reflectivity Rb, a low intensity laser light beam 5 with a power Pb is also emitted, which beam is detected by a monitoring photodiode 6. As known in the art, the monitoring photodiode 6 converts the received light to a back facet monitoring (BFM) current for controlling the laser diode's injection current in a feed-back loop.
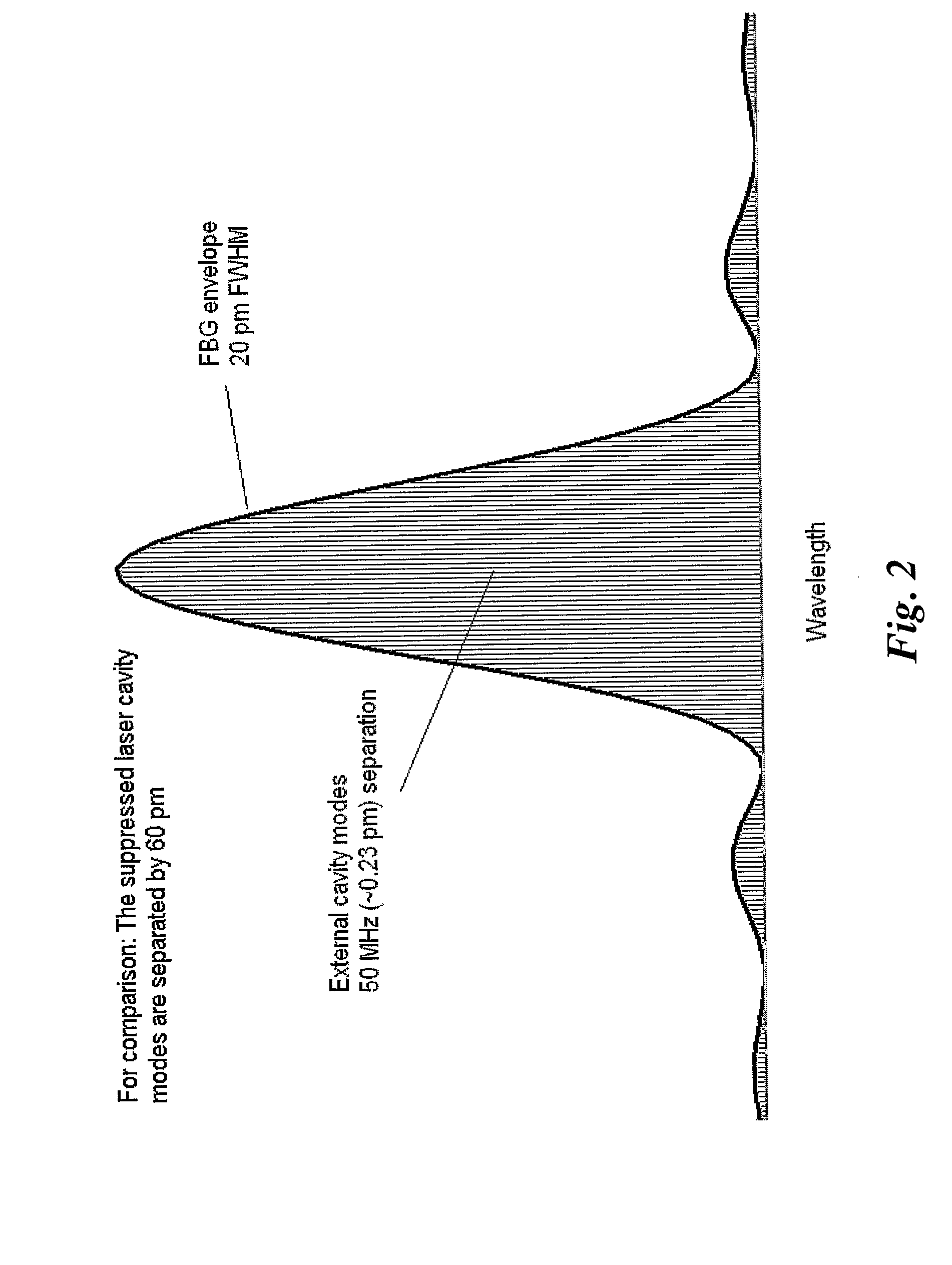
[0038]The laser beam 4 exiting the laser diode's front facet 2 is coupled into a suitable guide means 8, preferably an optical fiber, via a fiber lens 7 which focuses the laser beam 4 into the input end of the optical fiber 8. Within the fiber 8, an optical reflector 9, e.g. a fiber Bragg grating (FBG), is provided. The FBG may be fabricated by expo...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com