Protein Design Automation for Protein Libraries
a protein library and protein technology, applied in the field of computational methods, can solve the problems of inability to produce more than a tiny fraction of potential changes, all handicapped, and inability to mutagenesis and functional screening so many mutants
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Computational Prescreening on β-lactamase TEM-1
[0254]Preliminary experiments were performed on the β-lactamase gene TEM-1. Brookhaven Protein Data Bank entry 1BTL was used as the starting structure. All water molecules and the SO42− group were removed and explicit hydrogens were generated on the structure. The structure was then minimized for 50 steps without electrostatics using the conjugate gradient method and the Dreiding II force field. These steps were performed using the BIOGRAF program (Molecular Simulations, Inc., San Diego, Calif.). This minimized structure served as the template for all the protein design calculations.
[0255]Computational Pre-Screening
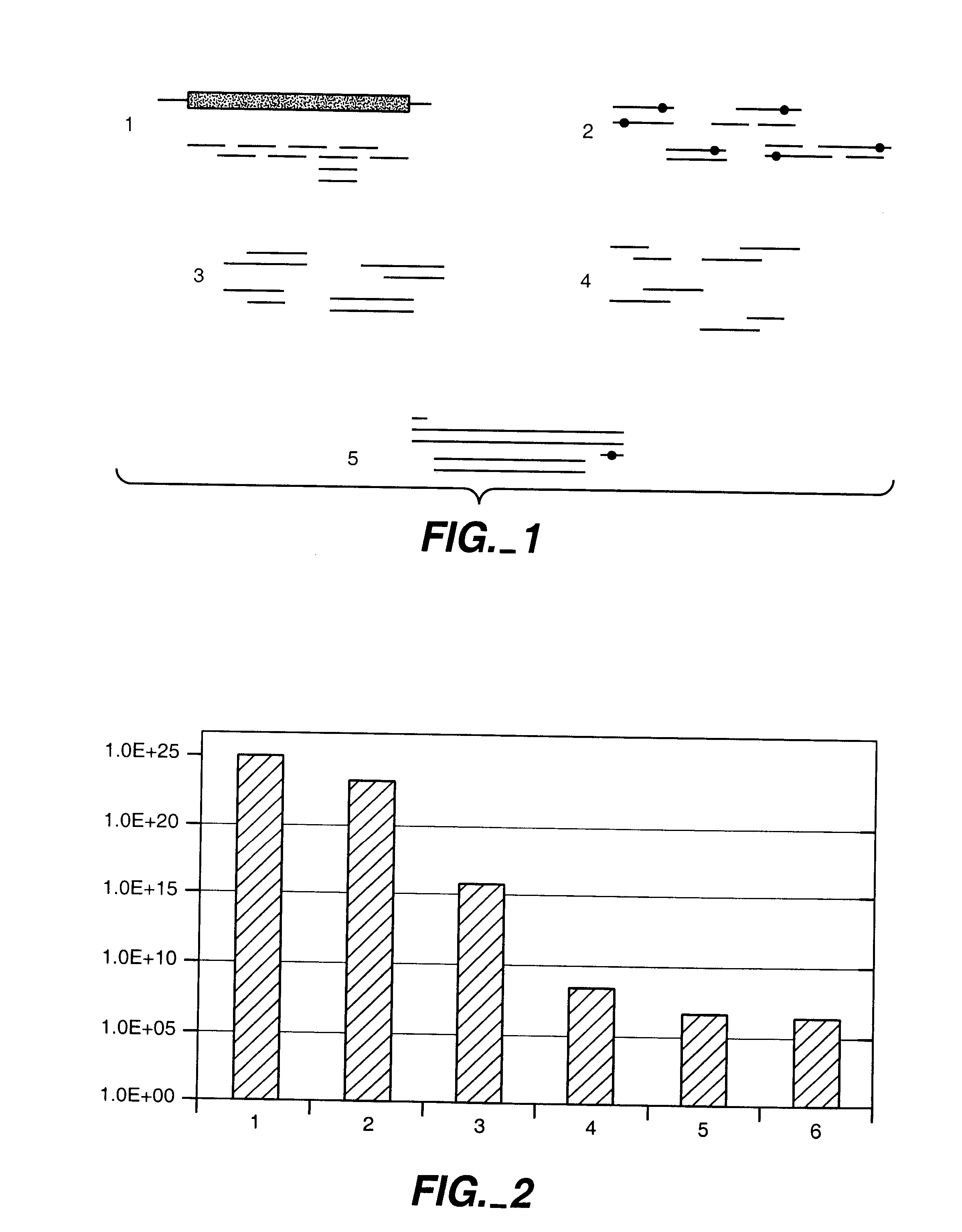
[0256]Computational pre-screening of sequences was performed using PDA. A 4 Å sphere was drawn around the heavy side chain atoms of the four catalytic residues (S70, K73, S130, and E166) and all amino acids having heavy side chain atoms within this distance cutoff were selected. This yielded the following 7 positions: F72, Y1...
example 2
Secondary Library Generation of a Xylanase
[0284]PDA Pre-screening Leads to Enormous Reduction in Number of Possible Sequences
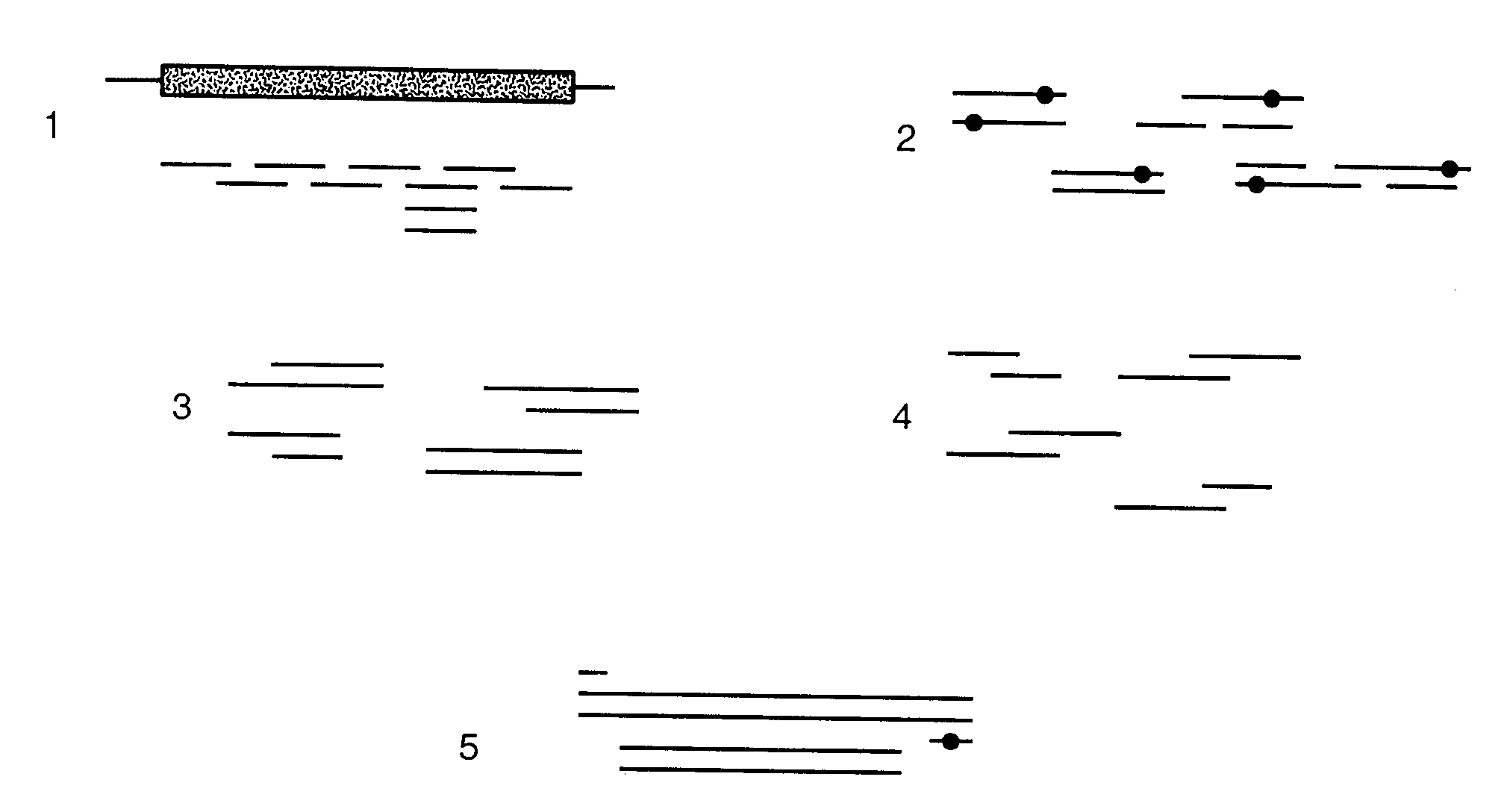
[0285]To demonstrate that computational pre-screening is feasible and will lead to a significant reduction in the number of sequences that have to be experimentally screened, initial calculations for the B. circulans xylanase with and without the substrate were performed. The PDB structure 1XNB of B. circulans xylanase and 1BCX for the enzyme substrate complex were used. 27 residues inside the binding site were visually identified as belonging to the active site. 8 of these residues were regarded as absolutely essential for the enzymatic activity. These positions were treated as wild type residues, which means that their conformation was allowed to change but not their amino acid identity (see FIG. 2).
[0286]Three of the 20 naturally occurring amino acids were not considered (cysteine, proline, and glycine). Therefore, 17 different amino acids were still possib...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| frequency | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| structure | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Structure | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com