Forming Tool
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
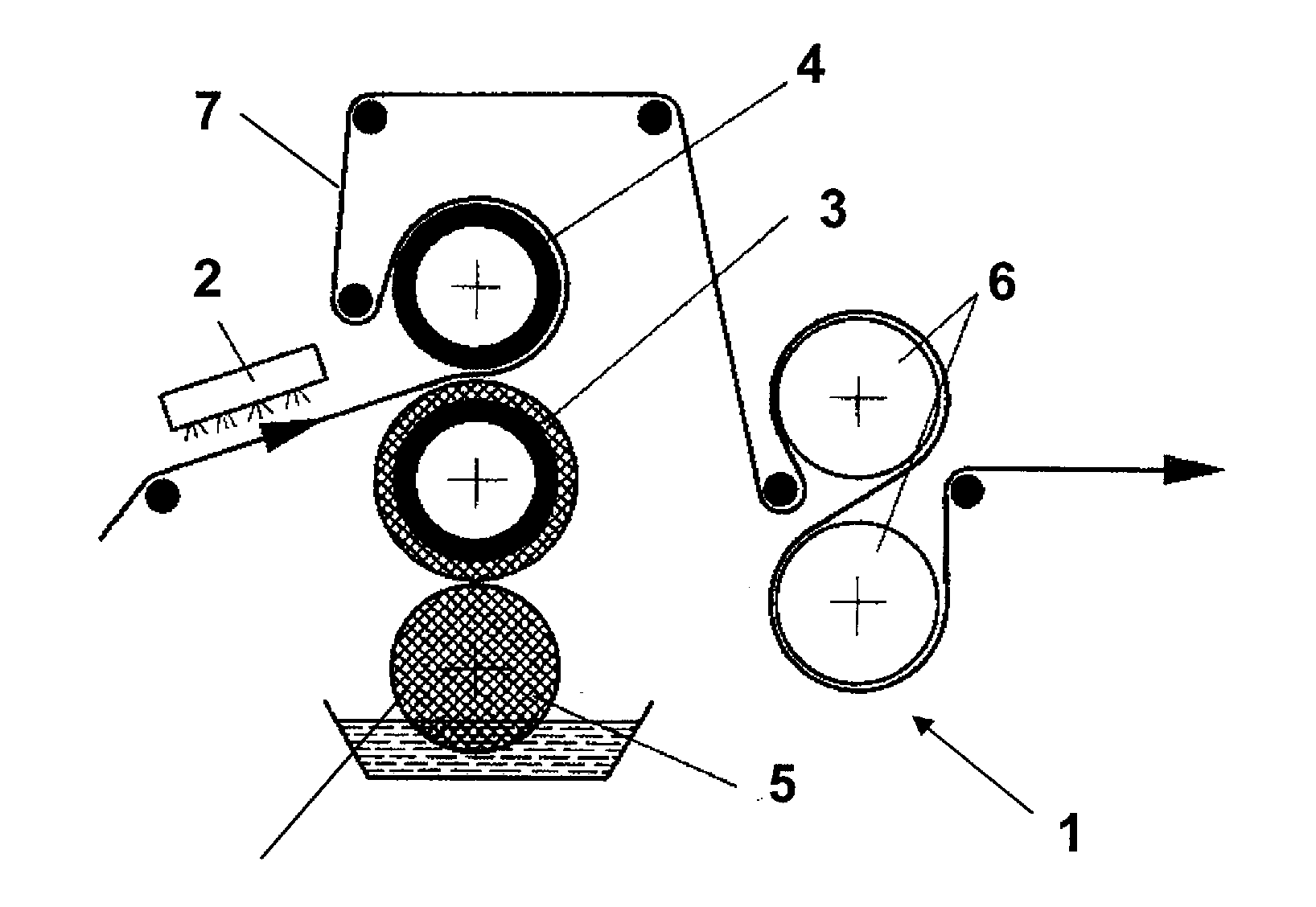
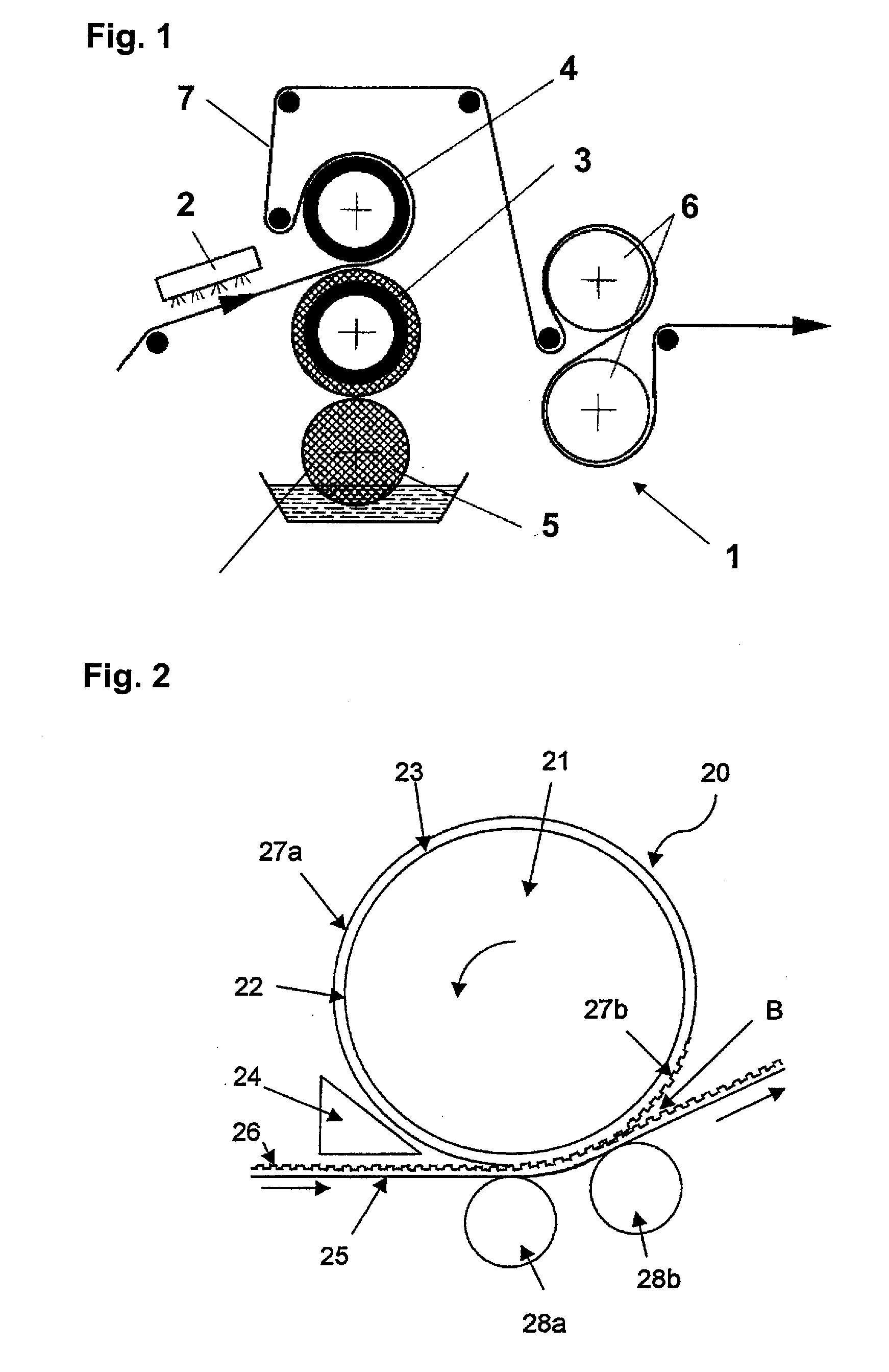
[0066]In FIG. 1 the embossing calender 1 contains an infrared heater 2 to soften the continuous sheet material 7 or at least its surface. The sheet material 7 can be a plastic sheet, or a sheet made of one or more materials other than plastic, coated with a plastic material, in particularly a thermoplastic material. Sheet material can comprise e.g. a metal, reinforcing fibres or fibre fabrics. The softened or melted plastic surface of the sheet material is then embossed by means of a chilled embossing roll 4 coated with metallic glass, which interacts with a second roll 3 producing a counter-pressure to the sheet material 7 passing the roll gap. The calender unit 1 further comprises a cooling roll 5 to cool the counter-pressure roll 3 and cooling rolls 6 to cool the sheet material.
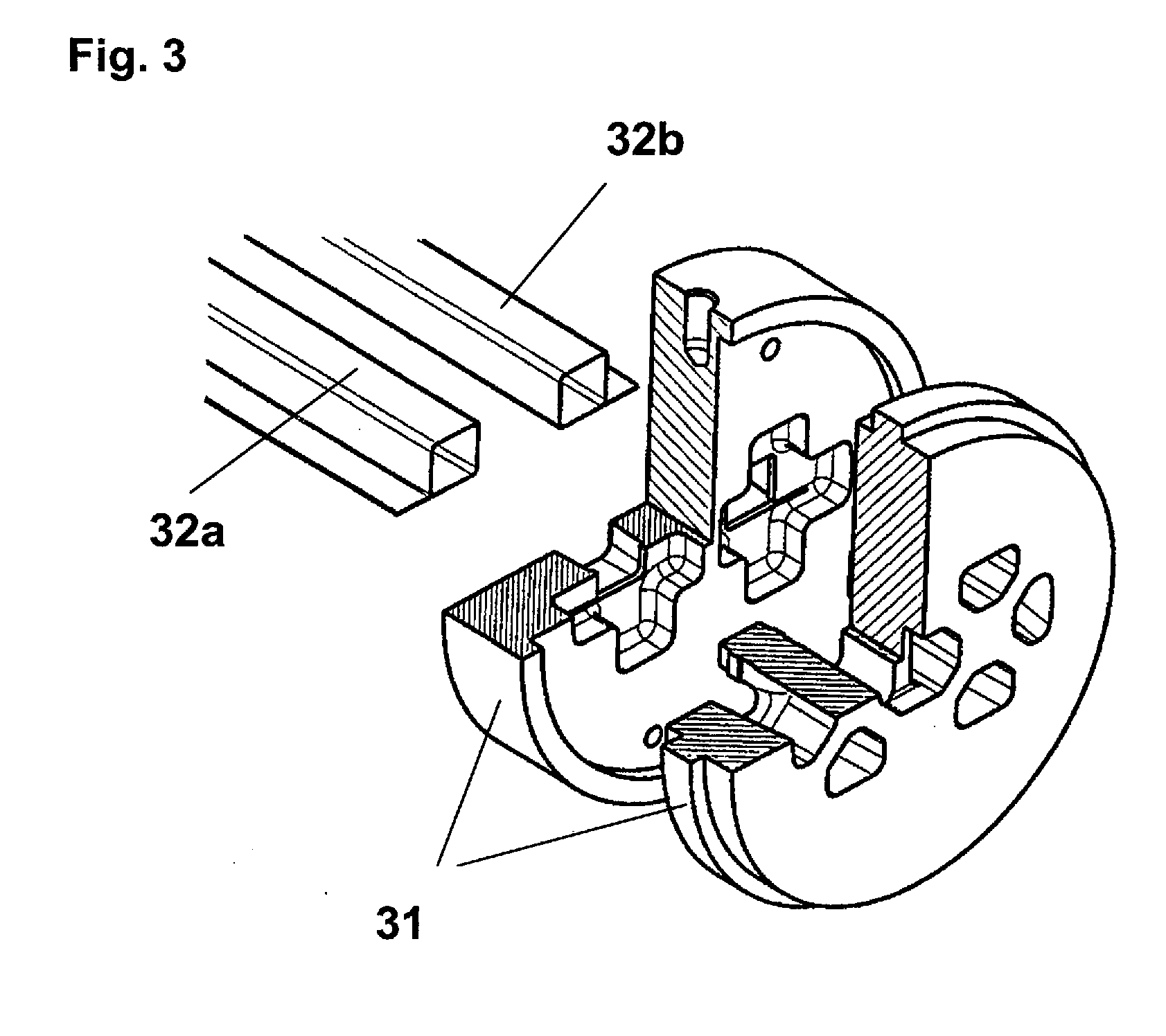
[0067]In FIG. 2 the forming tool 20 is in the form of a cylindrical work roll of a polymer processing unit as e.g. described under FIG. 1. The forming tool 20 comprises a cylindrical substrate 21 and a met...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com