Magnetic wheel
a magnetic wheel and wheel body technology, applied in the field of magnetic wheels, can solve the problems of difficult dislocation and limit to the steepness of the travel path, and achieve the effect of increasing the traction efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
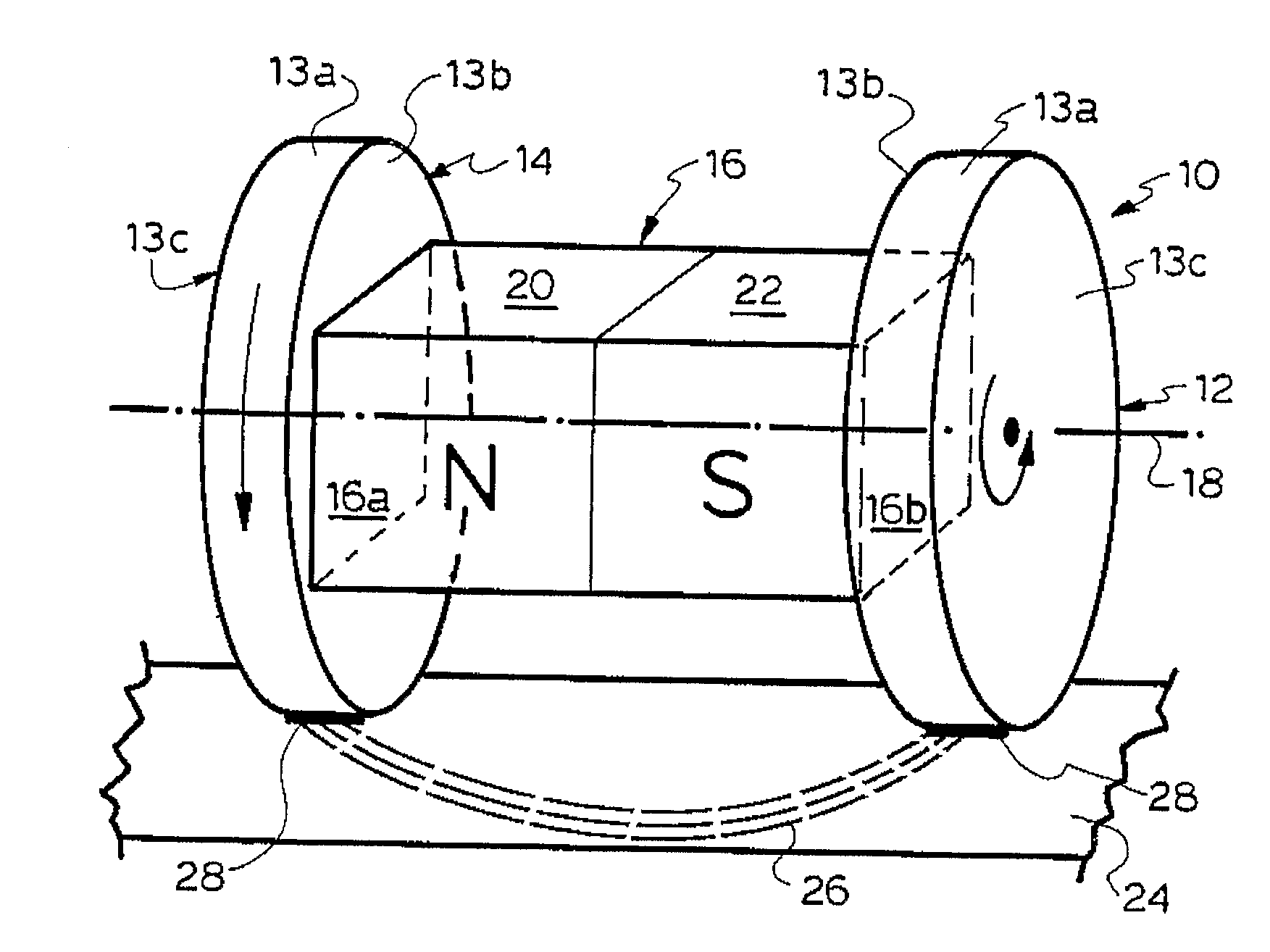
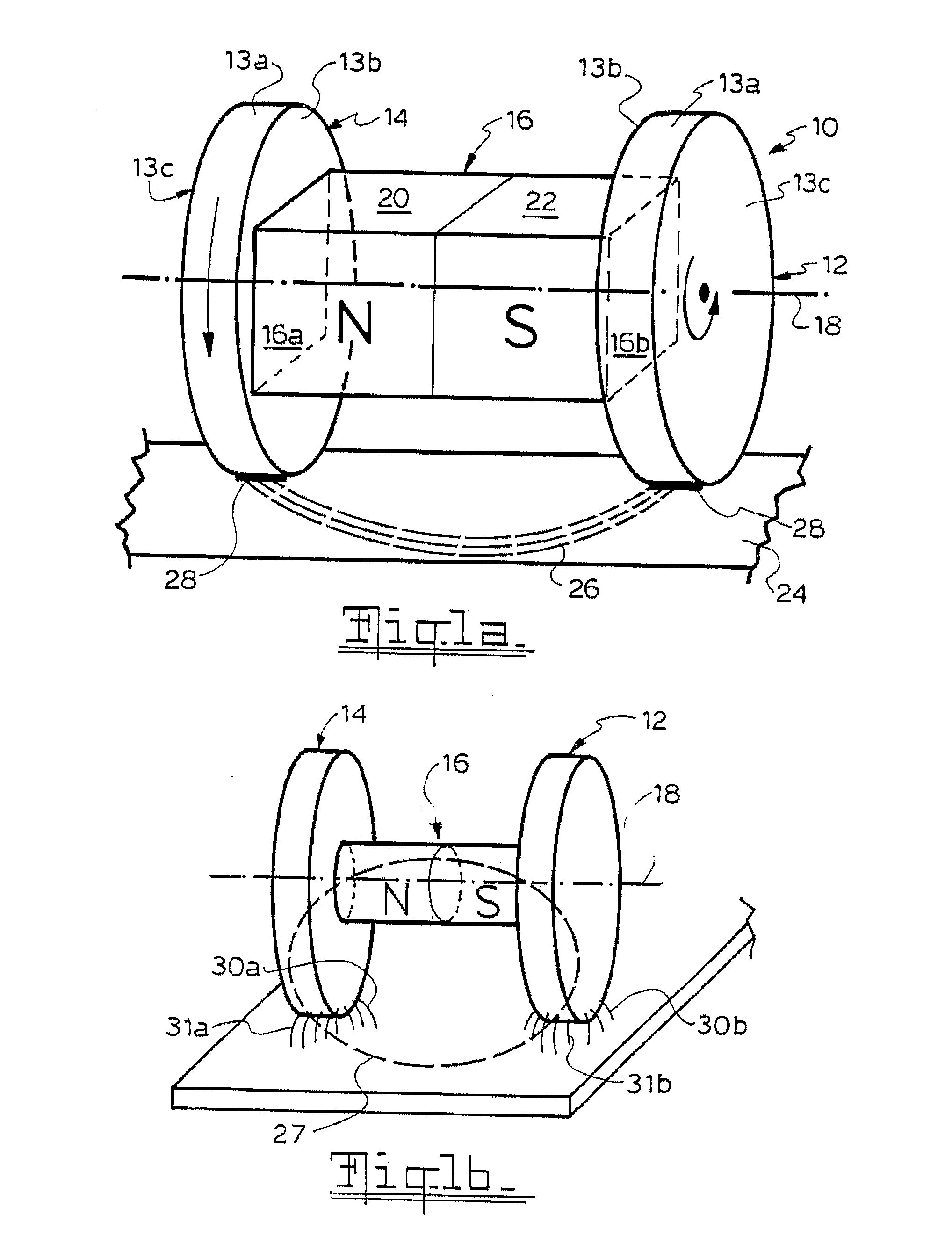
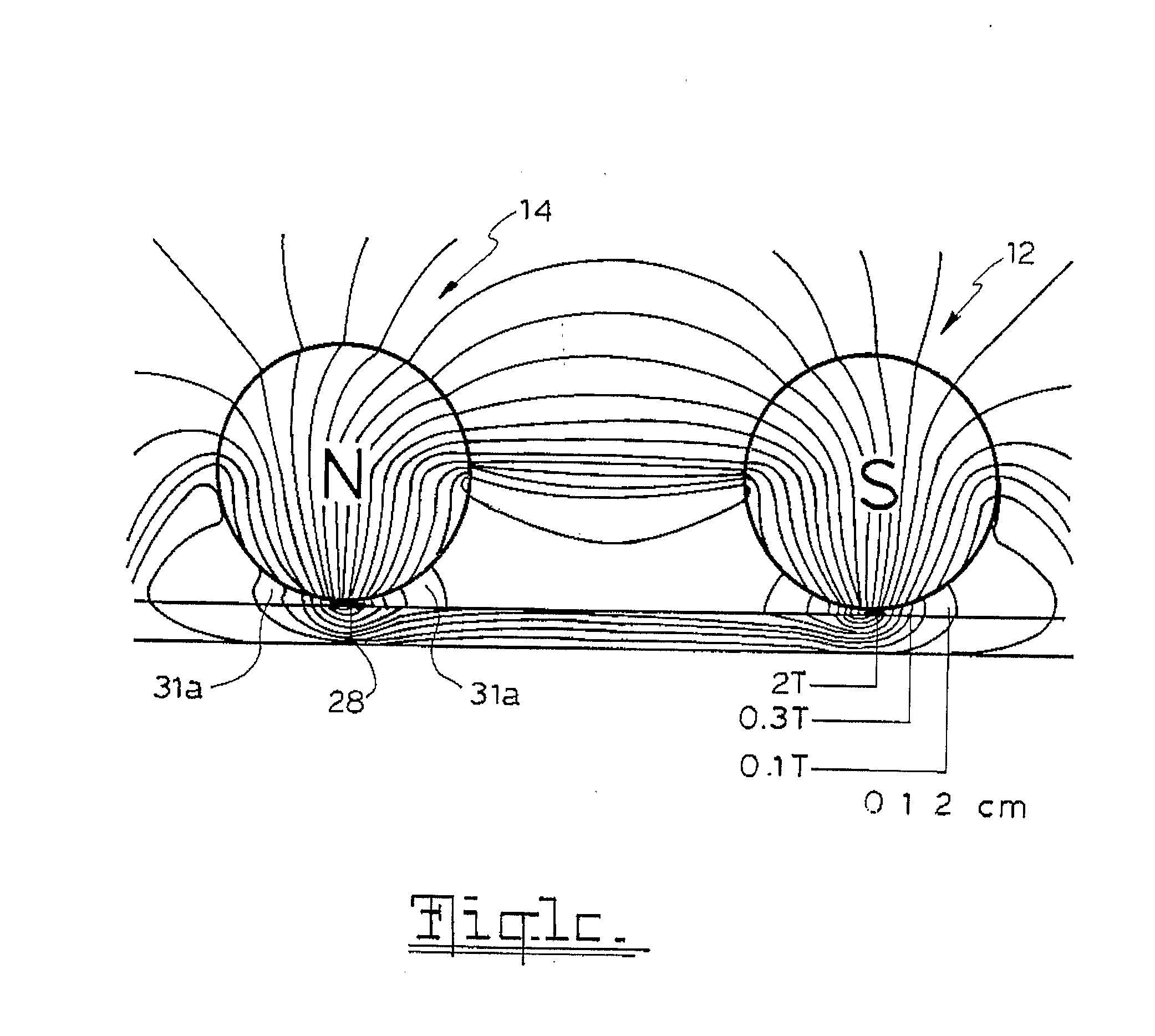
[0087]A basic magnetic wheel unit as illustrated in FIGS. 1a and 1b has already been described above. Such units can be incorporated in numerous and different machines and appliances. It should be noted that the active magnetic material (ie permanent magnets) or other magnetic flux source (eg electromagnet) can be received within a dedicated housing; thus, the actual shape of the magnetic flux unit 16 in FIGS. 1 and 2 is illustrative only and not representative of the actual shape of such units.
[0088]As can be best understood by having reference to FIGS. 2a to 2c, depending on the number of and specific types of dipole magnets employed as magnetic flux source, magnetic wheel units having different pole wheel numbers and arrangements are possible.
[0089]FIG. 2a illustrates a twin wheel configuration unit 10 utilising a single magnet 16 and two rotatable pole wheels 14, 16 as previously described with reference to FIG. 1a.
[0090]FIG. 2b illustrates an arrangement with two pairs of pole...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| width×90 | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com