Diesel Engine Aftertreatment Control Operation with Waste Heat Recovery
a technology of aftertreatment control and waste heat recovery, which is applied in the direction of machine/engine, exhaust treatment electric control, separation process, etc., can solve the problems of affecting the operation affecting the efficiency of the heater, so as to reduce the potential of self-regeneration and reduce the effect of particulate matter
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
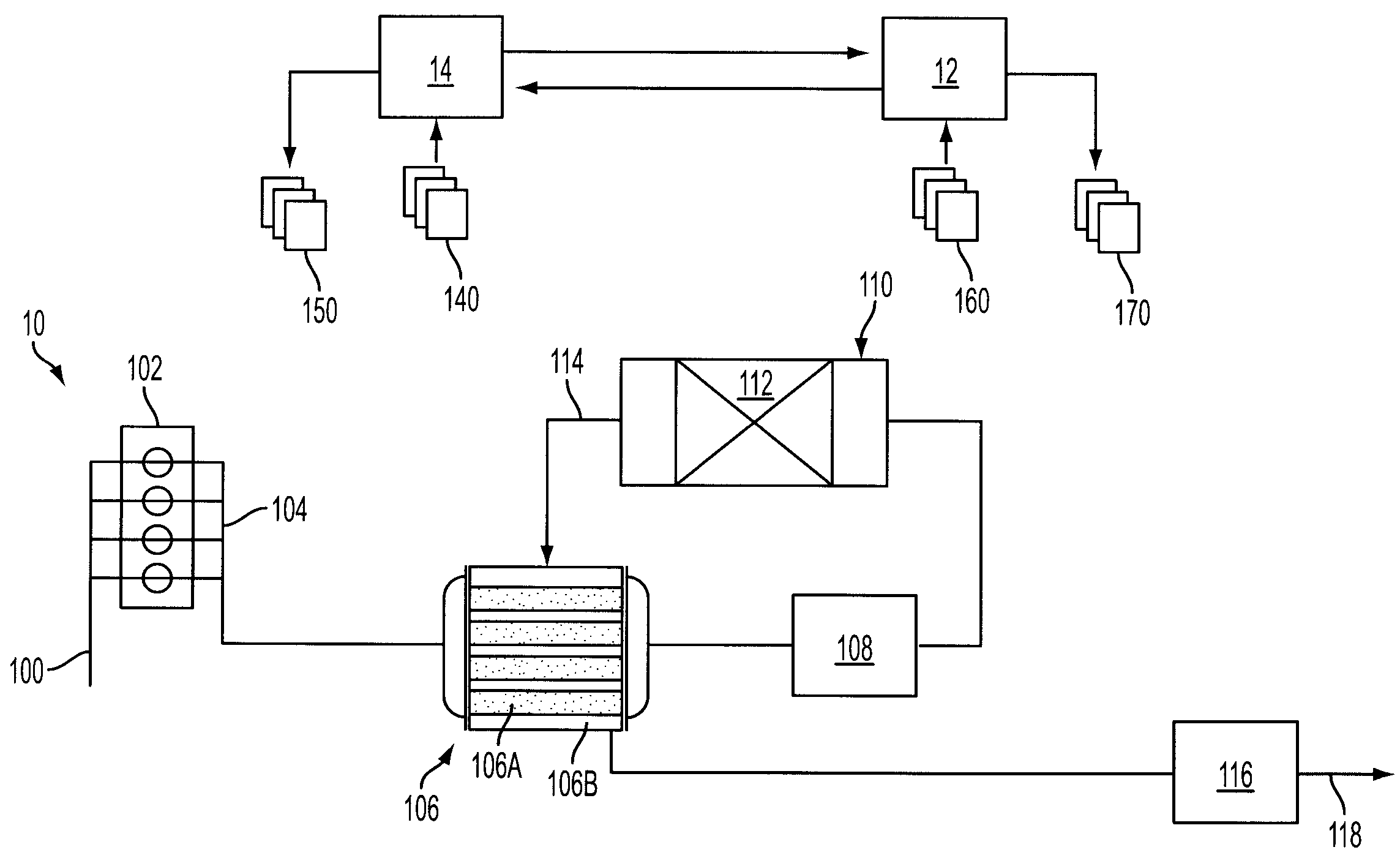
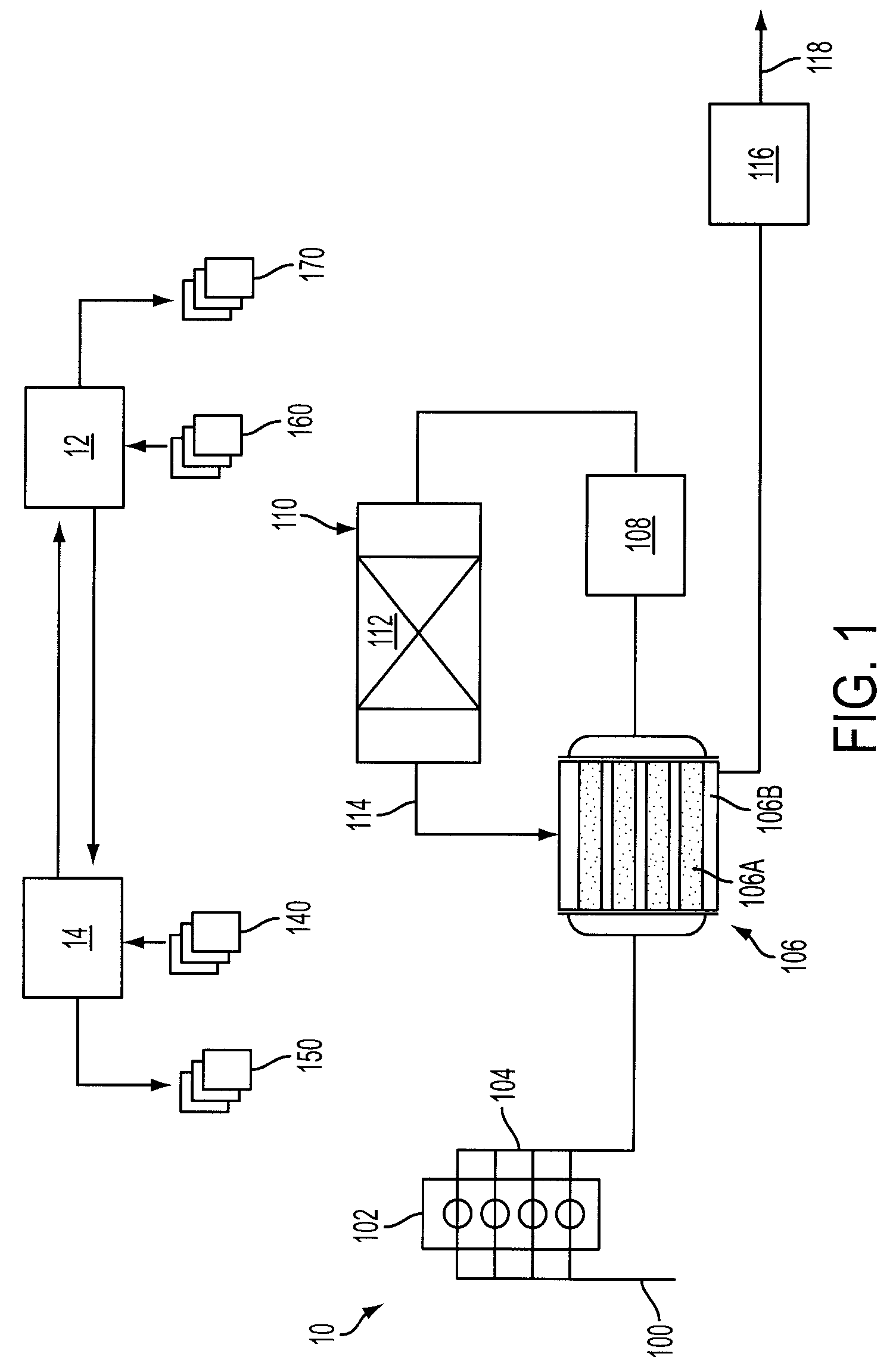
[0007]Referring to FIG. 1, engine 10 may include an intake manifold 100 which may be fluidly coupled to a bank of combustion cylinders 102. Combustion cylinders 102 may communicate with an exhaust manifold 104. A heat transfer device 106 may be coupled to exhaust manifold 104. Heat transfer device 106 may comprise at least two sides 106A and 106B, which permit the transfer of heat between gases on each side without commingling the gases. Heat transfer device 106 may be of various kinds. For example, heat transfer device 106 may be a shell-and-tube heat exchanger, a plate heat exchanger, etc., and, while not shown in FIG. 1, heat transfer device 106 may incorporate baffles on one or more sides to facilitate efficient heat transfer.
[0008]A first side 106A of heat transfer device 106 may be coupled to a heater 108 located downstream of first side 106A of heat transfer device 106. Heater 108 may provide heat from an external, fuel-fired flame, from the combustion of fuel injected into t...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| reaction rate | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| pressure | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com