Method for controlling a pump arrangement, and pump arrangement
a technology of pump arrangement and control mechanism, which is applied in the direction of machines/engines, positive displacement liquid engines, lighting and heating apparatus, etc., can solve the problems of only minimal pump operation, undesired fluctuations of pressure and flow rate in the delivered product, and delay the delivery of substitute pumps to achieve the desired delivery, etc., to achieve the effect of reducing hydraulic braking torque, facilitating acceleration to the target rotational speed, and reducing volume flow
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
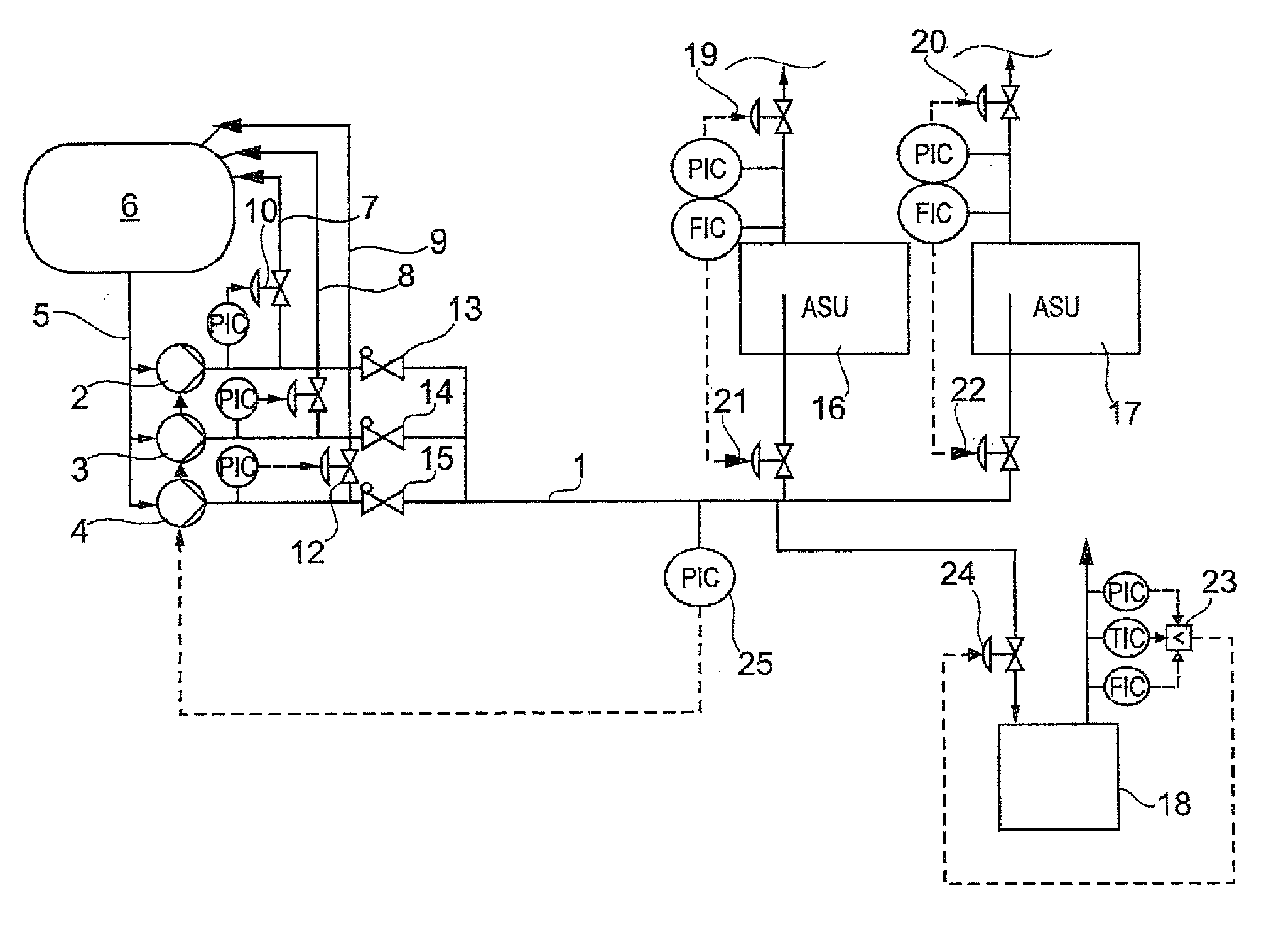
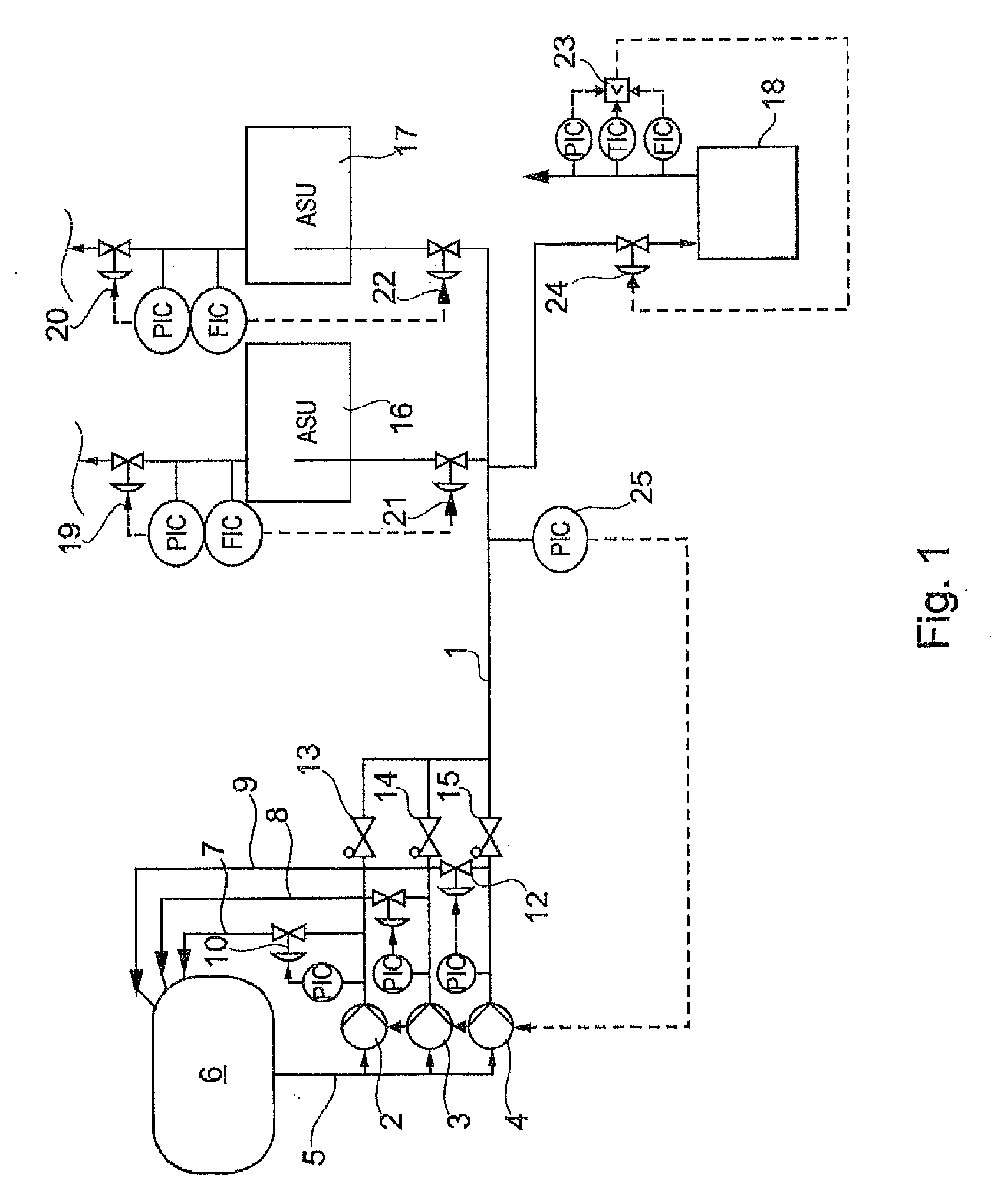
[0030]In air separation units with internal compression, for example, cryogenic air or liquids (LIN, LOX, LAR=liquid nitrogen, oxygen, argon) are brought to an operating pressure by pumping or delivery, and are routed to a heat exchanger of the air separation unit (ASU) in question within which the corresponding cryogenic liquid is evaporated. In order to enable the respective process to be continued in case of failure of one of the pumps, redundant pumps are provided as substitute pumps in the case of failure of the working pump, properly speaking. It is also conceivable that several individual plant components are supplied with pressurized cryogenic liquid from a common reservoir or tank. This is represented schematically in FIG. 1, for example.
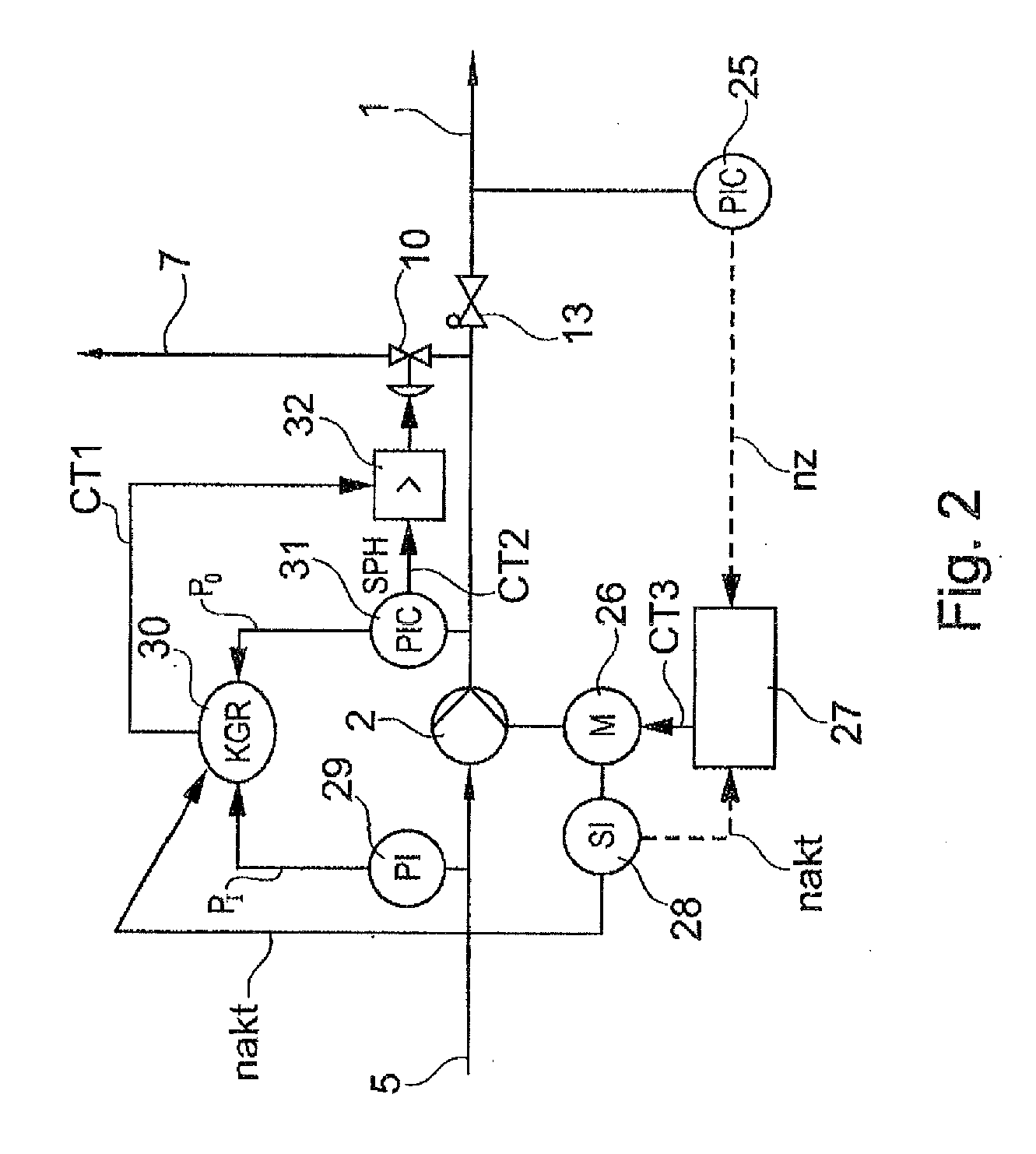
[0031]A common high-pressure liquid line 1 is provided, which is supplied with high-pressure liquid by the three pumps 2, 3, 4. The pumps are supplied with the corresponding product via a supply line 5 from a joint reservoir or tank 6. For ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com