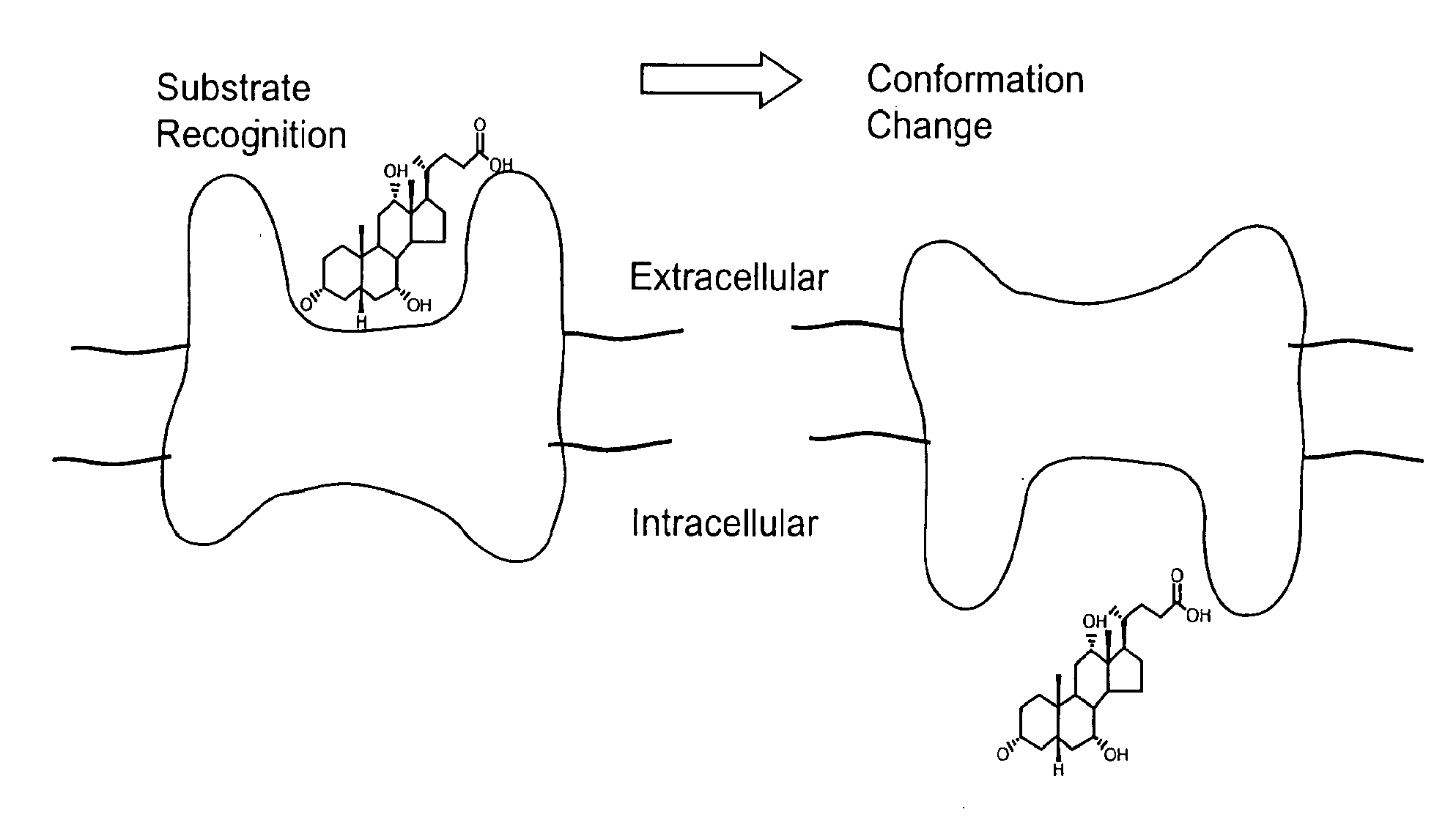
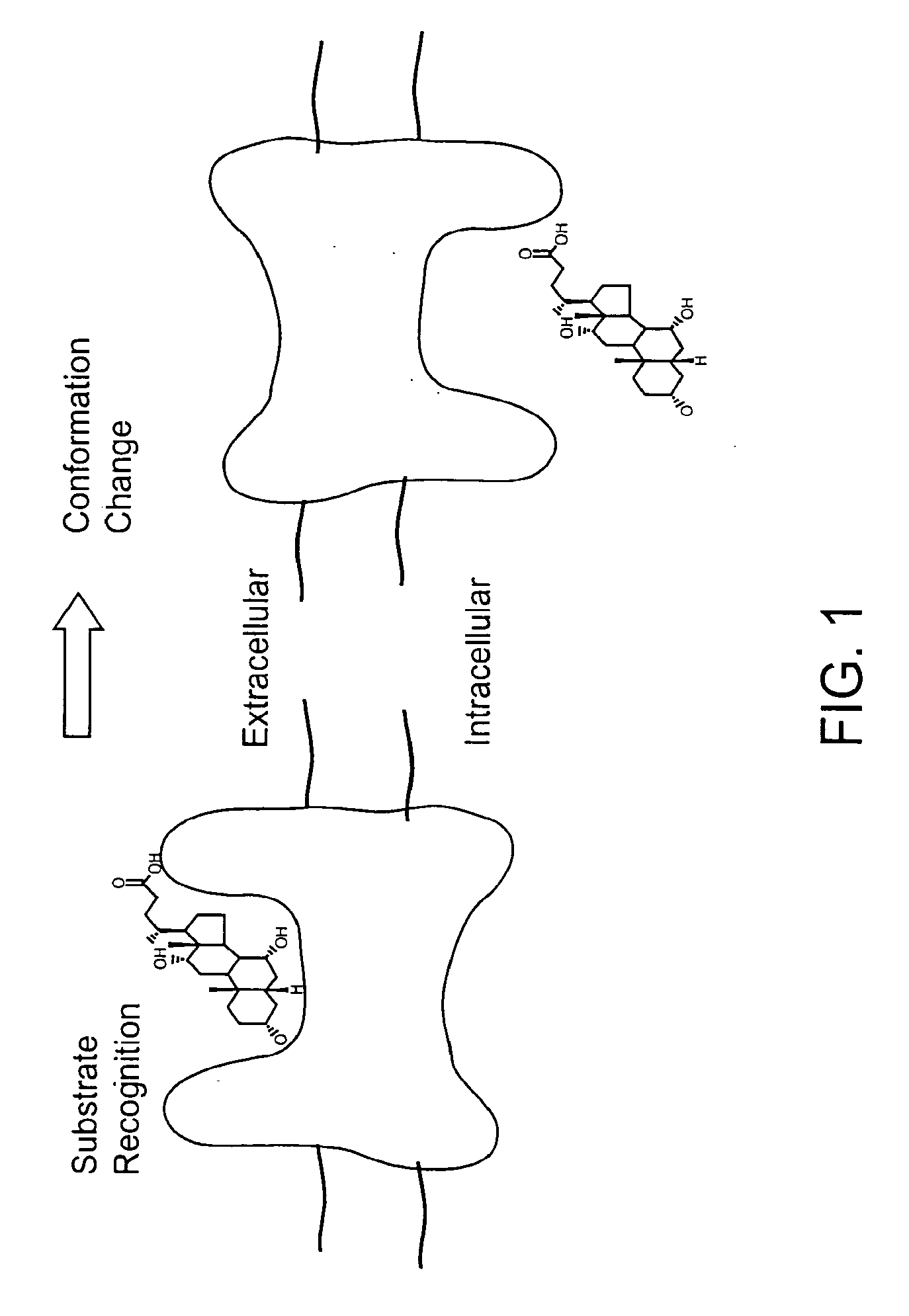
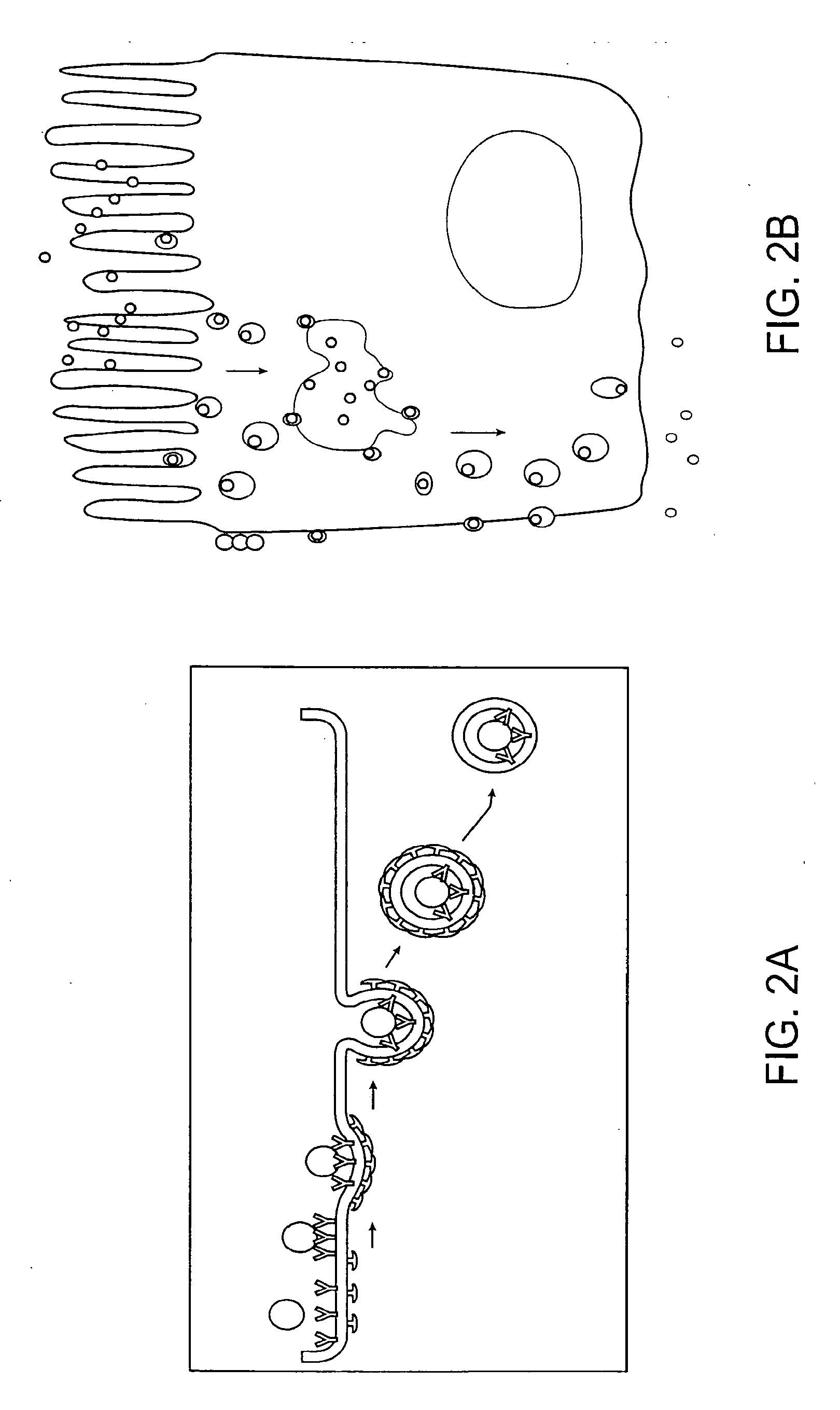
Substrates and screening methods for transport proteins
a technology of transport proteins and substrates, applied in the field of conjugatorial chemistry and pharmaceutical agent delivery, can solve the problems of inability to efficiently formulate compounds for oral bioavailability, many agents fail at the preclinical or early clinical stage, and the target of pharmaceutical agents is largely ignored, so as to improve cellular uptake and improve the effect of high throughput screening formats
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Preparation of Cells Expressing Exogenous Transport Proteins
I. Transfection and Selection of Transporter-Expressing Cell Lines
[0226]CHO K1 cells (107 / ml) were transfected by electroporation (400V, 250 μfarads) with 40 μg of transporter DNA with neo as the selectable marker. After allowing two days for integration of the DNA into the cellular genome, G418 (1.0 mg / ml) was added. The cells were selected for ten days. The selected population was then incubated at 37° C. for 30 min in transport buffer containing a fluorescent substrate for the transporter. For hPEPT1 and rPEPT1, 500 μM XP10486 was used as the fluorescent substrate (see Example 4 for the preparation and structure of XP 10486); the transport buffer utilized with these particular transporters contained 150 mM NaCl, 3 mM KCl, 1 mM CaCl2, 1 mM MgCl2, 1 mM NaH2PO4, 5 mM glucose and 5 mM MES, pH 6.0.
[0227]The cells were then cloned using a Cytomation MoFlo flow cytometer gated on the most highly fluorescent cell population and ...
example 2
Protocols for Direct Uptake Assays
I. Methods for Detecting Fluorescent Substrate Uptake
[0228]A. Bile Acid Transporters
[0229]Day 1: Seed cells (e.g., CHO IBAT or CHO LBAT) at 100K / well into clear bottom black 96-well tissue culture treated plates.
[0230]Day 2: Wash cells 2× with HBSS buffer (HBSS from Gibco, 10 mM Hepes, pH 7.0) at 100 μl / well.
[0231]Add 50 μl of various concentrations of compounds dissolved in HBSS buffer (Hanks Balanced Salt Solution) or buffer alone to each well.
[0232]Incubate 1 hr at RT in the dark (to minimize any negative effects of light on fluorescent properties of putative substrate).
[0233]Read Input Fluorescent Units (FU) in Tecan Spectrafluor instrument, measuring from the bottom of the well. Appropriate excitation and emission wavelengths are utilized as determined by instrument at optimal gain.
[0234]Wash each well 4× with 100 μl / well HBSS at 4° C.
[0235]Add HBSS at 50 μl / well.
[0236]Determine amount of fluorescent substrate transported by measuring FU in wel...
example 3
Library Screening Methods for Cells Expressing Carrier-Type Transport Proteins
I. Screening 200 Member Fluorescent Dipeptide Library
[0296]A. Synthesis of Dipeptide Library
[0297]Wang resin preloaded with the following 20 protected amino acids can be obtained from Novabiochem: Fmoc-Gly, Fmoc-Ala, Fmoc-Val, Fmoc-Leu, Fmoc-Ile, Fmoc-Met, Fmoc-Pro, Fmoc-Cys(Trt), Fmoc-Ser(OtBu), Fmoc-Thr(OtBu), Fmoc-Asn(Trt), Fmoc-Gln(Trt), Fmoc-Asp(OtBu), Fmoc-Glu(OtBu), Fmoc-Lys(Boc), Fmoc-Arg(Pmc), Fmoc-Phe, Fmoc-Tyr(OtBu), Fmoc-His(Trt), Fmoc-Trp(Boc). 100 mg of each resin (loading ˜1 mmole / g) is pooled and shaken with 20 mL of a 20% (v / v) solution of piperidine in DMF for 20 min. The resins are washed with DMF (3×), CH2Cl2, MeOH, and CH2Cl2 again, then dried in vacuo and divided into 2 equal aliquots. The first is treated with 20 mL of a DMF solution containing α-Fmoc-γ-Alloc-diaminobutyric acid (250 mM), HATU (250 mM) and DIEA (500 mM). The resin is agitated for 8 h then filtered and washed with DMF...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com